网络SOCKET编程报告
XX 大 学 实 验 报 告
年 月 日
课题名称: 计算机网络 实验名称:SOCKET编程实现聊天程序 班级: 姓名: 同组人: 指导老师评定: 签名:
一、实验目的
1、掌握网络应用程序的开发方法;
2、掌握Client/ Server结构软件的设计与开发方法;
3、掌握Socket机制的工作原理;
4、会利用编程的方法实现Socket的工作机制,实现聊天程序。
二、实验前的准备
1、阅读教材关于TCP/IP协议和Socket的相关内容;
2、阅读WinSock编程指南;
3、阅读本实验所附内容;
4、熟悉Eclipse开发工具。
三、实验内容
使用Win32 Socket 函数实现聊天程序:能相互对发文本消息。
四、实验步骤和实验源程序
实验步骤:
1、打开java设计软件Elipse,分别建立两个新工程,取名为TalkProject;
2、在刚建立的工程下建里两个类ChatServer和ChatClient;
3、在两个类下分别编写源程序,利用Socket实现聊天软件;
4、运行服务器程序后,再运行客户端程序,就可以实现聊天了。
实验源代码:
ChatServer:
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
public class ChatServer {
boolean started = false;
ServerSocket ss = null;
List<Client> clients =Collections.synchronizedList(new
ArrayList<Client>());
//List<Client> clients =Collections.synchronized(new
ArrayList<Client>());
//clients是共享变量,通过Collections.synchronized(…)做同步化处理
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ChatServer().start();
}
public void start() {
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(8888); // 创建一个监听Socket对象
started = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
while (started) {
Socket s = ss.accept(); // 等待客户端发起连接
Client c = new Client(s);
System.out.println("a client connected!");
new Thread(c).start(); // 启动线程
clients.add(c); // 向共享变量中添加
}
ss.close(); // 关闭Socket
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
class Client implements Runnable { // 实现Runnable接口
private Socket s;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
private boolean Connected = false;
public Client(Socket s) {
this.s = s;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream()); // 创建输入流
dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream()); // 创建输出流
Connected = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void send(String str) {
try {
dos.writeUTF(str); // 向输入流中写入数据
} catch (IOException e) {
clients.remove(this); // 出错时(客户可能已断线),移除一个客户端
}
}
public void run() {
try {
while (Connected) {
String str = dis.readUTF(); // 从输出流中读取数据
synchronized(clients){ // 对共享的列表进行遍历时必须要同步化
Iterator<Client> it = clients.iterator(); // 返回一个迭代器
while(it.hasNext()) {
Client c = it.next();
c.send(str); // 将数据发送出去
}//while
}//synchronized
} //while(Connected)
dis.close(); // 关闭输入流
dos.close(); // 关闭输出流
s.close(); // 关闭Socket
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Client closed!");
}
finally{
clients.remove(this);
// 确保线程结束时从共享变量中删除自己(比如从客户机读数据时出错,
// 客户机可能已掉线,线程会结束)
}//try
}//run
}
}
ChatClient:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JButton;
public class ChatClient extends Frame {
Socket s = null;
DataOutputStream dos = null;
DataInputStream dis = null;
private boolean Connected = false;
TextField tf = new TextField();
TextArea ta1 = new TextArea();
TextArea ta2 = new TextArea();
Button bt1 = new Button("发送");
Thread thread = new Thread(new ClientThread()); // 创建线程
public static void main(String[] args) { new ChatClient().call();
}
public void call() {
bt1.setBackground(Color.cyan);
setLocation(400, 300);
setSize(400, 300);
setLayout(null); 局管理器
setBackground(Color.cyan);
tf.setBounds(250, 40, 70, 25);
ta1.setBounds(30, 40, 200, 80);
ta2.setBounds(30, 140, 200, 80);
bt1.setBounds(265, 250, 70, 30);
tf.setBounds(30, 240, 200, 35);
tf.addActionListener(new MyListener()); 注册事件监听器
add(tf);add(bt1);
add(ta1);add(ta2);add(tf);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { 关闭窗口 // 取消布 // //
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { disconnect();
System.exit(0);
}
});
bt1.addActionListener(new MyListener()); // 注册事件监听器
setVisible(true);
connect();
thread.start(); // 启动线程
}
public void connect() {
try {
s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream()); // 返回一个输出流
dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream()); // 返回一个输入流
System.out.println("connected!");
Connected = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void disconnect() {
try {
dos.close(); // 关闭输出流
dis.close(); // 关闭输入流
s.close(); // 关闭Socket
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private class MyListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String str = tf.getText().trim(); // 获取文本框中的数据
tf.setText("");
ta2.append(str+"\n"); // 将文本框中
的数据添加到文本区中
try {
dos.writeUTF(str); // 向输出流中写入数据
dos.flush(); // 刷空流 } catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private class ClientThread implements Runnable { public void run() {
try {
while (Connected) {
String str = dis.readUTF(); // 从输出流中读取数据
ta1.append(str+"\n");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
六、实验小结
。
第二篇:网络编程实验报告
网络编程技术实验报告
一实验目的:
网络编程技术是计算机科学与技术专业、网络工程专业、软件工程专业的一 门专业基础课程。本课程以Java技术为主讲授,Java语言是当前最流行的网络 编程语言。本课程是一门实用性和综合运用性都很强的课程,实践教学环节是教 学过程中必不可少的重要内容。通过实验,让学生熟悉JDK中的主要内容,掌 握用JDK调试和运行程序的方法,掌握网络编程的基本思想和开发方法、面向 对象编程的思想,JAVA中的基本方法和技术,能够熟练使用JAVA设计、编写 程序,特别是基于TCP/IP的Socket编程,并能运用这些知识方法完成C/S和 B/S结构程序的设计工作。通过实验,提高学生使用Java语言程序设计开发的能 力,提高应用面向对象技术分析和解决实际问题的能力,并在此基础上强化学生 的实践意识、提高其分析问题、解决问题的能力以及动手能力和创新能力。
