初一英语必知最基础语法总结
英语基础知识概述
一、词类
1、名词:主要指各种人或事物的名称,也可以指抽象的概念。例如:bag,hero
2、代词:可以代替名词及其名词作用的短语、不定式、动词的-ing形式、从句或句子。如:I,we,you,that
3、数词:表示数目多少或顺序先后的词。One,ten,first
4、冠词:a,an,the用来说明名词所表示的人或事物,这三个词常位于名词前。
5、介词:是一种“媒介”,表示句中某一词或短语与另一个词或短语的关系的词。如in,at,for,behind
6、形容词:描述事物特征的词,描述事物的大小、形状、颜色、等具体特征,也可用来陈述事物的状态。主要修饰名词、代词。如big,good,
7、副词:副词是一种用来修饰动词,形容词,副词或全句的词,说明时间,地点,程度,方式等概念。副词可以分成七类:
1) 时间和频度副词:
now,then,often,always,usually,early,today, lately,
2) 地点副词:
here, there, everywhere, anywhere, in, out, inside, outside, above, below,
3) 方式副词:
carefully, properly, anxiously, suddenly, normally, fast, well, calmly,
4) 程度副词:
much,little, very,rather,so,too,still, quite, perfectly, enough, extremely,
5) 疑问副词:
how, when, where, why.
6) 关系副词:
when, where, why.
7) 连接副词: how, when, where, why, whether.
8、连词:连接单词、短语、从句或句子的一种虚词,在句子中不单独做任何成分,大多数连词具有实义。如and,or,if,because
9、感叹词:用来表示人们的各种情感或情绪的词,在句中不做任何成分。如ah,oh
10、动词:用来表示动作或状态的,在句子中作谓语,是句子不可缺少的部分,用来说明主语是什么或者做什么。如is,do,like,can
二、人称与数
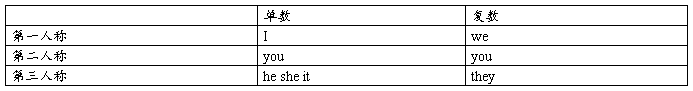
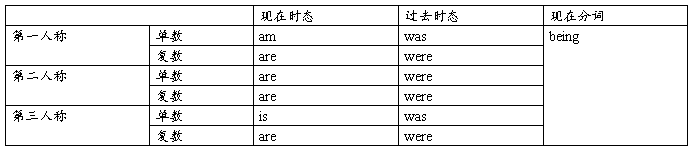
三、be动词:is am are
用法:I一定用am,复数含义的we,you,they后一定用are,除了以上两种之外全是is。
be 的用法口诀 我用am,你用are,is连着他,她,它;
单数名词用is,复数名词全用are。
变疑问,往前提,句末问号莫丢弃。
变否定,更容易,be后not莫忘记。
疑问否定任你变,句首大写莫迟疑。
四、句子的分类
1、陈述句:叙述一件事情或表明说话人的看法、态度等。语序一般为“主语+谓语”。
I like dogs. I am good at English
2、祈使句:表示请求或命令的句子,以动词原形开头。主语you通常省略。
Be sure to come on time.
3、疑问句:提出问题的句子,常见的有五种一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句、反诘疑问句、反义疑问句。Are you ready? What is it?
4、感叹句:表示喜怒哀乐等感情的句子。一般用How或What开头。
What a great pity! How beautiful she is!
