大学物理实验报告英文版--温度传感器
Physical Lab Report :Temperature Sensors
Writer: No:
This time in the lab, I come to do something about temperature sensors. Before the experiment, I know that temperature sensors are very widely used lab equipment. From the guide, I can find their outputs changes as a function of temperature. The most commonly used ones in the lab are Platinum resistors and semiconductor thermocouples.
In this experiment, I will describe the working principle of Platinum thermo-resistors, Semi-conductor thermo-resistor, and PN diode temperature sensor, and make measurements with them in the lab.
At the beginning, I use the ice water to get the reference point to zero degree is 2 degree. So, when I deal with the data, I have changed the temperature into correct ones already.
1. Semi-conductor thermo-resistor
Within range, the resistanc-temperature relation is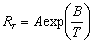
If we calibrate the resistance at a temperature T0 to be R0, we can rewrite this relation into
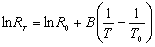
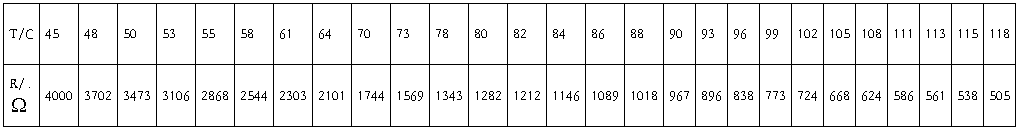
After I change the unit of temperature into K, I use computer to make a linear fit and get a graph as follows:
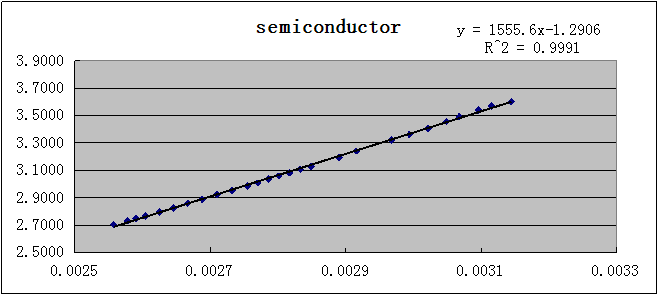
The slope of the line is equal to 1555.6, it means B=1555.6 K.which is a little bit smaller than the reference.
2.Platinum thermo-resistors
A platinum resistor has a temperature-resistance relation of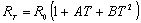
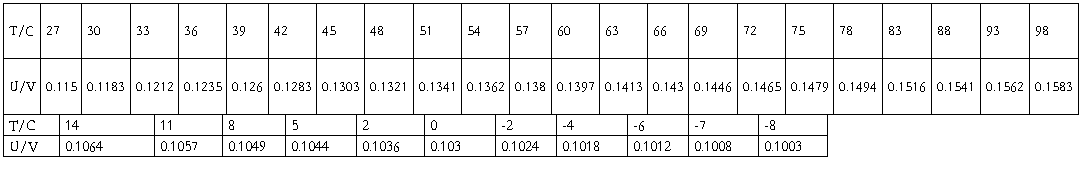

From the graph ,I get the coefficient of x2 is B=2.8*10-7 oC-2,the coefficient of x is A=6*10-4 C-1
3.PN diode temperature sensor
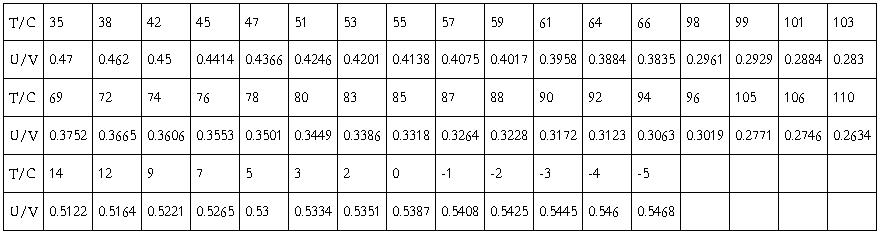
Semiconductor diodes begin conducting electricity only if a certain threshold voltage or cut-in voltage is present in the forward direction. The voltage drop across a forward-biased diode varies only a little with the current, and is a function of temperature; this effect can be used as a temperature sensor. Within a given range of temperature, the resistance varies linearly with temperature.
U=-0.0025T+0.5425,as the I=100μA,so,R=-25T+5424,the temperature is 25
Error analysis:
1.The temperature is tested indirectly, so the measured temperature is a little slower or higher than the correct one,If not precise, then our result of the coefficient is not that correct.
2.The ice-water is made by human, even its temperature is near 0, however, there still exists some worry weather it is 0 degree.
