毕业设计进展中期小结模板
表三:青岛科技大学本科毕业设计(论文)进展中期小结
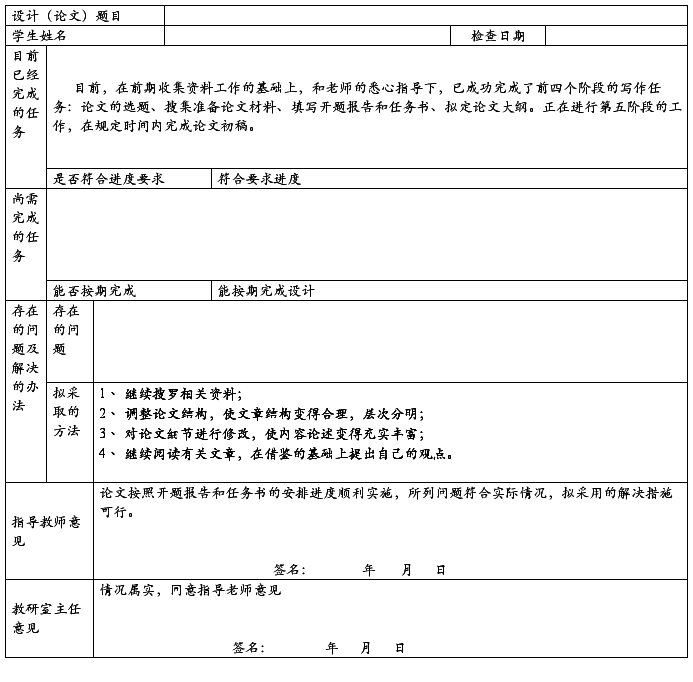
注:①本表应在第八学期的第8~9周内完成填写;
②以上三个表格作为学生档案资料由院(部)保存五年。
第二篇:毕业设计指导教师中期检查材料(模板)
毕业设计(论文)期中工作材料
学生姓名: 学院(系): 专 业: 设计(论文)题目: 小
标
题
:
*** 学 号: 2007.....
软件学院 xxxx
基于P2P的在线五子棋游戏的开发
***
指导教师:
材 料 目 录
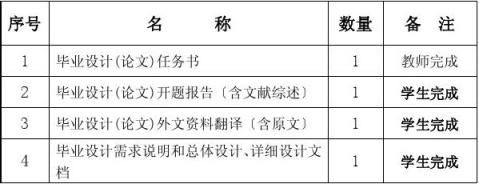
20xx年4月
华东交通大学毕业设计(论文)任务书

华东交通大学毕业设计(论文)开题报告书

课题类型:(1)A—工程设计;B—技术开发;C—软件工程;D—理论研究;
(2)X—真实课题;Y—模拟课题;Z—虚拟课题
(1)、(2)均要填,如AY、BX等。此部分可以附页
华东交通大学毕业设计(论文)开题报告书

