实验报告英文版
The determination of nitrogen content in the ammonium salt(Formaldehyde method)
一、The experiment purpose
1、To study the application of acid-base titration
2、Master the formaldehyde method principle and the method for determination of nitrogen content in the ammonium salt
3、The use of master the volumetric flask and pipet
二、The experimental principle
Because NH4 acid is too weak to directly with NaOH standard solution titration, we usually using formaldehyde is transformed into titratable acid:
4NH4++6HCOH=(CH2)6N4H++3H++6H2O
Products, hydrogen ions and (CH2)6N4H+ can be directly for accurate titration,titration product (CH2)6N4 is weak alkaline, so using phenolphthalein as indicator.
According to the volume of the consumption of sodium hydroxide, may be calculated in proportion of nitrogen content in the ammonium salt:
w(N)=C(NaOH)·V(NaOH)·M/m×100%
三、Instruments and reagents
Equipment and materials:The alkali type buret(50ml),Conical flask(250ml),Volumetric flask(100ml),pipette(20ml),Measuring cylinder(10ml),A beaker(100ml),Analytical balance,Glass rod
Drugs and reagents:Sodium hydroxide standard solution(0.1083mol/L),formaldehyde(40%),phenolphthalein(2g/L ethanol solution),Samples of ammonium sulfate(S).
四、The experimental steps
1、Accurately according to 0.60 ~ 0.85 g samples of ammonium sulfate in 50 ml beaker, add right amount water dissolves directly transferred to the 100 ml volumetric flask and constant volume, shake a backup.
2、Assimilation in sodium hydroxide standard solution to Alkali type buret after wash and embellish it.
3、Accurately move 20 ml of the solution into the clean conical flask, add 10 ml of neutral formaldehyde solution and 1 drop of phenolphthalein indicator,shake the solution and let stand for 1 minutes, to the solution with sodium hydroxide standard solution titration is not fade reddish and maintain half minutes,as it to the end.
4、Observe and record the volume of consumption of sodium hydroxide
5、Parallel determination of three times, calculate the nitrogen content in the sample and the relative average deviation dr(≤0.3%)
五、The experimental results and data processing
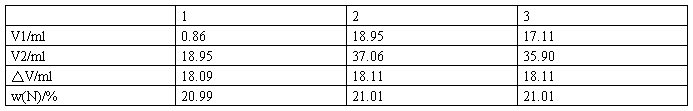
W(N)=(20.99%+21.01%+21.01%)/3=21.00%
d=(0.01%+0.01%+0.01%)/3=0.01%
dr=d/w(N)=0.01%/21.00%×100%=0.05%.
第二篇:机能实验报告英文版影响尿生成的因素
Function experiment report
Regulation of Urine Formation
本组承诺:本实验报告原创,绝无抄袭!
组员:
Influence factors of urine formation
[PURPOSE]:
Master influence factors of urine formation and analyzes the mechanism, further understand the renal excretory function.
[ANIMAL]:
Rabbit
[METHODS]:
Operation
Take one rabbit, weighing. According to 4ml/kg, find the vine at the edge of an ear and tnen inject into the 25% urethane solution for anesthesia. Observe the respiratoryrate, corneal reflection, skin clip kneading and muscle relaxation.
Operation in cervix: Separate the right vagus nerve and thread a period of line under it. Set aside.
Operation in abdomen: Firstly, ligate the external orifice of urethra in order to prevent the loss of urine when the bladder was stimulated during the experiment. Secondly, shear the ventral hair, and snip an incision about 3-5cm above the pubic symphysis along the linea alba abdominis, move out the bladder. Then choose the blood vessels less place on the bladder top, using three hemostatic forceps clamp it, cut the bladder open. Insert the cannular into the bladder immediately and then ligature.
Observation item
(1) Record the normal urine volume for five minutes, as normal control.
(2) The effect of the saline on the urine volume: Inject 20ml saline(38℃)into the vein in the ear margin of the rabbit within 1 minute. Observe the urine volume changes and record.
