科技英语论文范文
On-line Diagnosis OF Marine Diesel Crankshaft Crack
BASED ON Magnetic Memory*
LI Han-lin, LIN Jin-biao, CAI Zhen-xiong, LU Yong
(Marine Engineering Institute, Jimei University, Xiamen, Fujian 361021)
Abstract: This paper summarized recent diagnosis methods of marine diesel crankshaft crack and introduced the fundamental principle, development and application of metal magnetic memory testing (MMMT) diagnosis technology. Compared with other methods, a scheme developed from MMMT combined with torsional signal to make on-line diagnosis of crankshaft crack was proposed, and the on-line diagnosis experimental platform of diesel was designed. Finally, comments were also made on the on-line MMMT method.
Keywords: marine diesel; crankshaft; crack; metal magnetic memory
1 Introduction
Most of the crankshaft cracks on ocean marine diesel are deeply latent and difficult to detect artificially. In general, while the crack develops to a certain extent it will rupture and cause destructive breakage1. If inchoate stress concentration and tiny crack of crankshaft are detected on-line by Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods, the diesel can be stopped before the full development of the crack and thus rupture can be avoided. A new NDT method, MMMT developed rapidly recent years with advantages in such areas as cheap and simple sensors, measuring without impacting diesel operation and long-term on-line detection. Therefore, there will be a great foreground to use MMMT in crankshaft crack detection.
2 Dynamic Diagnosis of Crankshaft Crack
2.1 Static Diagnosis of Crankshaft Crack
Crankshaft crack is one of the fatal faults in diesels. There are some static NDT methods to diagnose crankshaft crack2 such as Ultrasonic Testing, Radiographic Testing, Magnetic Particle Testing, Penetrate Testing, Eddy Current Testing, Optical Holography, and Microwave Testing. These methods have taken an important part in crankshaft quality control and accident prevention. However, on the other hand there are several disadvantages of these methods. Firstly, all of them must find cracks already formed and can not detect unexpected ones. Secondly, they are unable to make on-line detection and fault diagnosis. Thirdly, most of them need surface pretreatment of the facilities before inspection. Finally, the accuracy of detection is affected by crankshaft configuration and personal skill.
2.2 Dynamic Diagnosis of Crankshaft Crack
At present there are some methods to diagnose shaft cracks on-line: rotor engine vibration displacement method, train wheel shaft temperature testing, acoustic emission and tortional vibration signal testing. However, vibration displacement method is unfit for diesel crankshaft crack diagnosis due to the strong vibration from reciprocating movement which makes it difficult to survey displacement and acceleration. Although there is local high temperature on the cracks, it is hard to inspect the change of the crankshaft temperature due to the high temperature of the lube oil in the diesels. Acoustic emission method is still in developing as great noise from diesel operation makes it difficult to measure high frequency acoustic wave emitted by crack. Therefore at present it is feasible to diagnose crankshaft crack on-line by using torsional vibration signal.
2.3 Crankshaft Crack Diagnosis Using Torsional Vibration Signal
Literature 3 brought forward a method using torsional vibration signal detected real-time from diesel to diagnose crankshaft fault. It studied crack fault diagnosis though measuring the characteristics of the torsional vibration of the shafting flywheel system, and presented that model frequency and damp were sensitive parameters of cracks. The torsional vibration measuring system of the diesel had several advantages such as: easy measuring, no direct contact, cheap sensor and longevity. It was a long-term reliable alarm method for diesel shafting crack. Research group in Marine Engine Institute of Jimei University has done the research of internal-combustion engine score fault with intelligent torsional vibration diagnosis system4, and it was a successful case of on-line fault diagnosis based on torsional vibration signal.
3 Metal Magnetic Memory Testing Technique
In the year 1997, Russian professor A. A. Dubov brought forward correlative theory of metal magnetic memory on the World Conference on NDT, developed MMM instruments and formed MMM NDT technique5.