二实验要求
要求学生熟悉JDK中的主要内容,掌握用JDK调试和运行程序的方法,掌 握网络编程的基本思想和开发方法、面向对象编程的思想,JAVA中的基本方法 和技术,能够熟练使用JAVA设计、编写程序,特别是基于TCP/IP的Socket编 程,并能运用这些知识方法完成C/S和B/S结构程序的设计工作。要注意培养学 生良好的编程习惯,自始至终贯彻课程中所介绍的程序设计风格。为保证尽量在 统一安排的上机时间内完成程序设计任务,学生应事先做问题分析,并做静态检 查。学生应记录实验中所遇到的问题,并写出详细的实验报告。课前准备上机程 序,上机认真调试,课后撰写实验报告,实验报告包括实验目的、实验内容、源 程序、实验结果及分析。
实验一 java基本语法
实验目的:
了解Java的数据类型,掌握各种变量的声明方式,理解运算符 的优先级,掌握Java基本数据类型、运算符与表达式,掌握顺序结构、选择 结构和循环结构语法的程序设计方法。
实验要求:
1、编写一个声明Java不同数据类型变量的程序。
2、编写使用不同选择结构的程序。
3、编写使用不同循环结构结构的程序。
实验内容:
1、编写一个声明Java不同数据类型变量的程序。
public class DataTypes
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
byte b=127;
short s=32767;
int i=2147483647;
long l=9223372036l;//为什么long表示的数比Int还小?
char c='c';
float f=1.23F;
double d=0.9E-3;
boolean bool=true;
System.out.println(" b="+b);
System.out.println(" s="+s);
System.out.println(" i="+i);
System.out.println(" l="+l);
System.out.println(" c="+c);
System.out.println(" f="+f);
System.out.println(" d="+d);
System.out.println(" bool="+bool);
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public class Testif
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
boolean leap;
int year=2014;
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0))//
System.out.println(year+"年是闰年");
else
System.out.println(year+"年不是闰年");
//方法二///////////////////////////////////////
year=2008;
if(year%4!=0)
leap=false;
else if(year%100!=0)
leap=true;
else if(year%400!=0)
leap=false;
else
leap=true;
if(leap==true)
System.out.println(year+"年是闰年");
else
System.out.println(year+"年不是闰年");
//方法三/////////////////////////////////////
year=2050;
if(year%4==0){
if(year%100==0){
if(year%400==0)
leap=true;
else
leap=false;
}
else
leap=false;
}
else
leap=false;
if(leap==true)
System.out.println(year+"年是闰年");
else
System.out.println(year+"年不是闰年");
}
}
2、编写使用不同选择结构的程序。
//使用switch语句/////////////////////////////////////
//1.编写程序用Switch语句实现从键盘上都1,2,3时,屏幕提示不同的信息
import java.io.*;
class SwitchTest
{
public static void main(String args[]) throw IOException
{
char a;
System.out.println("Enter a number from 1--3:");
a=(char)System.in.read();
switch(a)
{
case '1':
System.out.println("win a Car!");break;
case '2':
System.out.println("picked the goat");break;
case '3':
System.out.println("get to keep your100!");break;
default:System.out.println("entry");
}
}
}
3、编写使用不同循环结构结构的程序。
//for循环语句
import java.io.*;
class ForTest
{
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
int fahr,cels;
System.out.println("Celsius Fahrenheit");
for(cels=0;cels<=100;cels+=5)
{
fahr=cels*9/5+32;
System.out.println(cels+" "+fahr);
}
char a;
outer://this is the lable for the outer loop
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
a=(char)System.in.read();
if(a=='b')
break outer;
if(a=='c')
continue outer;
}
}
}
//while循环语句////////////////////////////////////////////
import java.io.*;
class WhileTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException
{
char ch;
System.out.println("按1/2/3数字可获大奖!");
System.out.println("按空格键后回车可退出循环操作");
while((ch=(char)System.in.read())!=' ')
{
System.in.skip(2);//跳过回车键
switch(ch){
case'1':
System.out.println("恭喜你获得大奖,一辆汽车");break;
case'2':
System.out.println("不错呀,你得到一台笔记本电脑");break;
case '3':
System.out.println("没白来,你得到一台冰箱");break;
default:
System.out.println("真不兴,你没有奖品!下次再来");
}
}
}
}
//多重循环
public class Mul99
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{ int i,j, n=9;
System.out.print(" * |");
for(i=1;i<10;i++)
System.out.print(" "+i);
System.out.print("\n-----|");
for(i=1;i<10;i++)
System.out.print("---");
System.out.println();
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
System.out.print(" "+i+" |");
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
System.out.print(" "+i*j);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
实验感想:
实验二 面向对象编程试验
实验目的:
通过编程和上机实验理解Java语言是如何体现面向对象编程基 本思想,熟悉类的封装方法以及如何创建类和对象,熟悉成员变量和成员方法的 特性,熟悉类的继承性和多态性的作用,熟悉包、接口的使用方法,掌握OOP 方式进行程序设计的方法。
实验要求:
1、编写程序实现类的定义和使用。
2、编写不同成员和不同成员方法修饰方法的程序。
3、编写体现类的继承性(成员变量、成员方法、成员变量隐藏)的程序 和多态性(成员方法重载、构造方法重载)的程序。
4、编写接口的定义和使用的程序。
5、编写包的定义和使用的程序。
实验内容-
1. 日期类输出当前日期
import java.io.*;
public class Date
{
private int year,month,day;
//private static thisYear;
public Date(int y,int m,int d){
this.year=y;
this.month=m;
this.day=d;
}
public void read(int y,int m,int d)
{
int y=System.in.read();
int m=System.in.read();
int d=System.in.read();
}
public void set(int y,int m,int d)
{
if(m>=1&&m<=12)
{
return m;
}else{
System.out.println("该日期错误");
}
if(d>=1&&d<=31)
{
return d;
}else
System.out.println("该日期错误");
}
public void show( )
{
System.out.println(this.day+"/"+this.month+"/"+this.year);
}
public static void main(String args[])throws IOException