五、句子成分 构成最简单句子的成分是主语和谓语,两者缺一不可。
1、主语:是一个句子中所要表达,描述的人或物,是句子叙述的主体。可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词和主语从句等来承担。
2、谓语:是用来说明主语做了什么动作或处在什么状态。谓语可以由动词来担任,一般放在主语的后面。一个句子中必须有一个谓语动词。
3、宾语:是动作的对象或承受者,常位于及物动词或介词后面。宾语可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词、宾语从句等来担任。
4、定语:用于描述名词,代词,短语或从句的性质,特征范围等情况的词叫做定语, 定语可以由名词,形容词和起名词和形容词作用的词,短语担任。如果定语是单个词,定语放在被修饰词的前面,如果是词组,定语放在被修饰词的后面。
5、状语:说明事物发生的时间,地点,原因,目的,结果方式, 条件或伴随情况,程度等情况的词叫状语。状语可以由副词, 短语以及从句来担任。
6、补语:是补充说明叙述的结果、程度、趋向、可能、状态、数量等的成分。
六、英语时态形式:(以动词work为例)
过去 现在 将来
一般 worked work/ works shall/will work
进行 was/were working am/is/are working
七、助动词
助动词本身没有实义,不能单独作谓语。只能和句子中的实义动词一起构成谓语。主要有:
1、be

2、have
3、do

4、will,would,shall,should
助动词will,shall用于构成一般将来时,would,should用于构成过去将来时;shall,should主要用于第一人称,will,would常用于一切人称。
八、物主代词
物主代词是表示所有关系的代词,分为形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。形容词性物主代词只能做定语,名词性物主代词只能做宾语。

九、反身代词
表示“我(们)自己”、“你(们)自己”、“他/她/它(们)自己”的代词称为反身代词。

十、一般疑问句与特殊疑问句
一般疑问句:用yes,no来回答的问句。如:Are your parents doctors?Yes,they both are。
特殊疑问句:就句中某一部分进行提问的疑问句叫特殊疑问句,特殊疑问句的引导词主要有what,who,which,where,how,why,whose等。
What will do next week?下周你做什么?
十一、常见句型
1.提问地点 Where are they?
2. 提问时间:
What’s the time? What time is it?
3.提问日期:
What’s the date today? What was the date yesterday?
4. 提问星期几:
What day is it today?
5.提问某人的生日:
When is one’s birthday?
6. 提问天气:
What is the weather like today? =How is the weather today?
7.提问数量
How many +名词复数+be+……? How many apples are there?
8.提问温度:
What’s today’s temperature? How about the temperature?
9. 提问人的相貌:
What does...look like?
10. 提问人的性格:
What is ... like?
11.询问对方情况:
What’s wrong with...sb.? What’s the matter with ...sb.?
12. 到该做什么事的时候了
It’s time to do sth. It’s time for sth.
13. 提建议用语:
Why not do sth.? Why don’t you do sth.?
What about sth. / doing sth.? It’s best to do sth. You’d better do sth.
十二、时态
英语中除了用时间状语表示动作发生的时间外,谓语动词本身也要有形式的变化来表示时间,这就是时态。英语中的时态大致可以分为三类:过去时态、现在时态、将来时态。
1、 一般现在时:用来表示一般时间发生的动作或行为,或是习惯性的动作或行为,或是普遍真理,而不一定强调动作是否在说话时正在发生。I am a student。
What do you often do after class
2、 一般过去时:主要表示过去某一时刻发生的动作或情况。句中的be动词和一般动词要用相对应的过去分词。I caught a cold yesterday。
I studied English three years ago
3、一般将来时:立足现在,描述将要发生的事情,常与表示将来的时间状语连用,如:next week,tomorrow,next year等。I will go to Hainan next week。
4、现在进行时:表示说话时正在进行的动作,或表示目前一段时间内正在进行的活动,与现在进行时连用的时间状语主要有now,these days等。I am listening to BBC now。
5、过去进行时:既可以表示过去某一时刻正在发生的动作,也可以表示过去某一段时间内正在发生或反复发生的动作。I was packing my books at that time。
6、过去将来时:立足于过去的某一个时间描述将来。常与two days later,the next week等连用。I told him I wouldn’t go home the following weekend。
7、现在完成时:是一种发生于过去、着眼于现在的时态;动作发生在过去,而强调点落在对现在的影响上,或描述从过去一直持续到现在的动作或状态。
I have lived in Qingdao for years。
8、过去完成时:在过去某一时刻前就已经完成的动作用过去完成时表示,即“过去的过去”。
I had expected to see you yesterday,but I was too busy。
十三、There be 句型
There be 句型常用来表达“某处有某物、某人或某事”,有时也可用来强调。其中there是引导词,无词义。
There is a small village below the mountain.