(3) The effect of the norepinephrine on the urine volume: Inject 1:10000 norepinephrine (0.3ml)into the ear margin of the rabbit. Observe the urine volume changes and record.
(4) The effect of glucose on the urine volume :Firstly, collect 2drops of urine to test glucose in urine as normal with a qualitative test paper. Then 20% glucose (1.5ml/kg)was injected into the vein in the rabbit’s ear ,and observe the urine volume changes and record.2drops of urine was collected to test glucose in urine qualitatively every 1 or 2 minutes.
(5) The effect on the urine volume when the peripheral end of the vagus nerve is stimulated: Ligate the right vagus nerve and cut it off. Use the computer to stimulate the peripheral end of the vagus nerve. Observe the urine volume changes and record.
(6) The effect of diuretic on the urine volume: Inject the furosemide into the ear margin of the rabbit. Observe the urine volume changes and record.
[RESULT]:
Various factors influence the urine volume changes
influencing factor urine volume urine glucose
normal ― ―
the saline ↑
noradrenaline ↓
glucose ↑ ++
the vagus nerve ↓
the furosemide ↑
[DISCUSSION]:
The process of the urine formation:The process of the urine formation including glomerular filtration and the reabsorption and secretion of the tubules. The power of the urine formation is the effective filtration pressure .First, the glomerular effective filtration pressure is depended on the three reasons: intraglomerular capillary pressure、colloid osmotic pressure of plasma and renal plasma flow(RPF). The intraglomerular capillary pressure is effected by the systemic arterial pressure mainly, when the arterial pressure is between 80~180mmHg,because of the autoregulation of the RPF, the intraglomerular capillary pressure can maintain at relatively stable level. But when the arterial pressure is higher than 180mmHg or lower than 80mmHg, the intraglomerular capillary pressure will change as the blood pressure, the glomerular filtration rate(GFR) will change relevantly. Besides, when the colloid osmotic pressure of plasma reduce ,the effective filtration pressur will rise, and the GFR will rise too. Second, the reason that effect on the urinary function of the renal tubule and the collecting tubule including the neuroregulation, humoral regulation and autoregulation. While one of the two reasons is effected, the urine volume will change.
plasma reduce ,the effective filtration pressur will rise, and the GFR will rise too. Second, the reason that effect on the urinary function of the renal tubule and the collecting tubule including the neuroregulation, humoral regulation and autoregulation. While one of the two reasons is effected, the urine volume will change.
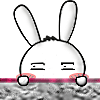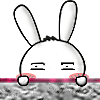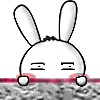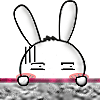
1)When inject in the normal saline 20ml once:(1)The blood volume will increase, the glomerulus plasma flow will increase ,the GFR will rise, so the urine volume will increase.(2)The blood volume increase, it will stimulate the left atrium and the atrium volume receptor, the receptor exciting .The impulse reach to the supraoptic nucleus and the paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus, the ADH will decrease, the reabsorption of water will decrease. So the urine volume will increase.(3) The blood volume increase, the blood is diluted, so the colloid osmotic pressure of plasma will decrease, the GFR rise, so the urine volume, will increase.
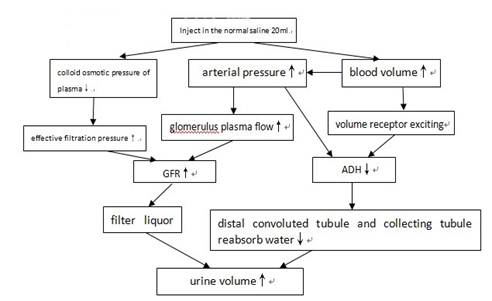
 2) When inject in norepinephrine in vein, it will combine with α-receptor in the smooth muscle of the periphery arteriole. The arteriole will contract, so the blood pressure will rise. The glomerulus plasma flow will decrease .The the colloid osmotic pressure of plasma will rise as well. As a result, the GFR will fall. So the urine volume will decrease.