{
Date s=new Date();
s.read();
s.set();
s.show();
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
2. 桌子类
public class Table
{
private String name;
private int longs;
private int weight;
private int height;
private int width;
public Table(String n,int l,int we,int h,int wi)
{
this.name=n;
this.longs=l;
this.weight=we;
this.height=h;
this.width=wi;
}
int Area()
{
return this.longs*this.width;
}
public void Display()
{
System.out.println("桌子名称:"+this.name+"\n"+"重量:"+this.weight+"\n"+"桌面宽度:"+this.width+"\n"+"桌面长度:"+this.longs+"\n"+"桌子高度:"+this.height+"\n"+"桌子面积"+this.Area());
}
public void ChangeWeight(int s)
{
this.weight=s;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Table T=new Table("xiaozuo",9,3,5,3);
T.Area();
T.Display();
T.ChangeWeight(90);
T.Display();
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class StaticDemo
{
static int x;
int y;
public static int getX(){
return x;
}
public static void setX(int newX){
x=newX;
}
public int getY(){
return y;
}
public void setY(int newY){
y=newY;
}
}
public class TestDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("静态变量"+StaticDemo.getX());
System.out.println("实例变量"+StaticDemo.getY());//非法编译时将出错
StaticDemo a=new StaticDemo();
StaticDemo b=new StaticDemo();
a.setX(1);
a.setY(2);
b.setX(3);
b.setY(4);
System.out.println("静态变量a.x="+a.getX());
System.out.println("静态变量a.y="+a.getY());
System.out.println("静态变量b.x="+b.getX());
System.out.println("静态变量b.x="+b.getY());
}
}
3. 继承和多态的作用
/*
Date:2014.11.23 9:56:00
@author:Devon
function:功能
?创建Rodent (啮齿动物):Mouse (老鼠),Gerbil (沙鼠),Hamster (大频 鼠)等
的一个继承分级结构。在基础类中,提供适用于所有Rodent的方法,并 在衍生类中覆盖它们,
从而根据不同类型的Rodent釆取不同的行动。创建一个 Rodent数组,在其中填充不同类型的Rodent,
然后调用自己的基础类方法,看 看会有什么情况发生。
*/
class Rodent
{
Rodent r[]=new Rodent[4];
public void TowTooth()
{
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Rodent rodent=new Rodent();
Mouth mouth=new Mouth();
Gerbil gerbil=new Gerbil();
Hamster hamster=new Hamster();
r[0]=rodent,r[1]=mouth,r[2]=gerbil,r[3]=hamster;
for(int i=0,i<r.lenth,i++)
{
r[i].TowTooth();
}
}
}
class Mouae extends Rodent
{
}
class Gerbil extends Mouse
{
}
class Hamster extends Gerbil
{
}
4、接口的定义和使用
interfaceTest.java
public class InterfaceTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x;
circle y= circle;
y.circle(2);
x=y.calculate.area();
System.out.println("\n面积为:"+x+"\n");
}
}
interface cal_area
{
double PI=3.14;
double claculate_area();
}
class circle implements cla_area
{
double r;
circle(double r)
{
this.r=r;
}
//实现接口中的抽象方法,求圆面积
public double calculate_area()
{
return PI*r*r;
}
}
5、包的定义和使用 ?创建自定义包Mypackage
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
package Mvpackage; //声明存放类的包
import java.util. * ; //引用 java.util 包
public class Test_YMD {
private int year,month,day;
public static void main(String[] args){}
public Test_YMD(int y,int m,int d) {
year = y;
month = (((m>=1) & (m<=12)) ? m :1);
day = (((d>=1) & (d<=31)) ? d :1);
}
public Test_YMD() {
this(0,0,0);
}
public static int thisyear() {
return Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.YEAR);//返回当年的年份
}
public int year() {
return year;//返回年份
}
public String toString(){
return year+"-n"+month+"n-"+day;//返回转化为字符串的年-月-日
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
import Mypackage.KY4_1_YMD;//引用 Mypackage 包中的 KY4_1_YMD 类
public class YMD_2 {
private String name;
private Test_YMD birth;
public static void main(String args[])
{
YMD_2 a = new YMD_2("张驰",1990,1,11);
a.output();
}
public YMD_2(String nl,Test_YMD dl){
name = nl;
birth = dl;
}
public YMD_2(String nl,int y,int m,int d){
this(nl,new Test_YMD(y,m,d));//初始化变量与对象
}
public int age() //计算年龄
{
return TESt_YMD.thisyear() - birth.yearO;//返回当前年与出生年的差即年龄
}
public void output()
{
System.out.println("姓名:"+name);
System.out.println("出生日期:"+birth.toString());
System.out.println("今年年龄:"+age());
}
实验感想:
实验三 异常处理程序设计
实验目的:
了解Java中异常处理(exception)的作用及常用的异常类,掌握异常处理的设计方法。
实验要求:
理解系统异常处理的机制和创建自定义异常的方法。
实验内容:
Class InsufficientFoundsException extends Exception
{
private BankAccount m-ba;
private double getAmount;
InsufficientFoundsException(BankAccount ba,double dAmount)
{
super("Insufficient founds in account");
m-ba=ba;
getAmount=dAmount;
}
public String toString()
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
sb.append("Insufficient founds in account");
sb.append(m-ba.getAccountNumber());
sb.append("\nBalance was");
sb.append(m-ba.Balance())
sb.append("\ngetAmount was");
sb.append(getAmount);
return sb,toString();
}
}
public class TestExcepl
{
public static void main( string args[] ){
int 1=0;
String greeting[]={ "Hello", "Only", "Test"}
while(I<4){
try{
System.out.println(greeting[I]);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException e
{
system.out.println( " 越界");
I = -l }finally{