就近原则:there be 句型中的be动词根据临近be动词的名词的数而定。
There is an apple and two oranges in the bag.
十四、a/an(不定冠词)
1、a用在以辅音字母开头,或以读做辅音的元音字母开头的单词前面:
a man一个男人 a university一所大学 a hat一顶帽子
a European一个欧洲人 a one-way street一条单行马路
2、an用在以元音字母(a,e,i,o,u)开头,或以不发音的h字母开头的单词前面:
an apple一个苹果 an island一个岛 an uncle一位大叔 an onion一个洋葱 an egg一个鸡蛋 an hour一小时
3、an还用在发音以元音开头的单个字母前面:
An L-plate一块“实习驾驶”车牌 an MP一个国会议员
an SOS一个呼救信号 an‘x’一个x字母、X形的东西或未知数
第二篇:初一英语语法总结
一、 词法 1、名词 A)、名词的数
我们知道名词可以分为可数名词和不可数名词,而不可数名词它没有复数形式,但可数名词却有单数和复数之分,复数的构成如下:
一)在后面加s。如:fathers, books, Americans, Germans, apples, bananas
二)x, sh, ch, s, tch后加es。如:boxes, glasses, dresses, watches, wishes, faxes
三)1)以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加es 如:baby-babies, family-families, duty-duties, comedy-comedies, documentary-documentaries, story-stories
2)以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。如:day-days, boy-boys, toy-toys, key-keys, ways
四)以o结尾加s(外来词)。如:radios, photos, 但如是辅音加o的加es:如: tomatoes西红柿, potatoes马铃薯
五)以f或fe结尾的变f为v再加es(s)。如:knife-knives, wife-wives, half-halves, shelf-shelves, leaf-leaves, yourself-yourselves
六)单复数相同(不变的)有:fish, sheep, deer鹿子, Chinese, Japanese
七)一般只有复数,没有单数的有:people,pants, shorts, shoes, glasses, gloves, clothes, socks
八)单词形式不变,既可以是单数也可以是复数的有:police警察局,警察, class班,同学, family家,家庭成员
九)合成的复数一般只加主要名词,多数为后一个单词。如:action movie-action movies, pen pal-pen pals; 但如果是由man或woman所组成的合成词的复数则同时为复数。如:man doctor-men doctors, woman teacher-women teachers
十)有的单复数意思不同。如:fish鱼 fishes鱼的种类, paper纸 papers报纸,卷子,论文, work工作 works作品,工厂, glass玻璃 glasses玻璃杯,眼镜, orange桔子水 oranges橙子, light光线 lights灯, people人 peoples民族, time时间 times时代, 次数, chicken 鸡肉 chickens 小鸡
十一) 单个字母的复数可以有两种形式直接加s或’s。如:Is (I’s), Ks (K’s)。但如是缩略词则只加s。如:IDs, VCDs, SARs
十二) 特殊形式的有:child-children, man-men, woman-women, foot-feet, mouse-mice, policeman-policemen, Englishman-Englishmen
B)名词的格
当我们要表示某人的什么东西或人时,我们就要使用所有格形式。构成如下:
一)单数在后面加’s。如:brother’s, Mike’s, teacher’s
二)复数以s结尾的直接在s后加’,如果不是以s结尾的与单数一样处理。如:Teachers’ Day教师节, classmates’; Children’s Day六一节, Women’s Day三八节
三)由and并列的名词所有时,如果是共同所有同一人或物时,只加最后一个’s,但分别拥有时却分别按单数形式处理。如:Mike and Ben’s room迈克和本的房间(共住一间),Mike’s and Ben’s rooms迈克和本的房间(各自的房间)
2、代词 项目 人称代词 物主代词 指示代词 反身代词
人称 主格 宾格 形容词 名词性
第一人称 单数 I me my mine myself
复数 we us our ours ourselves
第二人称 单数 you you your yours yourself
复数 you you your yours yourselves
第三人称 单数 she her her hers herself
he him his his himself it it its its this that itself
复数 they them their theirs these those themselves
3、动词 A) 第三人称单数
当动词是第三人称单数时,动词应该像名词的单数变动词那样加s,如下:
一)一般在词后加s。如:comes, spells, waits, talks, sees, dances, trains
二)在x, sh, ch, s, tch后加es。如:watches, washes, wishes, finishes
三)1)以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加es。如:study-studies, hurry-hurries, try-tries
