数据结构查找算法实验报告
数据结构实验报告
实验第四章:
实验: 简单查找算法
一.需求和规格说明:
查找算法这里主要使用了顺序查找,折半查找,二叉排序树查找和哈希表查找四种方法。由于自己能力有限,本想实现其他算法,但没有实现。其中顺序查找相对比较简单,折半查找参考了书上的算法,二叉排序树查找由于有之前做二叉树的经验,因此实现的较为顺利,哈希表感觉做的并不成功,感觉还是应该可以进一步完善,应该说还有很大的改进余地。
二.设计思想:
开始的时候提示输入一组数据。并存入一维数组中,接下来调用一系列查找算法对其进行处理。顺序查找只是从头到尾进行遍历。二分查找则是先对数据进行排序,然后利用三个标志,分别指向最大,中间和最小数据,接下来根据待查找数据和中间数据的比较不断移动标志,直至找到。二叉排序树则是先构造,构造部分花费最多的精力,比根节点数据大的结点放入根节点的右子树,比根节点数据小的放入根节点的左子树,其实完全可以利用递归实现,这里使用的循环来实现的,感觉这里可以尝试用递归。当二叉树建好后,中序遍历序列即为由小到大的有序序列,查找次数不会超过二叉树的深度。这里还使用了广义表输出二叉树,以使得更直观。哈希表则是利用给定的函数式建立索引,方便查找。
三.设计表示:
四.实现注释:
其实查找排序这部分和前面的一些知识联系的比较紧密,例如顺序表的建立和实现,顺序表节点的排序,二叉树的生成和遍历,这里主要是中序遍历。应该说有些知识点较为熟悉,但在实现的时候并不是那么顺利。在查找到数据的时候要想办法输出查找过程的相关信息,并统计。这里顺序查找和折半查找均使用了数组存储的顺序表,而二叉树则是采用了链表存储的树形结构。为了直观起见,在用户输入了数据后,分别输出已经生成的数组和树。折半查找由于只能查找有序表,因此在查找前先调用函数对数据进行了排序。
在查找后对查找数据进行了统计。二叉排序树应该说由于有了之前二叉树的基础,并没有费太大力气,主要是在构造二叉树的时候,要对新加入的节点数据和跟数据进行比较,如果比根节点数据大则放在右子树里,如果比根节点数据小则放入左子树。建立了二叉树后,遍历和查找就很简单了。而哈希表,应该说自我感觉掌握的很不好,程序主要借鉴了书上和ppt上的代码,但感觉输出还是有问题,接下来应该进一步学习哈希表的相关知识。
其实原本还设计了其他几个查找和排序算法,但做到哈希表就感觉很困难了,因此没有继续往下做,而且程序还非常简陋,二叉树和哈希表的统计部分也比较薄弱,这也是接下来我要改进的地方。
具体代码见源代码部分。
5.详细设计表示:
6.用户手册:
程序运行后,用户首先要输入数据的个数。接下来输入一组数据并根据提示进行顺序查找,二分查找,二叉排序树查找和哈希表查找等操作,由于操作直接简单这里不再详述。
7.调试报告:
应该说在调试这个程序的过程中自己发现了很多不足,这次实验让我学到了不少东西,但应该说这个程序可实现的功能还是偏少,不太实用,接下来有待改进。
8.源代码清单和结果:
#include <stdio.h>
#define LENGTH 100
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define INFMT "%d"
#define OUTFMT "%d "
/* #define NULL 0L */
#define BOOL int
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define LEN 10000
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BSTNode
{
ElemType data;
struct BSTNode *lchild, *rchild;
} BSTNode, *BSTree;
typedef BSTree BiTree;
/* 插入新节点 */
void Insert(BSTree *tree, ElemType item)
{
BSTree node = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode));
node->data = item;
node->lchild = node->rchild = NULL;
if (!*tree)
*tree = node;
else
{
BSTree cursor = *tree;
while (1)
{
if (item < cursor->data)