system, out.println("总会运行"}
I++
}
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public class Excep2Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("这是一个异常处理的例子\n");
try{
int i=10;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("异常是:"+e.getMessage());
}
finally {
System.out.println("flnally 语句被执行”);
}
}
}
试验感想:
实验四:多线程程序设计
实验目的:
理解线程的概念、线程的生命周期,掌握多线程的编程:继承 Thread 类与使用 Runnable 接 口。
实验要求:
掌握两种创建线程的方法:一种是创建用户自己的线程子类, 另一种是在用户自己的类中实现Rimable接口。
实验内容:
//Thread线程
class FruitThread extends Thread
{
public FruitThread(String str)
{
super(str);
}
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println(i+" "+getName());
try{
sleep((int)(Math.random()*3000));
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
}
}
}
}
public class TowFruit
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
FruitThread apple=new FruitThread("苹果");
FruitThread banana=new FruitThread("香蕉");
apple.start();
banana.start();
}
}
class TowFruit1 implements Runnable
{ String name;
public TowFruit1(String name)
{
this.name=name;
}
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println(name);
Thread.yield();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{ TowFruit1 apple=new TowFruit1("苹果");
TowFruit1 banana=new TowFruit1("香蕉");
Thread t1=new Thread(apple);
Thread t2=new Thread(banana);
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
public class ThreadVSRunnable extends Thread implements Runnable
{ String name;
public ThreadVSRunnable(String str)
{
super(str);
name=Tstr;
}
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<20;i++)
{
System.out.println("第"+i+"Thread"+getName());
// System.out.println(name);
//sleep///////////////////////
/*try{
sleep((int)(Math.random()*10000));
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
}*/
//yeild///////////////////////////
Thread.yield();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FruitThread apple=new FruitThread("Thread 生产的 苹果");
FruitThread banana=new FruitThread("Thread 生产的 香蕉");
apple.start();
banana.start();
FruitThread apple1=new FruitThread("Runnable 生产的 苹果");
FruitThread banana1=new FruitThread("Runnable 生产的 香蕉");
Thread t1=new Thread(apple1);
Thread t2=new Thread(banana1);
t1.start();
t2.start();
//System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
实验结果:
实验感想:
实验五:系统I/O程序设计
实验目的:
理解数据流的概念、Java流的层次结构及文件的概念;熟悉图形 用户界面基本组件的使用方法,熟悉如何使用布局管理器对组件进行管理及如何 使用Java的事件处理机制。
实验要求:
1、掌握字节流和字符流的基本使用方法。
2、能够创建、读写、更新文件。
3、掌握在Applet容器中添加组件的方法,掌握使用布局管理器对组件进行 管理的方法。
4、理解Java的事件处理机制,掌握为不同组件编写事件处理程序的方法。
5、掌握编写独立运行的窗口界面的方法。
6、了解对话框及Java Swing组件的使用方法。
实验内容:
public class IOinTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
byte[] buffer=new byte[255];
System.out.println("请在下面输入一行字符:\n");
try {
System.in.read();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("读取输入字符出错,错误信息为:"+e.toString()+"\n");
}
System.out.println("您刚才输入的一行字符为:\n");
String inputStr=new String(buffer,0);
System.out.println(inputStr);
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.io.*;
class FileStreamsTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:/einput.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("eoutput.txt");
int c;
while ((c = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(c);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("FileStreamsTest:" + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("FileStreamsTest:" + e);
}
}
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class ButtonTest extends Applet {
Label ll;
Button bl, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6;
public void init() {
setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 3)); // 设置网格布局(3 行3 列共9 个网格)
ll = new Label("标签 1");
bl = new Button("按钮 1");
b2 = new Button("按钮2");
b3 = new Button("按钮3");
b4 = new Button("按钮4");
add(ll);
add(bl);
add(b2);
add(b3);
add(new Label());
add(b4);
add(new Button("按钮5"));
add(new Button(" 按钮6"));
add(new Label("标签2"));
}
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class ComponentTest extends Applet {
public void init() {
// 设置最底层# Applet容器为顺序布局
setFont(new Font("Ariar", Font.PLAIN, 20));
Label l = new Label("这是最底层的 Applet 容器中的标签", Label.CENTER);
add(l);
Panel panel1 = new Panel();
add(panel1);
panel1.setBackground(Color.blue);
panel1.setForeground(Color.red);
panel1.setLayout(new BorderLayout());// 设置边界布局
panel1.add("North", new Button("北"));
panel1.add("South", new Button("南"));
panel1.add("East", new Button("东"));
panel1.add("West", new Button("西"));
panel1.add("Center", new Label("这是在 Panell 面板中部添加的标签"));
Panel panel2 = new Panel();
add(panel2);
panel2.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); // 设置网格布局
Choice c = new Choice();// 创建下拉式列表
c.addItem(" 北京");
c.addItem("上海");
c.addItem("天津");
Label ll = new Label("这是在Panel2面板中的标签");
Button b1 = new Button("Panel2 中的按钮");