2)以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。如:plays, says, stays, enjoys, buys
四)以o结尾加es。如:does, goes 五)特殊的有:are-is, have-has
B) 现在分词
当我们说某人正在做什么事时,动词要使用分词形式,不能用原形,构成如下:
一)一般在后加ing。如:spell-spelling, sing-singing, see-seeing, train-training, play-playing, hurry-hurrying, watch-watching, go-going, do-doing
二)以不发音e的结尾的去掉e再加ing。如:dance-dancing, wake-waking, take-taking, practice-practicing, write-writing, have-having
三)以重读闭音节结尾且一个元音字母+一个辅音字母(注意除开字母组合如show –showing, draw-drawing)要双写最后的辅音字母再加ing。如:put-putting, run-running, get-getting, let-letting, begin-beginning
四)以ie结尾的变ie为y再加ing。如:tie-tying系 die-dying死 lie-lying 位于
4、形容词的级
我们在对两个或以上的人或物进行对比时,则要使用比较或最高级形式。构成如下:
一) 一般在词后加er或est(如果是以e结尾则直接加r或st)。如:
greater-greatest, shorter –shortest, taller –tallest, longer –longest, nicer- nicest, larger -largest
二)以重读闭音节结尾且1个元音字母+1个辅音字母(字母组合除外,如
few-fewer fewest)结尾的双写结尾的辅音再加er /est。如:big-bigger biggest, red-redder reddest, hot-hotter hottest
三) 以辅音字母+y结尾的变y为i加er/est。如:happy-happier happiest, sorry-sorrier sorriest, friendly-friendlier friendliest(more friendly most friendly), busy-busier busiest, easy-easier easiest
四)特殊情况:(两好多坏,一少老远)
good/well - better best many/much - more most bad/ill – worse worst
little- less least old- older/elder oldest/eldest far- farther/further farthest/furthest
5、数词 (基变序,有规则;一、二、三,自己背;五、八、九、十二;其它后接th;y结尾,变为i, eth跟上去。) first, second, third; fifth, eighth, ninth, twelfth; seventh, tenth, thirteenth, hundredth; twenty-twentieth, forty-fortieth,
ninety-ninetieth
二、句式
1.陈述句 肯定陈述句
a) This is a book. (be动词)
b) He looks very young. (连系动词)
c) I want a sweat like this. (实义动词)
d) I can bring some things to school. (情态动词)
e) There’s a computer on my desk. (There be结构)
否定陈述句
a) These aren’t their books. b) They don’t look nice. c) Kate doesn’t go to No. 4 Middle School.
d) Kate can’t find her doll. e) There isn’t a cat here. (=There’s no cat here.)
2. 祈使句
肯定祈使句 a) Please go and ask the man. b) Let’s learn English! c) Come in, please.
否定祈使句a) Don’t be late. b) Don’t hurry.
3. 疑问句
1) 一般疑问句 a) Is Jim a student? b) Can I help you? c) Does she like salad? d) Do they watch TV? e) Is she reading?
肯定回答: a) Yes, he is. b) Yes, you can. c) Yes, she does. d) Yes, they do. e) Yes, she is.
否定回答: a) No, he isn’t. b) No, you can’t. c) No, she doesn’t. d) No, they don’t. e) No, she isn’t.
2) 选择疑问句 Is the table big or small? 回答 It’s big./ It’s small.
3) 特殊疑问句
① 问年龄 How old is Lucy? She is twelve.
② 问种类 What kind of movies do you like? I like action movies and comedies.
③ 问身体状况 How is your uncle? He is well/fine.
④ 问方式 How do/can you spell it? L-double O-K.
How do we contact you? My e-mail address is cindyjones@163.com. ⑤ 问原因 Why do you want to join the club?