3.1 Theory of Metal Magnetic Memory Testing
Under the condition of the existence of the outside magnetic field, usually the magnetic field of the earth, there will appear a phenomenon in the stress concentration zone of ferromagnetic components with load that permeability of material besides the zone reduces and surface leak magnetic field increases, which is called magnetostriction. It will makes the surface magnetic field of the ferromagnetic accessory increase, and the magnetic field can remember the location of disfigurement and stress concentration zone, thus it is named metal magnetic memory.
At present, one of the most popular explanation to the magnetic memory is that, loaded by alternating stresses, unsymmetrical elasto-plastic strain will take place in the magnetic domain formed by spontaneous magnetization in ferromagnetic material, and then unequal magnetic flux density will be induced by tensile and compressive stress6. Within the magnetic field of the earth, disfigurement and stress concentration zone of ferromagnetic components will produce maximum leak magnetic field, and there will be maximum tangential component HpX of the magnetic field intensity and zero normal component HpY.
3.2 Metal Magnetic Memory Testing Instruments and Their Practical Use

Research on magnetic memory testing instruments in foreign is in pace with the technological development. Foremost of all were TSC-1M (see Fig. 1), TSCM-2FM and TSC-IM-4 stress concentration magnetic testing instrument developed by Energodiagnostika Ltd. of Russia. These instruments were associated with different types of sensor for various requirements. Software of these instruments for signal analysis and data processing was also developed in Russia. For example, MM-System data processing software produced by Energodiagnostika Ltd. was able to analyze MMM signal and display the signal in three models: 2-D, 3-D and polar coordinates model (see Fig. 2).
Internal MMM testing instruments were mainly developed by Eddysun (Xiamen) Electronic CO., LTD. In the year 2000, EMS-2000 metal magnetic memory diagnosis instrument (see Fig. 3) with different types of sensor was produced by the company for ferromagnetic components disfigurement diagnosis. At the same time, M3DPS (see Fig. 4) software for signal analysis and data processing was developed to locate early fatigue damage7.
Applications of MMM testing in China has developed rapidly focusing on crack testing of steel welding line, pressure vessel, aeronautical structure, thermal power plant and so on. Firstly, in the field of steel material weld testing, it was mainly used for dissimilar steel welding, hull structure steel plate welding8, early diagnosis of welding disfigurement, welding line quality examination, power plant EH oil pipe fillet welding joint, high pressure boiler pipe seat fillet welding joint and so on. Secondly, it was applied in pressure vessel testing for high pressure bottle, vessel welding residual stress measurement and so on. Thirdly, it was applied in aeronautical structure testing for earlier disfigurement and plane undercarriage inspection. Fourthly, it was applied in thermal power plant testing for steam turbines component, blades crack, throttle valve and reheat tube crack diagnosis.
4 On-line Diagnosis of Crankshaft Crack Using Metal Magnetic Memory Testing
4.1 Crankshaft Crack Metal Magnetic Memory Testing
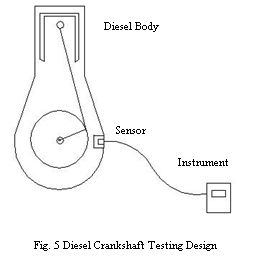
Marine diesel engine crankshafts are mainly made up from ferromagnetic material. According to MMM theory, stress concentration zone on crankshaft will produce maximum tangential component HpX of the magnetic field intensity and zero normal component HpY with alternation of symbol. With scanning inspection of the surface magnetic field of crankshaft by MMM testing sensor and instrument, the stress concentration zone will be found out according to the zero normal component of the field intensity, and then the existence of crack on the crankshaft can be estimated indirectly. With this method, the location of cracks can be found out without interrupting normal operation of the diesel, and give an alarm in time to remind engineers of operation condition of the diesel.