2) When inject in norepinephrine in vein, it will combine with α-receptor in the smooth muscle of the periphery arteriole. The arteriole will contract, so the blood pressure will rise. The glomerulus plasma flow will decrease .The the colloid osmotic pressure of plasma will rise as well. As a result, the GFR will fall. So the urine volume will decrease.
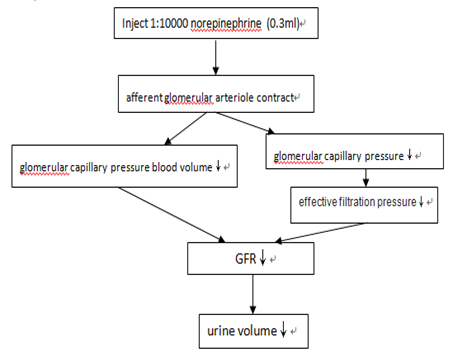
3)When inject glucose into the vein of the ear, the urine volume will increase. When the glucose concentration rise to 160-180mg/100ml, there will be glucose in the urine. The blood glucose concentration is calld renal glucose threshold. When the concentration pass the renal glucose threshold ,a great quantity of the glucose filter out from the glomerulus can’t be reabsorbed by renal tubule epithelial cells totally. When the concentration rise to 300mg/ml, all reabsorption of the glomerulus will reach to the limit. If there arised a great quantity of the glucose in the blood plasma, the renal tubule osmotic pressure will rise, it will hinder renal tubule reabsorbing water. So the glucose will exhaust with urine and the urine volume will increase. The normal person’s renal tubule can reabsorb glucose to the blood plasma, there will be infinitesimal glucose in the urine and it can’t be found out in the urine. But when the concentration exceed the renal glucose threshold, it will can be detected by the qualitative test paper. It will find that the glucose concentration rise obviously.
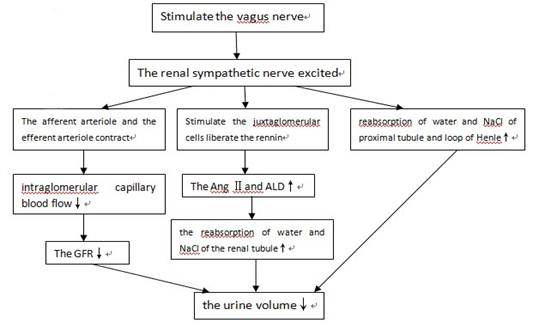
 4) Stimulate the vagus nerve will make renal sympathetic nerve excited. The afferent arteriole and the efferent arteriole will contract at the same time, and the former one will contract more obviously, the intraglomerular capillary blood flow will decrease, the GFR will fall too, the urine volume will decrease. The stimulation will reach to the juxtaglomerular apparatus and it will stimulate the juxtaglomerular apparatus. The juxtaglomerular cells will liberate the rennin. It will cause more angiotensinⅡ(Ang Ⅱ)and aldosterone (ALD) liberate . The Ang Ⅱand ALD will increase the reabsorption of water and NaCl of the renal tubule. Stimulating the vagus nerve will increase the reabsorption of water and NaCl of the proximal tubule and the loop of Henle. These all will increase the urine volume.
4) Stimulate the vagus nerve will make renal sympathetic nerve excited. The afferent arteriole and the efferent arteriole will contract at the same time, and the former one will contract more obviously, the intraglomerular capillary blood flow will decrease, the GFR will fall too, the urine volume will decrease. The stimulation will reach to the juxtaglomerular apparatus and it will stimulate the juxtaglomerular apparatus. The juxtaglomerular cells will liberate the rennin. It will cause more angiotensinⅡ(Ang Ⅱ)and aldosterone (ALD) liberate . The Ang Ⅱand ALD will increase the reabsorption of water and NaCl of the renal tubule. Stimulating the vagus nerve will increase the reabsorption of water and NaCl of the proximal tubule and the loop of Henle. These all will increase the urine volume.