第二篇:大学物理实验 温度传感器研究
大学物理实验 温度传感器研究
一.课题背景
1.课题的意义
传感器网络在我们日常生活中的应用越来越多,他的实用性也逐渐的被人们所接受。温度检测就是传感器网络中不可缺少的一个重要部分,我的课程设计,就是制作传感器网络中的温度检测部分。
整个系统由单片机控制,温度传感器采用18B20,单片机控制采集到的温度输出到四个数码管上进行显示。
关于DS1820 的应用,主要是与不同型号的单片机进行对接,从而设计了不同形式的温度监测系统。例如,对汽车轮胎的温度监测与报警。还有的利用DS1820 设计了多点分布式温度监测系统,实现了对多点温度的同步监测等。本系统除具有温度测量与报警功能之外,还通过一定的控制电路实现了对加热系统的自动控制。
2.方案论证
温度传感器DS1820,集成了温度传感器、信号调整电路、A/D 采样和转换电路、存储器等部件。它可以直接以数字量的形式输出被测环境的温度而不需要配加其它外围电路。另外,多个DS1820 可以共用一条数据总线与CPU 进行通信,与传统的温度传感器(AD590、LM35)一个器件需要一条数据线相比,具有十分突出的优越性。 测温范围- 55 ℃~ + 125℃,在- 10℃~ +85℃时精度为± 0. 5℃, 可编程的分辨率为9~12 位,对应的可编程温度分别为0.5℃、0.25℃、0.125℃、0.0625℃,转换时间为750ms 。
89S51的主频足以用来控制18b20,引脚数目也能轻松的控制在32以内。整个系统可以稳定的运行。系统的成本也可以很低。如果使用FPGA控制就会使成本加大,反而浪费了资源。
有上述论证得出,此方案有效可行。
3.设计要求基础条件
89C51系列单片机;
单片机开发系统;
计算机;
数字温度传感器DS18B20;
电路外围标准元件;
万用表等
台式计算机或笔记本电脑
二.目的意义
随着人们生活水平的不断提高,单片机控制无疑是人们追求的目标之一,它所给人带来的方便也是不可否定的,其中数字温度计就是一个典型的例子,但人们对它的要求越来越高,要为现代人工作、科研、生活、提供更好的更方便的设施就需要从数单片机技术入手,一切向着数字化控制,智能化控制方向发展。 温度的测量在工业上的应用时相当广泛的,能够做出准确、稳定、快速的温度测量装置是很有难度的。这次毕业设计能让我对仪器仪表类的电子设计有更深
入的研究,锻炼了我在电子设计方面的能力。有了这次设计的经验,就可以帮助我在以后设计出更优良的电子仪器。这也是对我们在大学学习阶段的考察,让我们学以致用,把理论上的知识转化为实际应用中的经验,这个转变对于我们的就业是至关重要的。
三.技术要求
1.主要功能:
(1). 设计一个温度测量与显示系统
(2). 完成原理样机硬件组装、电路调试、软件设计、编程与系统调试;
(3). 编制工作程序,绘制系统原理图、硬件电路图、软件流程图并给出软件程序。
2.量化的技术指标:
1. 测量温度范围-10~40℃
2. 精确到小数点后1位
3. 测量时间小于1s
四.电路框图或软件流程图
五.可能遇到的困难
第一,在整个设计中,18B20的控制是个难题,如果出现问题,可以认真的研究18B20的时序和工作原理。第二,单片机的电路设计也可能是出现问题的地方。外围电路的设计和下载电路的设计都很重要。第三,检测的精度也是系统的重中之重。准确的数据需要外围电路的优化和控制的精准。
-
大学物理实验-温度传感器实验报告
关于温度传感器特性的实验研究摘要温度传感器在人们的生活中有重要应用是现代社会必不可少的东西本文通过控制变量法具体研究了三种温度传感…
-
大学实验报告系列之温度传感器
大学物理实验报告注1所有电子版实验报告必须使用统一摸版内容按统一规定编辑2学院班姓名等用宋体正文五号不要加粗3实验名称用宋体正文四…
-
温度传感器实验报告
温度传感器DS18B20实验报告一实验目的12复习掌握Protueskeil软件的使用了解掌握DS18B20的工作原理以及编程方法…
-
温度传感器实验报告
温度传感器实验报告摘要温度是表征物体冷热程度的物理量一般只能通过物体随温度变化的某些特征来间接测量温度传感器就是将温度信号转换成易…
-
温度传感器实验报告
电子092班林楚狄32号温度传感器实验报告一实验目的1了解各种电阻的特性与应用2了解温度传感器的基本原理与应用二实验器材传感器特性…
-
温度传感器课程设计报告
温度传感器课程设计报告组员专业年级学院系别完成日期指导教师1目录1引言32设计要求33工作原理34方案设计45单元电路的设计和元器…
-
大学物理实验-温度传感器实验报告
关于温度传感器特性的实验研究摘要温度传感器在人们的生活中有重要应用是现代社会必不可少的东西本文通过控制变量法具体研究了三种温度传感…
-
大学实验报告系列之温度传感器
大学物理实验报告注1所有电子版实验报告必须使用统一摸版内容按统一规定编辑2学院班姓名等用宋体正文五号不要加粗3实验名称用宋体正文四…
-
温度传感器实验报告
温度传感器DS18B20实验报告一实验目的12复习掌握Protueskeil软件的使用了解掌握DS18B20的工作原理以及编程方法…
-
温度传感器实验报告
电子092班林楚狄32号温度传感器实验报告一实验目的1了解各种电阻的特性与应用2了解温度传感器的基本原理与应用二实验器材传感器特性…
-
传感器实验报告
第一次实验做实验一金属箔式应变计性能应变电桥实验二金属箔式应变计三种桥路性能比较第二次实验做实验十四电感式传感器差动变压器性能实验…