In the design, the sensor of the instrument will be placed into the body of the diesel through the guide door of the diesel, and it can directly scan zones with the most probable existence of stress concentration, such as locations near oil bore and fillet. In case the normal component of magnetic field intensity of the location shows a change from positive to negative or from negative to positive, it means that there may be tiny crack or stress concentration taking place, and at the same time, the instrument will record in a log and give an alarm. The method is simple, effective and feasible to on-line testing on operating diesel on ships.
4.2 Design for Crankshaft Crack Testing Simulation Experiment
In order to put MMM crankshaft crack testing method into practical application to ships, simulation experiment should be done, and the model experiment platform is built from a two cylinders diesel. The platform takes shaft accessory as the research object, and uses standard ball bearings to support shaft. By means of replacing shaft and bearings, the platform is able to do simulate experiment for shafts in different sharp or length such as roll shaft and crankshaft. The shaft is connected to electromotor by adapting flange, and the motor controlled by transducer can drive the shaft with different rotate speed to simulate running of uniform velocity and accelerated velocity. The bearings are fixed on steel foundation by two bearing seats, and the shell on the steel foundation is made up from organic glass to make the observation and the installation of the MMM sensor easy. There is lube oil deposited in the steel foundation and heated up by electro thermal coil. Heated lube oil is pumped to the top of the shell by a small gear oil pump and injected to shaft and bearings to lubricate them and simulate high temperature in diesel. Then the oil flows into oil sump forming a cycle. The MMM sensor is installed in the sides of the platform body through a probe hole, and its installation angle, depth and horizontal location can be adjusted to scan the magnetic field intension of the whole shaft to find the stress concentration zone.
At the same time, stress distribution of diesel crankshaft with crack will be analysized by finite element method software ANSYS and the magnetic field intension model varied with time and temperature will also be constructed for calculation. All of these simulations are fundamental to MMM crack testing of crankshaft9.
5 Conclusion
MMM crankshaft crack testing method is a new technique used for on-line inspection, and there are some issues to deal with in further study. The first one is quantificational relation between leak magnetic field intension near crack and stress, surrounding magnetic field, and the depth and width of crack10. Secondly, there are several factors having certain impacts to the MMM signal such as temperature, residual magnetic field and surface roughness, therefore, data processing should be done to eliminate these impacts.
At present, marine diesel crankshaft crack testing is still being done by means of static method in China. MMM testing may solve the problem of early stress concentration inspection. This method has the advantages as cheap and simple sensors, measuring without affecting diesel operation and long-term on-line detection. It may forecast stress concentration zone and avoid hidden trouble of crankshaft rupture accident. Combined with torsional signal, MMM testing on-line diagnosis of crack will be achieved.
References
1. Peixin Yuan and Heji Yu, Crack Fault Diagnosis in Shaft. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 1997(1), 12-16 (in Chinese).
2. Wenhu Huang, Songbo Xia and Ruiyan Liu, Theory, Technique and Application of Equipment Fault Diagnosis, Beijing, Academic Publisher, 1996 (in Chinese).
3. Wanyou Li, Zhenxiong Cai, Zhiqiu Wang and Hongxing Hua, Diagnosis of Crankshaft Crack in Diesel Using Torsional Vibration. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2004(11), 1028-1031 (in Chinese).
4. Wanyou Li, Zhenxiong Cai, Yan Liu and Zhiqiu Wang, Research on Diagnosis Method for Diesel Cylinder Score Using Torsion Vibration Signal. Ship Engineering, 2003(5), 19-23 (in Chinese).
5. A. A. Dubov, Principal Features of Metal Magnetic Memory Method And Inspection. 16th WCNDT 20## World Conference on NDT, Montreal, Canada.
6. Weichang Zhong, Theoretical Fundamentals of the Metal Magnetic Memory Diagnostics: Spontaneous Magnetization of Ferromagnetic Materials by Elastic-Plastic Strain. NDT, 2001(10), 424-426 (in Chinese).