{
if (NULL == cursor->lchild)
{
cursor->lchild = node;
break;
}
cursor = cursor->lchild;
}
else
{
if (NULL == cursor->rchild)
{
cursor->rchild = node;
break;
}
cursor = cursor->rchild;
}
}
}
return;
}
void showbitree(BiTree T)
// 递归显示二叉树的广义表形式
{
if(!T) {printf("空");return;}
printf("%d",T->data); // 打印根节点
if(T->lchild ||T->rchild)
{
putchar('(');
showbitree(T->lchild); // 递归显示左子树
putchar(',');
showbitree(T->rchild); // 递归显示右子树
putchar(')');
}
}
/* 查找指定值 */
BSTree Search(BSTree tree, ElemType item)
{
BSTree cursor = tree;
while (cursor)
{
if (item == cursor->data)
return cursor;
else if ( item < cursor->data)
cursor = cursor->lchild;
else
cursor = cursor->rchild;
}
return NULL;
}
/* 中缀遍历 */
void Inorder(BSTree tree)
{
BSTree cursor = tree;
if (cursor)
{
Inorder(cursor->lchild);
printf(OUTFMT, cursor->data);
Inorder(cursor->rchild);
}
}
/* 回收资源 */
void Cleanup(BSTree tree)
{
BSTree cursor = tree, temp = NULL;
if (cursor)
{
Cleanup(cursor->lchild);
Cleanup(cursor->rchild);
free(cursor);
}
}
void searchtree(BSTree root)
{
char choice;
printf("中序遍历的结果为:\n");
Inorder(root);
printf("\n\n");
ElemType item;
BSTree ret;
/* 二叉排序树的查找测试 */
do
{
printf("\n请输入查找数据:");
scanf("%d", &item);
getchar();
printf("Searching...\n");
ret = Search(root, item);
if (NULL == ret)
printf("查找失败!");
else
printf("查找成功!");
printf("\n继续测试按y,退出按其它键。\n");
choice = getchar();
} while (choice=='y'||choice=='Y');
Cleanup(root);
}
searchhash(int *arr,int n)
{
int a[10];
int b,i,j,c;
j=1;
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
a[i]=0;
printf("以下为哈希表输出\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
c=arr[i]%7;
A: if(a[c]==0)a[c]=arr[i];
else {c=(c+1)%7;j++;a[c]++;goto A;}
printf("\n%d在哈希表的第%d位,第%d次放入哈希表\n",arr[i],c,j);
j=1;}
}
void SequenceSearch(int *fp,int Length);
void Search(int *fp,int length);
void Sort(int *fp,int length);
void SequenceSearch(int *fp,int Length)
{
int data;
printf("开始使用顺序查询.\n请输入你想要查找的数据.\n");