panel2.setBackground(Color.green);
panel2.add(ll);
panel2.add(b1);
panel2.add(c);
}
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
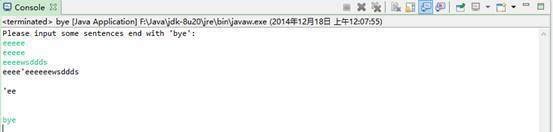
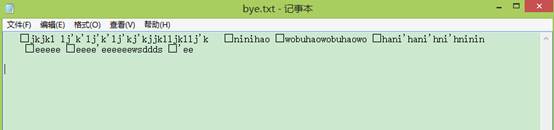
4、从标准设备中输入若干行英文句子,直到输入”bye”结束,将这些字符串 写入文件。
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.io.*;
publicclass bye {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Please input some sentences end with 'bye':");
BufferedReader keyin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
String s;
RandomAccessFile f = new RandomAccessFile("e:\\bye.txt", "rw");
boolean ss;
while ((s = keyin.readLine()) != null) {
ss = s.endsWith("bye");
if (ss)
System.exit(0);
else
{
System.out.println(s);
f.seek(f.length());
f.writeUTF(s);
}
}
}
}
5、从键盘输入一个整型数,一个双精度型和一个字符串,用DataOutputStream 将这些数据输出到文件中,然后用DatalnputStream从文件中读出这些数据并打 印到标准输出设备
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
publicclass TestDataOutputStream {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
File newFile = new File(
"e:\\TestDataOutputStream.txt");
try {
FileOutputStream fOut = new FileOutputStream(newFile);
DataOutputStream dOut = new DataOutputStream(fOut);
System.out.println("Please input Integer:");
int i = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
System.out.println("Please input Float:");
float f = Float.parseFloat(bf.readLine());
System.out.println("Please input Double:");
double d = Double.parseDouble(bf.readLine());
System.out.println("Please input Boolean:");
boolean b = new Boolean(bf.readLine()).booleanValue();
dOut.writeInt(i);
dOut.writeFloat(f);
dOut.writeDouble(d);
dOut.writeBoolean(b);
dOut.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
6、一个窗口中,在四个位置循环显示四种不同颜色的正方形,当鼠标点击 时,停止循环显示,再次点击,恢复显示
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
publicclassCycleRecTestextends JFrame
{
JButton playButton;
JButton stopButton;
public CycleRecTest()
{
setTitle("图形循环显示");
setSize(470, 470);
final CycleRec pane = new CycleRec();
Container content = getContentPane();
content.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
content.add(pane, "Center");
addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter()
{
publicvoid mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)
{
if (pane.isPlay())
pane.stop();
else
pane.play();
}
});
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args)
{
JFrame app = new CycleRecTest();
app.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
app.setVisible(true);
}
}
classCycleRecextends JPanel implements Runnable
{
private Thread show;
private Color blackCor = Color.black;
private Color blueCor = Color.blue;
private Color cyanCor = Color.cyan;
private Color greenCor = Color.green;
int imgID = 0;
boolean bPlay = true;
public CycleRec()
{
}
publicvoid paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
if (imgID == 0)
{
fillR(g, 100, 100, 100, blackCor);
fillR(g, 200, 100, 100, blueCor);
fillR(g, 100, 200, 100, cyanCor);
fillR(g, 200, 200, 100, greenCor);
}
elseif (imgID == 1)
{
fillR(g, 100, 100, 100, cyanCor);
fillR(g, 200, 100, 100, blackCor);
fillR(g, 100, 200, 100, greenCor);
fillR(g, 200, 200, 100, blueCor);
}
elseif (imgID == 2)
{
fillR(g, 100, 100, 100, greenCor);
fillR(g, 200, 100, 100, cyanCor);
fillR(g, 100, 200, 100, blueCor);
fillR(g, 200, 200, 100, blackCor);
}
elseif (imgID == 3)
{
fillR(g, 100, 100, 100, blueCor);
fillR(g, 200, 100, 100, greenCor);
fillR(g, 100, 200, 100, blackCor);
fillR(g, 200, 200, 100, cyanCor);
}
}
publicstaticvoid fillR(Graphics g, int x, int y, int length, Color color)
{
g.setColor(color);
g.fillRect(x, y, length, length);
}
publicvoid run()
{
int showpic = 0;
while (bPlay = true)
{
imgID = showpic;
repaint();
pause(1000);
showpic++;
if (showpic > 3)
showpic = 0;
}
}
publicvoid pause(int time)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(time);
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
publicvoid play()
{
if (show == null)
{
show = new Thread(this);
bPlay = true;
show.start();
}
}
publicvoid stop()
{
if (show != null)
{
show = null;
bPlay = false;
}
}
publicboolean isPlay()
{
if (show != null)
returntrue;
else
returnfalse;
}
}

7、在窗口的一个区域进行鼠标操作:mouseEnter,mouseExit、 mousePress,mouseDrage、mouseClick。在窗口的另一个区域以文字显不鼠标所进 行的相应操作。另外当鼠标进行mousePress、mouseDrage、mouseClick操作时, 将显示一个图片。当鼠标拖拉时,图片随鼠标移动。
package com.devon.demo01;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
publicclass MyClass {
private JFrame fm = new JFrame("鼠标移动示例");
private JLabel lb = new JLabel("拖动测试对象");
private Thread th = new Thread(new dothread());
privateboolean canmove = false;
private Component com = null;
private Point pt = new Point();
MyClass() {
fm.setLayout(null);
fm.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);
fm.setBounds(300, 200, 450, 300);