⑥ 问时间 What’s the time? (=What time is it?) It’s a quarter to ten a.m.. What time do you usually get up, Rick? At five o’clock.
When do you want to go? Let’s go at 7:00.
⑦ 问地方 Where’s my backpack? It’s under the table.
⑧ 问颜色 What color are they? They are light blue. What’s your favourite color? It’s black.
⑨ 问人物 Who’s that? It’s my sister.
Who is the boy in blue? My brother.
Who isn’t at school? Peter and Emma.
Who are Lisa and Tim talking to?
⑩ 问东西 What’s this/that (in English)? It’s a pencil case.
What else can you see in the picture? I can see some broccoli, strawberries and hamburgers.
11问姓名 What’s your aunt’s name? Her name is Helen./She’s Helen. What’s your first name? My first name’s Ben.
What’s your family name? My family name’s Smith.
12 问哪一个 Which do you like? I like one in the box.
13 问字母 What letter is it? It’s big D/small f.
14 问价格 How much are these pants? They’re 15 dollars.
15 问电话号码 What’s your phone number? It’s 576-8349.
16 问谓语(动作) What’s he doing? He’s watching TV.
17 问职业(身份) What do you do? I’m a teacher.
What’s your father? He’s a doctor.
三、时态
1、一般现在时
表示普遍、经常性的或长期性的动作时使用一般现在时,它有:
Be 动词:She’s a worker. Is she a worker? She isn’t a worker.
情态动词:I can play the piano. Can you play the piano? I can’t play the piano. 行为动词:They want to eat some tomatoes. Do they want to eat any tomatoes? They don’t want to eat any tomatoes.
Gina has a nice watch. Does Gina have a nice watch? Gina doesn’t have a watch.
2、现在进行时
表示动词在此时正在发生或进行就使用进行时态,结构为sb be v-ing sth + 其它.
I’m playing baseball. Are you playing baseball? I’m not playing baseball. Nancy is writing a letter. Is Nancy writing a letter? Nancy isn’t writing a letter. They’re listening to the pop music. Are they listening the pop music? They aren’t listening to the pop music.
-
初一英语语法总结
一、初一英语语法——词法初一英语语法虽然是从简单的一些日常用语出发的,但语法中常会有一些知识点看起来很细小,容易被忽视,但这些知识…
-
初一英语语法总结
初一英语语法总结--词法(一)一、初一英语语法——词法1、名词A)、名词的数我们知道名词可以分为可数名词和不可数名词,而不可数名词…
-
初一 英语 语法 总结
初一英语语法总结一.词汇⑴单词1.介词:in,on,under,behind,near,at,of1).in表示在……中,在……内…
-
初一英语语法总结
初一英语语法总结一、初一英语语法——词法1、名词A)、名词的数我们知道名词可以分为可数名词和不可数名词,而不可数名词它没有复数形式…
-
初一英语语法总结
⑴单词1.介词:in,on,under,behind,near,at,of1).in表示在……中,在……内。例如:inourcla…
-
初一英语上册人教版unit 7知识点总结及试题
Unit7Howmucharethesesocks词汇短语(词性,意思)多少不客气。一双给你。看一看廉价出售我买了。_______…
-
初一-初三英语语法总结(全)
1(see、hear、notice、find、feel、listento、lookat(感官动词)+doeg:Ilikewatch…
-
初一英语教学期末总结
初一英语备课组一、从期末考试情况总结教学方式、方法本次初一英语期末考试为南海区统考,120分为满分,全级平均分为99.3分,优秀率…
-
外研版初一英语期末复习 知识点总结
初一英语期末复习知识点总结Module11.befrom+地点来自……be(is,am,are)befrom=comefrom2.…
-
初一英语教育实习总结
9月x日下午,当我们第一次踏进西川中学的大门时,为期三个月的实习也拉开了序幕。此次有幸来到丽江顶岗实习我真的比较高兴,来的那天收到…
-
初一英语期末教学工作总结
本学期,我担任七年级英语教学工作,在工作中从各方面严格要求自己,积极向老教师请教,结合本校的实际条件和学生的实际情况,认认真真工作…