scanf("%d",&data);
for(int i=0;i<Length;i++)
if(fp[i]==data)
{
printf("经过%d次查找,查找到数据%d.\n",i+1,data);
return ;
}
printf("经过%d次查找,未能查找到数据%d.\n",i,data);
}
void Search(int *fp,int length)
{
int data;
printf("开始使用顺序查询.\n请输入你想要查找的数据.\n");
scanf("%d",&data);
printf("由于二分查找法要求数据是有序的,现在开始为数组排序.\n");
Sort(fp,length);
printf("数组现在已经是从小到大排列,下面将开始查找.\n");
int bottom,top,middle;
bottom=0;
top=length;
int i=0;
while (bottom<=top)
{
middle=(bottom+top)/2;
i++;
if(fp[middle]<data)
{
bottom=middle+1;
}
else if(fp[middle]>data)
{
top=middle-1;
}
else
{
printf("经过%d次查找,查找到数据%d.\n",i,data);
return;
}
}
printf("经过%d次查找,未能查找到数据%d.\n",i,data);
}
void Sort(int *fp,int length)
{
printf("现在开始为数组排序,排列结果将是从小到大.\n");
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
for(int j=0;j<length-i-1;j++)
if(fp[j]>fp[j+1])
{
temp=fp[j];
fp[j]=fp[j+1];
fp[j+1]=temp;
}
printf("排序完成!\n下面输出排序后的数组:\n");
for(int k=0;k<length;k++)
{
printf("%5d",fp[k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
struct hash
{ int key;
int si;
};
struct hash hlist[11];
int i,adr,sum,d;
float average;
void chash(int *arr,int n)
{ for(i=0;i<11;i++)
{ hlist[i].key=0;
hlist[i].si=0;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ sum=0;
adr=(3*arr[i])%11;
d=adr;
if(hlist[adr].key==0)
{ hlist[adr].key=arr[i];
hlist[adr].si=1;
}
else { do
{d=(d+(arr[i]*7)%10+1)%11;
sum=sum+1;
}while(hlist[d].key!=0);
hlist[d].key=arr[i];
hlist[d].si=sum+1;
} }
}
void dhash(int *arr,int n)
{ printf("哈希表显示为:");
for(i=0;i<11;i++)
printf("%4d",i); printf("\n");
printf("哈希表关键字:");
for(i=0;i<11;i++)
printf("%4d",hlist[i].key);
printf("\n");
printf("查找长度是: ");
for(i=0;i<11;i++)
printf("%4d",hlist[i].si);
printf("\n");
average=0.0;
for(i=0;i<11;i++)
average=average+hlist[i].si;
average=average/n;
printf("平均长度:asl(%d)=%f\n",n,average);
}
void main()
{
int count;
int arr[LENGTH];
ElemType item;
char choice;
BSTree root = NULL, ret; /* 必须赋予NULL值,否则出错 */