fm.addMouseListener(new mouselisten());
lb.setBounds(10, 10, 100, 25);
// lb.hide();
th.start();
fm.getContentPane().add(lb);
fm.show();
}
class dothread implements Runnable {
publicvoid run() {
// TODO 自动生成方法存根
while (true) {
if (canmove) {
if (fm.getMousePosition() != null) {
pt.x = fm.getMousePosition().x;
pt.y = fm.getMousePosition().y;
lb.setLocation(pt);
}
}
}
}
}
class mouselisten implements MouseListener {
publicvoid mouseClicked(MouseEvent arg0) {
if (arg0.getButton() == 1) {
canmove = true;
}
else {
canmove = false;
}
}
publicvoid mouseEntered(MouseEvent arg0) {
}
publicvoid mouseExited(MouseEvent arg0) {
}
publicvoid mousePressed(MouseEvent arg0) {
canmove = false;
}
publicvoid mouseReleased(MouseEvent arg0) {
canmove = false;
}
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
new MyClass();
}
}

8.计算器
package Frame;
public class Compute {
public static void main(String args[])
{
ComputeFrame s=new ComputeFrame();
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package Frame;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ComputeFrame extends JFrame {
private JPanel EditTextPanel,ButtonPanel;
private JTextField input;
private JButton numbutton[];
private JButton btnDot, btnPosMinus, btnBackspace, btnDivide1, btnEqual, btnClear;
private JButton btnAdd, btnSubtract, btnMultiply, btnDivide;
private JButton btnX2, btnX3, btnXY, btnSin, btnCos, btnTan, btnSqrt, btnN, btnLeft, btnRight;
private int i;
ComputeControler comControler;
public ComputeFrame()
{
this.setBounds(300, 300, 400, 300);
//this.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE(this);
setVisible(true);
setLocation(400, 200);
EditTextPanel=new JPanel();
ButtonPanel=new JPanel();
input =new JTextField(20);
comControler=new ComputeControler(input);
input.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.HEIGHT);
input.setEditable(false);
numbutton=new JButton[10];
for( i=0;i<10;i++)
{
numbutton[i]=new JButton(""+i);
}
btnDot=new JButton(".");
btnPosMinus=new JButton("+/-");
btnBackspace=new JButton("Backspace");
btnDivide1=new JButton("1/x");
btnEqual=new JButton("=");
btnClear=new JButton("C");
btnAdd=new JButton("+");
btnSubtract=new JButton("-");
btnMultiply=new JButton("*");
btnDivide=new JButton("÷");
btnLeft = new JButton("(");
btnRight = new JButton(")");
btnX2 = new JButton("x^2");
btnX3 = new JButton("x^3");
btnXY = new JButton("x^y");
btnSqrt = new JButton("sqrt");
btnSin = new JButton("sin");
btnCos = new JButton("cos");
btnTan = new JButton("tan");
btnN = new JButton("n!");
EditTextPanel.add(input);
//布局
ButtonPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(6, 5));
ButtonPanel.add( btnLeft ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnRight ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnSin ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnCos ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnTan ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnX2 ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnX3 ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnXY ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnSqrt ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnN ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[7] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[7].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[8] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[8].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[9] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[9].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( btnAdd ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnClear ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[4] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[4].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[5] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[5].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[6] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[6].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( btnSubtract ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnBackspace ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[1] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[1].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[2] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[2].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[3] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[3].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( btnMultiply ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnDivide1 ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( numbutton[0] ).setForeground(Color.blue);
numbutton[0].setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( btnDot ).setForeground(Color.blue);