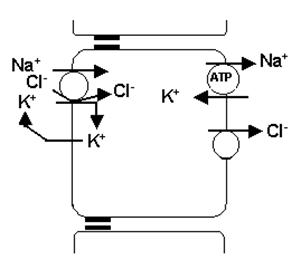
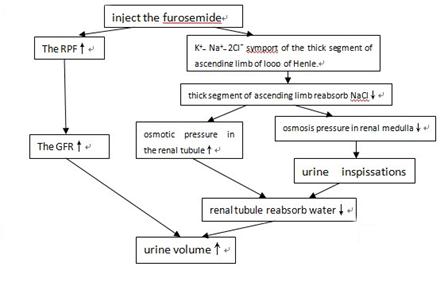
 5)When inject the furosemide into the vein, it will stop the K+_ Na+_ 2Clˉ symport of the thick segment of ascending limb of loop of Henle. Hinder the osmosis gradient of renal medulla forming. The osmotic pressure in the renal tubule will rise. As a result, the urine inspissations will lower. The renal tubule reabsorb water will be depleted immensely. The urine volume will increase.
5)When inject the furosemide into the vein, it will stop the K+_ Na+_ 2Clˉ symport of the thick segment of ascending limb of loop of Henle. Hinder the osmosis gradient of renal medulla forming. The osmotic pressure in the renal tubule will rise. As a result, the urine inspissations will lower. The renal tubule reabsorb water will be depleted immensely. The urine volume will increase.




[CONCLUSION]:
1. Injecting saline , glucose and furosemide into the vein will cause the increment of the urine volume.
2.Injecting norepinephrine into the vein or stimulate the vagus nerve to descend the blood pressure within limits will decrease the urine volume.
3. Injecting saline into the vein will influence on the glomerular filtration including intraglomerular capillary pressure, colloid osmotic pressure of plasma and RPF.
4. Injecting norepinephrine influence on the glomerular filtration and the most important is influence on the intraglomerular capillary pressure.
5. Injecting glucose influence on the reabsorption and secretion of the tubules. It influence on the the solute concentration in the renal tubule. It belongs to humoral regulation.
6. Stimulating the vagus nerve influence on the reabsorption and secretion of the tubules. It influence on the renal sympathetic nerve. It influence on the three reasons.
7. Injecting furosemide influence on the reabsorption and secretion of the tubules. It influence on the humoral regulation.
-
英文实验报告模板
Determinationofheavymetalsinsoilbyatomicabsorptionspectrometry(AA…
-
英文实验报告的格式和写法
英文实验报告的格式和写法转20xx10040603一份最标准的实验报告的格式1Abstract2Introduction3Meth…
- 物理实验报告 英文版
-
英文版实验报告
PreparationofAspirinPurposeofexperimentUnderstandprinciplesandmethodsofprep…
-
大学物理实验报告英文版--全息照相
physicallabreportHolographyWriterBackgroundsLightsareelectromagneticwavesAm…
-
英文实验报告模板
Determinationofheavymetalsinsoilbyatomicabsorptionspectrometry(AA…
-
英语读写实验报告(跳舞)
课程实验报告专业年级课程名称大学英语读写I指导教师姚倩学生姓名徐杨钦陈双双马倩滕文文赵再凤雷琴学号实验日期20xx年12月16日实…
-
英语专业国际商务谈判实验报告
广东商学院华商学院专业实习记录本实习单位实习时间院系专业学号410080211姓名李雪萍教务处制2说明1填写实习记录本是为了使学生…
-
3_《外贸英语函电(双语)》课程实验报告
外贸英语函电双语课程实验报告书一实验目的外贸英语函电是国际贸易专业一门主干课程本课程注重理论与实践相结合既要讲授对外贸易业务各个环…
-
1 外贸英语函电实验报告模板(已包含实验报告书封皮)
外贸英语函电课程实验报告学期1011学年第2学期姓名彭骅学号20xx07070110指导教师祝福云班级国贸08120xx年月日外贸…