BOOL finish = FALSE;
printf("请输入你的数据的个数:\n");
scanf("%d",&count);
printf("请输入%d个数据\n",count);
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
item=arr[i];
if (-10000 != item)
Insert(&root,item);
}
printf("当前已经生成的数列:\n");
for( i=0;i<count;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n当前已经生成的二叉树:\n");
showbitree(root);
printf("\n\n");
int choise=0;
do
{
printf("\n1.使用顺序查询.\n2.使用二分查找法查找.\n3.利用二叉排序树查找.\n4.利用哈希表查找.\n5.退出\n");
scanf("%d",&choise);
if(choise==1)
SequenceSearch(arr,count);
else if(choise==2)
Search(arr,count);
else if(choise==3)
searchtree(root);
else if(choise==4)
{chash(arr,count);dhash(arr,count);}
else if(choise==5)
break;
} while (choise==1||choise==2||choise==3||choise==4||choise==5);
}
输出和结果:
当程序开始运行时,显示如下:
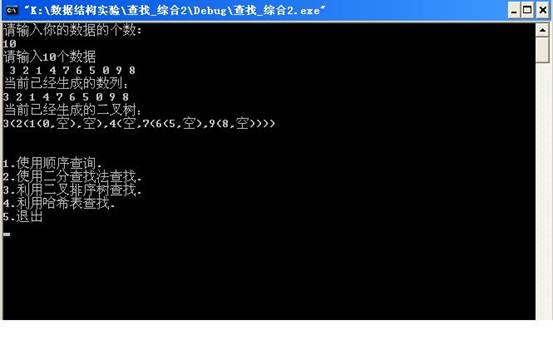
当用户输入10并再次输入数据 3 2 1 4 7 6 5 0 9 8 后,输出结果如下:
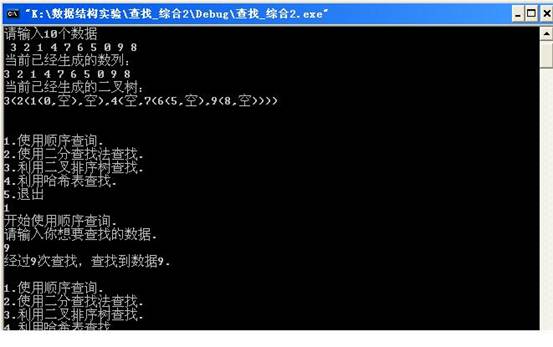
当用户输入1,在输入9后,输出结果如下:
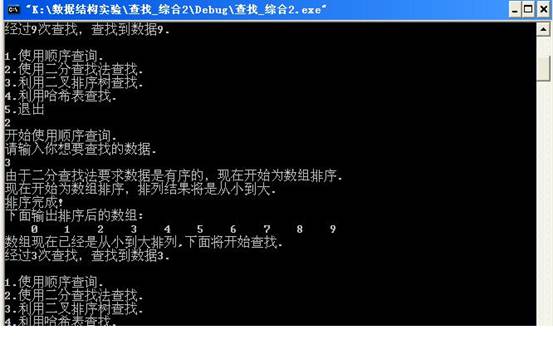
当用户输入2,并输入3后,输出显示如下:
当用户在输入3,并且在输入6后,显示如下:
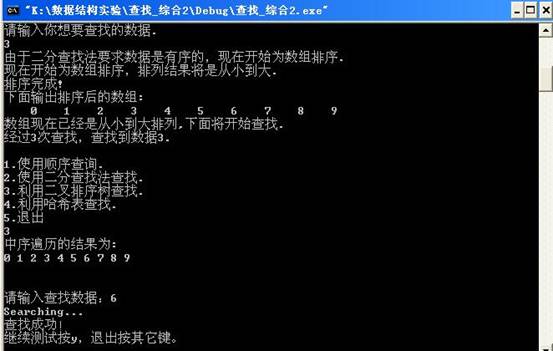
当用户输入4后,输出的哈希表如下:
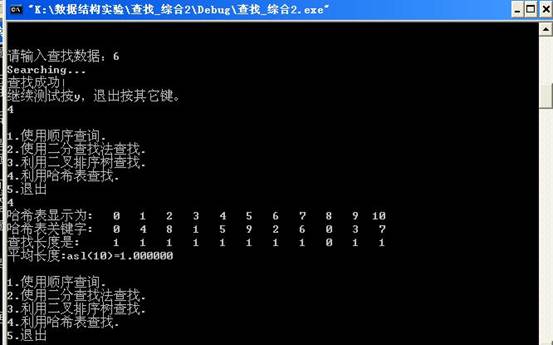
当输入5后,程序结束。
-
数据结构查找实验报告
实验题91设计一个程序exp91cpp输出在顺序表36210185749中采用顺序方法找关键字5的过程程序如下文件名exp91cp…
-
数据结构实验报告 实验五 查找算法
昆明理工大学信息工程与自动化学院学生实验报告201201学年第一学期课程名称数据结构开课实验室年月日一实验内容查找算法其中线性表的…
-
数据结构查找实验报告
实验报告课程名称实验项目数据结构查找姓名xx专业班级学号网络工程网络132130402xxxx计算机科学与技术学院实验教学中心20…
-
数据结构查找算法实验报告
100410528孙晨添数据结构实验报告实验第四章实验简单查找算法一需求和规格说明查找算法这里主要使用了顺序查找折半查找二叉排序树…
-
《数据结构》实验报告查找
实验四查找一实验目的1掌握顺序表的查找方法尤其是折半查找方法2掌握二叉排序树的查找算法二实验内容1234建立一个顺序表用顺序查找的…
-
数据结构实验报告-静态查找表中的查找
数据结构实验实验一静态查找表中的查找一、实验目的:1、理解静态查找表的概念2、掌握顺序查找和折半查找算法及其实现方法3、理解顺序查…
-
数据结构上机实验报告
实验一线性表的基本操作实验目的学习掌握线性表的顺序存储结构链式存储结构的设计与操作对顺序表建立插入删除的基本操作对单链表建立插入删…
-
数据结构-实验8查找的算法
81实现顺序查找的算法一实验目的1熟悉掌握各种查找方法深刻理解各种查找算法及其执行的过程2学会分析各种查找算法的性能二实验内容81…
- 数据结构图实验报告
-
焦作数据结构实验报告
河南省高等教育自学考试实验报告册计算机及应用专业本科段数据结构姓名李威威准考证号所属地市焦作市实验地点焦作大学实验实训中心实验日期…
-
信息检索实验报告
信息检索课程结业报告姓学信息检索与web搜索应用背景及概念信息检索InformationRetrieval是指信息按一定的方式组织…