btnDot.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( btnPosMinus ).setForeground(Color.blue);
btnPosMinus.setBackground(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
ButtonPanel.add( btnDivide ).setForeground(Color.red);
ButtonPanel.add( btnEqual ).setForeground(Color.red);
//为每个按钮设置监听
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
numbutton[i].addActionListener(comControler);
}
btnDot.addActionListener(comControler);
btnPosMinus.addActionListener(comControler);
btnBackspace.addActionListener(comControler);
btnDivide1.addActionListener(comControler);
btnEqual.addActionListener(comControler);
btnClear.addActionListener(comControler);
btnAdd.addActionListener(comControler);
btnSubtract.addActionListener(comControler);
btnMultiply.addActionListener(comControler);
btnDivide.addActionListener(comControler);
btnX2.addActionListener(comControler);
btnX3.addActionListener(comControler);
btnXY.addActionListener(comControler);
btnSin.addActionListener(comControler);
btnCos.addActionListener(comControler);
btnTan.addActionListener(comControler);
btnSqrt.addActionListener(comControler);
btnN.addActionListener(comControler);
btnLeft.addActionListener(comControler);
btnRight.addActionListener(comControler);
add( EditTextPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH );
add( ButtonPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER );
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
package Frame;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class ComputeControler implements ActionListener{
JTextField textField;
//integer1 ,integer2
String op1, op2, operator;
String errMsg = "Error";
//the state for now ,begin state = 0
int state = 0;
ComputeControler( JTextField tf)
{
textField = tf;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed( ActionEvent e )
{
String s;
s = e.getActionCommand();
switch( state )
{
case 0:
inputState0(s);
break;
case 1:
inputState1(s);
break;
case 2:
inputState2(s);
break;
case 3:
inputState3(s);
break;
case 4:
inputState4(s);
break;
case 5:
inputState5(s);
break;
default:
System.out.println( "Unknow state error!" );
System.exit(1);
}
}
private boolean isDigit( String s )
{
boolean b;
b = s.equals("0")||s.equals("1")||s.equals("2")||s.equals("3")||s.equals("4")
||s.equals("5")||s.equals("6")||s.equals("7")||s.equals("8")||s.equals("9");
return b;
}
private int fN( float fop1 )
{
int ruslt=0;
if ( fop1 == 0 || fop1 == 1 )
{
ruslt = 1;
}
else
{
ruslt = (int) (fop1 * fN(fop1-1) );
}
return ruslt;
}
private boolean isOperator(String s)
{
return s.equals("+")||s.equals("-")||s.equals("*")||s.equals("/")
||s.equals("x^2")||s.equals("x^3")||s.equals("x^y")
||s.equals("sqrt")||s.equals("sin")||s.equals("cos")
||s.equals("tan")||s.equals("n!")||s.equals("(")||s.equals(")");
}
//state 0 start
private void inputState0( String s )
{
if ( isDigit(s)||s.equals("+/-")||s.equals(".") )
{
state = 2;
textField.setText("0");
inputState2(s);
}
if ( isOperator(s) )
{
op1 = "0";
operator = s;
state = 4;
}
if ( s.equals("1/x") )
{
textField.setText(errMsg);
state = 1;
}
}
//state 1 error
private void inputState1( String s )
{
if ( isDigit(s)||s.equals("+/-")||s.equals(".") )
{
textField.setText("0");
state = 0;
inputState0(s);
}
else
{
state = 0;
textField.setText("0");
}
}
//state 2 op1 reading,op1 is being input
private void inputState2( String s )
{
if ( isDigit(s) )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( text.equals("0") )
text = s;
else
text = text + s;
textField.setText(text);
}
if ( s.equals(".") )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( !text.contains(".") )
{
text = text + s;
textField.setText(text);
}
}
if ( s.equals("+/-") )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( text.charAt(0) == '-' )
text = text.substring(1);
else
text = "-" + text;
textField.setText(text);
}
if ( isOperator(s)||s.equals("1/x") )
{
state = 3;
op1 = textField.getText();
inputState3(s);
}
if ( s.equals("=") )
{
state = 3;
op1 = textField.getText();
}
if ( s.equals("C") )
textField.setText("0");
if ( s.equals("Backspace") )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( text.length() == 1 )
textField.setText("0");
else
textField.setText( text.substring(0, text.length()-1) );
}
}
//state 3 op1 read only, only op1 was input ,op2 = operator = null
private void inputState3( String s )
{
if ( isDigit(s)||s.equals(".") )
{
op1 = "";
textField.setText("0");
state = 2;
inputState2(s);
}
if ( s.equals("+/-") )
{
state = 2;
op1 = "";
inputState2(s);
}
if ( isOperator(s) )
{
operator = s;
state = 4;
if (operator.equals("x^2")|| operator.equals("x^3")||operator.equals("sin")
||operator.equals("cos")||operator.equals("tan")||operator.equals("sqrt")
||operator.equals("n!"))