7. Junming Lin, Xingzeng Yu and Chunjing Lin, Software M3DPS for Metal Magnetic Memory Diagnostic Instrument. NDT, 2001(7), 286-288 (in Chinese).
8. Qilin Qian, Hailiang Gao, Huihua Zhang and Junming Lin, Theory and Application of Hull Structure Steel Plate Welding Based on Metal Magnetic Memory Diagnosis. Ship Building Technique, 2002(1), 25-27 (in Chinese).
9. Zhi Hu and Jilin Ren, Stress Analysis and Magnetic Memory Testing of Ferromagnetic Items. NDT, 2001(7), 286-288 (in Chinese).
10. Hui Ding, Han Zhang, Xiaohong Li and Xishan Wen. The Theoretical Model For Detecting Cracks By Metal Magnetic Memory Technique. NDT, 2002(2), 78-81(in Chinese).
中文标题及摘要
船舶柴油机曲轴裂纹的磁记忆在线诊断*
摘 要:综述了目前船舶柴油机曲轴裂纹的诊断方法,介绍了金属磁记忆技术的基本原理及其发展应用。与其他方法相比较,提出了应用磁记忆结合扭振信号对曲轴裂纹进行在线诊断的方案,最后指出此方法的优缺点等。
关键词:船舶柴油机;曲轴裂纹;金属磁记忆
作者简介
##,男,1983年1月,##大学轮机工程学院,硕士研究生,从事轮机自动化及其控制方面研究。
* This research is supported by Nature Science Funding Project of Fujian Province A0410022.
* 本文受福建省自然科学基金项目 船舶动力装置轴系裂纹故障的磁记忆动态诊断技术研究(A0410022)04-05资助。
-
气象科技英语论文大纲
论气象科技英语中长句的翻译方法摘要:长句是一种很常见的英语语言现象,在气象科技英语中尤为如此。如果一个句子太长,则往往会造成理解和…
-
科技英语论文写作学习感想
科技英语论文写作学习感想班级:姓名:layhot学号:指导老师:《科技英语论文写作》感想今年是我第一次踏入西安交通大学,以前对她有…
-
科技英语论文范文
On-lineDiagnosisOFMarineDieselCrankshaftCrackBASEDONMagneticMemor…
-
英语 科技 论文 word 范文
XXX英语科技论文姓名xxx学号xxxx班级xxx20xx年6月19日Evaluationofthearticleentitled…
-
英文科技论文写作的一些要点
科技英语论文的写作要点总体原则3CCorrect正确Clear清楚Concise简洁1论文题名11基本要求1准确Accuracy题…
-
写英文科技论文的几点心得
写英文科技论文的几点心得(转)(20xx-04-2912:47:53)转载标签:分类:积累沉淀校园在国外呆了几年,总结一下发论文的…
-
科技英语论文写作学习感想
科技英语论文写作学习感想班级:姓名:layhot学号:指导老师:《科技英语论文写作》感想今年是我第一次踏入西安交通大学,以前对她有…
-
英文科技论文中的语言技巧,不可不看
英文科技论文中的语言技巧,不可不看a)如何指出当前研究的不足以及有目的地引导出自己的研究的重要性通常在叙述了前人成果之后,用How…
-
教你怎么写英文科技论文
如何撰写英文科技论文如何撰写英文科技论文英文科技论文写作是国际学术交流必需的技能。在撰写英语科技论文时,除了遵循科技论文的基本要求…
-
英文科技论文写作常用句型
现在把科技英文写作的一些常用句型套路用语转折强调用语甚至是一些搞定评阅人的一些技巧拿出来与大家分享希望新虫门能从中受惠顺利跨国发表…
-
气象科技英语论文大纲
论气象科技英语中长句的翻译方法摘要:长句是一种很常见的英语语言现象,在气象科技英语中尤为如此。如果一个句子太长,则往往会造成理解和…