{
inputState6(s);
}
}
if ( s.equals("1/x") )
{
Float fOp1 = new Float(op1);
if ( fOp1.floatValue() ==0.0 )
{
state = 1;
//error
textField.setText(errMsg);
}
else
{
float f = 1.0f/fOp1.floatValue();
op1 = String.valueOf(f);
textField.setText(op1);
}
}
if ( s.equals("C") || s.equals("Backspace") )
{
state = 0;
textField.setText("0");
}
}
//state 2, op1 and operator are read, op2 = null
private void inputState4( String s )
{
if ( isDigit(s)||s.equals("+/-")||s.equals(".") )
{
textField.setText("0");
state = 5;
inputState5(s);
}
if ( isOperator(s))
operator = s;
if ( s.equals("1/x") )
{
state = 3;
operator = "";
inputState3(s);
}
if ( s.equals("C") || s.equals("Backspace") )
{
state = 0;
textField.setText("0");
}
}
//state5,op2 reading,in reading of op2
private void inputState5( String s )
{
if ( isDigit(s) )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( text.equals("0") )
text = s;
else
text = text + s;
textField.setText(text);
}
if ( s.equals(".") )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( !text.contains(".") )
{
text = text + s;
textField.setText(text);
}
}
if ( s.equals("+/-") )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if (text.charAt(0) == '-' )
text = text.substring(1);
else
text = '-' + text;
textField.setText(text);
}
if ( isOperator(s) )
{
op2 = textField.getText();
Float f1, f2;
f1 = new Float(op1);
f2 = new Float(op2);
float fop1, fop2;
fop1 = f1.floatValue();
fop2 = f2.floatValue();
if ( operator.equals("+") )
fop1 = fop1 + fop2;
else if ( operator.equals("-") )
fop1 = fop1 - fop2;
else if ( operator.equals("*") )
fop1 = fop1 * fop2;
else if ( operator.equals("/") )
{
if ( fop2 != 0.0f )
fop1 = fop1 / fop2;
else
{
state = 1;
textField.setText(errMsg);
return;
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("Unknown operator error!");
state = 1;
textField.setText(errMsg);
return;
}
//here we got good calculating result
op1 = String.valueOf(fop1);
textField.setText(op1);
operator = s;
state = 4;
}
if ( s.equals("1/x") )
{
op1 = textField.getText();
state = 3;
inputState3(s);
}
if ( s.equals("=") )
{
op2 = textField.getText();
Float f1, f2;
f1 = new Float(op1);
f2 = new Float(op2);
float fop1, fop2;
fop1 = f1.floatValue();
fop2 = f2.floatValue();
if ( operator.equals("+") )
fop1 = fop1 + fop2;
else if ( operator.equals("-") )
fop1 = fop1 - fop2;
else if ( operator.equals("*") )
fop1 = fop1 * fop2;
else if ( operator.equals("/") )
{
if ( fop2 != 0.0f )
fop1 = fop1 / fop2;
else
{
state = 1;
textField.setText(errMsg);
return;
}
}
else if ( operator.equals("x^y") )
fop1 = (float) Math.pow( fop1, fop2 );
else
{
System.out.println("Unknown operator error!");
state = 1;
textField.setText(errMsg);
return;
}
//here we got good calculating result
op1 = String.valueOf(fop1);
textField.setText(op1);
state = 3;
}
if ( s.equals("C") )
{
state = 0;
textField.setText("0");
}
if ( s.equals("Backspace") )
{
String text = textField.getText();
if ( text.length() == 1 )
textField.setText("0");
else
textField.setText( text.substring(0, text.length()-1) );
}
}
//state6, new calculation
private void inputState6( String s )
{
Float f1;
f1 = new Float(op1);
float fop1;
fop1 = f1.floatValue();
if ( operator.equals("sqrt") )
{
if ( fop1 < 0 )
{
textField.setText(errMsg);
return;
}
else
fop1 = (float) Math.sqrt( fop1 );
}
else if ( operator.equals("x^2") )
fop1 = fop1 * fop1;
else if ( operator.equals("x^3") )
fop1 = fop1 * fop1 * fop1;
else if ( operator.equals("sin") )
fop1 = (float) Math.sin( fop1 );
else if ( operator.equals("cos") )
fop1 = (float) Math.cos( fop1 );
else if ( operator.equals("tan") )
fop1 = (float) Math.tan( fop1 );
else if( operator.equals("n!") )
fop1 = this.fN(fop1);
op1 = String.valueOf(fop1);
textField.setText(op1);
}
}
实验感想:
-
网络编程实验报告
网络编程课程设计报告题目姓名学院专业班级学号指导教师基于Linux网络聊天室的设计陈佳悦陈雄兰信息科学技术学院网络工程网络工程10…
-
网络编程试验报告
武汉理工大学学生实验报告书实验课程名称网络软件编程技术开课学院计算机科学与技术学院指导老师姓名学生姓名学生专业班级软件sy1101…
-
网络编程实验报告
20xx年秋季学期计算机网络编程实验报告班级计121班学号12101020xx8姓名刘杰总成绩评语指导教师签字日期实验一登陆页面及…
-
网络编程实验报告
计算机科学与工程学院网络工程专业20XX级网络编程实验大作业报告网络编程实验大作业报告即时通讯软件的设计与实现完成日期20xx41…
-
网络编程实验报告
实验一TCPSocketAPI程序设计一预备知识1网络编程基本概念网络上的计算机间的通讯实质上是网络中不同主机上的程序之间的通讯在…
-
12月学生会总结
12月月总结桂香送走了秋天,风雨迎来了冬天,在这丝毫不感觉到寒冷的冬日里,我的学生会工作生活也在忙碌而紧凑的步伐中度过了一个学期。…
-
矿山见习工作总结
20xx年x月见习总结第一个月参加工作,虽进行的只是看似简单的岗前培训,但在这期间还有很多不足之处需要深刻的反省,通过总结和反省,…
-
学雷锋活动总结
细柳街道石匣小学“学雷锋”系列德育活动总结细柳街道石匣小学20xx年x月20xx年石匣小学“学雷锋”系列德育活动总结雷锋精神是我们…
-
城管局近五年工作总结
20xx年以来,在市委、市政府的正确领导下,在有关部门和全社会的支持参与下,我局上下团结奋进,开拓创新,不断转变工作理念,不断创新…
-
20xx年度财务部工作总结
岁月如梭,光阴似箭,20xx年已经过去,崭新的20xx已经到来,回顾过去,在公司领导无微不至的关怀下、及各部门的协同努力下,我们克…