毕业设计(论文)外文资料翻译
外文出处:
附 件: A.外文翻译 -原文部分

附录A 外文翻译 -原文部分
Study on Resources Locating Technology of P2P Network With the network technology advances and power of PCs enhances, which makes the rapid development of peer-to-peer(P2P) computing pattern. The computing pattern of Internet is transforming from C/S to P2P. P2P technology has been seen as one of the most popular computer technology in twenty-one century. P2P networks ignore obvious difference between server and client. Nodes collaboration made by network interflow improved the utilization of resources and bandwidth; enhanced network expansibility, reliability.
Unlike other traditional systems, P2P systems demonstrate some challenges to resource searching technique in the networks. In order to utilize various resources in P2P networks, those resources should be effectively found first. Resources locating is a key issue of P2P network and a research hotspot as well. Based on a network topology, the resources locating models of P2P system can be classified as structured P2P networks and unstructured P2P networks. Compared with unstructured P2P networks, structured P2P networks have the advantages of efficiency. The core of Resources locating of structured P2P networks is the P2P routing algorithm. The efficiency, scalability, and the resilience to failure of the P2P algorithm are of great significance to P2P applications. The thesis makes some researches on the efficient search (location) of P2P network. Following from the analysis of Chord routing protocol, its inadequacies exists that need to discussed and proposed measures for improvement.
Chord protocol topology: Chord using one-dimensional Ring Topology, to each node and
the document is given an m-bit key identifier by Consistent Hashing. Node identifier (Nid) are through the node IP address hash transformation received, document identifier (Kid) are through the contents of the document hash transform received, node identifiers and document identifiers are exist in a one-dimensional discrete annular space.
Chord routing algorithm: According to the allocation method of Chord keywords, any one of your keywords are can only appear in the corresponding nodes on follow-up, and the subsequent nodes are unique. Routing algorithm is used to query whether a keyword exists in one of the whole nodes of Chord ring, this particular keyword if it exists, just return message of have find it; if there is no found so without the keywords message.
Routing process is as follows:
1) Node send a request of search, first of all, check whether keyword index at the local, if there is then return, or else turn to the next step.
2) Search routing table information of local node, get the node that keywords closest and less than the keywords value. Send request directly to the node, then the node receiving the query request to repeat this step until the search to the target node.
Problem existence of Chord:
a) Routing delay: Chord protocol is work at the application layer, it is mapped to a unified logic space through the hash function nodes and the document
index, and making a self- organization coverage net according to its own
mechanism.
b) Node heterogeneity: In P2P networks, status of each node is equal, which
based on the load balancing point of view. But this equality is unrealistic, in fact, nodes in P2P network are prevailing differences, also as the storage capacity、CPU capacity、network capacity and time-activities of node. However, such differents are did not consider between these nodes in Chord network.
The new model——TChord Resource Locator System:
Based on the current Routing model information, it is a group-based overlay network resource locator model——Tchord.
First, according to the heterogeneity of nodes, TChord have take full account of the use of "comprehensive performance node," node-based online heterogeneity, we use the relative stability that so-called super-node Chord to become a regional base in the first node, adaptive model of a two-tier structure of P2P networks. The upper layer an adaptive Chord network made up of super-nodes , and the lower is grouped by super-nodes that it is central server of general-nodes. Super-node to join or leave upper layer network at not to protect the entire logic topology consistented, only a simple update node precursor, successor node routing table, the other adjust the local cache at super-node when the message forward to dynamically to makes network routing logic topology tend to be consistent, thus ensuring the efficiency of query. The lower node to retain this group Super backup node in the super-node failure when re-selection to generate a new super-node.
Secondly, considering the node’s location information, to add in the proximity table at supp-
er-node in upper layer is in order to keep consistent relationship between improved Chord net to-
pology and the physical network topology.
Routing algorithm TChord Description:
Construction of neighbor table: Super-node using neighbors table to store the collected in- formation of neighboring nodes. Every adjacency record list is a dual Group contains ID values
and neighboring IP. Collect neighbor table information is through landmark binning algorithms and RTT (Round Trip Time). The principle is set several public overall landmark nodes, and the geographical location of landmark nodes should scattered as far as possible. Measurement delay
time of each node and the public overall landmark nodes, then order delay in
accordance by asc- ending or descending. Thinking the same sequence of landmark nodes are considered as the same region in physics, then do further distinction of nodes in the region by RTT method. Add node to their own table when the measured area of a node delay time is less than a particular threshold on the node, when the neighbor node table Maximum number of neighbors when the deletion of the table furthest physical distance node. The following algorithm process is to build a neighbor table:
In TChord system, use "heartbeat" algorithm to ensure the node’s validity in neighbors table in cycle. Each super-node would delete lapsing neighbor node from
the current node’s Proximity Table when a focus node has detected left the coverage net by heartbeat algorithm. In addition, if it found a new neighbor node, the two nodes will exchange their neighbor node proximity table, that means add the nodes which only present in their neighbors Proximity Table. The correctness of routing depend on the state of node’s successor and Proximity Table of super node only be used to optimize routing efficiency. Therefore, the heartbeat cycle of Proximity Table must equal to maintenance cycle of node’s Finger Table.
Super-node caching strategy:
In order to speed up the resource locator and reduce the query hops in TChord system, led a group of the different nodes can duplicate inquiries at the group house, the model take up super node cache management strategy to reduce the number of inter-group duplicate search. Each sup
super-node at backbone must have the memory space for resource query Cache.
Specific strategy of cache management is: Setup a counter for each ordinary node in group, when an ordinary node release new resource initialized to 1 on the
corresponding data, so the resources queried on the Record by the counter. It is the keywords overheating when the times been visited reach a threshold, then several network nodes will connect the node to transmission in a certain period.
Ordinary node sent the resources index to the other super-node in its own group. At the same
time, sent the keyword index to super-node in its physical neighbor table to update their cache content. Update cache content by cache indexing algorithm when the super-node cache overran the Maximum Record, which based on configuration file. Commonly used such as FIFO, LRU and LFU, etc. .
Advantage of this approach lies in the fact that if a document has been visited more than our pre-determined threshold, then we consider this document are the generally welcomed document in current networks, so within a period of time there will be a lot of users search the document. Been caching strategy, the super-node to see own query cache firstly when super-node receive
inquiry request from group-node. If there is indexing records matching ObjKey then immediately return else send request of resources inquiries at backbone. This allows the network to do a large part of the internal inquiry could be completed in the group. Because of the information stored in cache is popular and nearby, so improve search efficiency and reduce network traffic and reduce the routing overhead and time overhead storage.
The core of routing algorithm is choice of logical next-hop. Different from Chord, TChord improved the algorithm of decide the nest-hop not only depend on Finger Table, but also Proximity Table. At the same time, this algorithm select the next-hop node is in a balanced strategy base on the physical distance and the logical jump, not just wholly use neighbor table node replace routing table on logic next-hop. Resume treatment of node ineffective:
In Chord, all pointer table including node n must be replaced by n put n successor nodes when node n fails. In addition, the failure of node n should not affect the process of ongoing inquiry in system. The most critical steps in failure treatment is to maintain successor pointer correctly. In order to guarantee this, each Chord node including should include a recent follow-up list at the mount of r.
If node n noted its subsequent node failure, it will use first normal node to replace
the failure node in the successor list. In TChord system, a variety of operating mainly executive in the super-node in upper layer, so when an ordinary node failure, the entire network topology do not have a huge impact. Up only report error when query the resources that the node releases. However, when the super-node fails, not only the entire group can not work, but also the normal operation of the main network will be affected, such as message transmit. Therefore, we only consider failure treatment of super-node.
A copy of the node detecting whether the super-node failure through the timing Ping commend. When confirmation the super-node failure, then resume treatment are as follows:
First, Backup node will replace the ineffective super-node as the group's new super-node, added to its own with ineffective super-node’s copy information. And then choose the best node in comprehensive evaluation as backup node from the list of backup nodes. Add the list of backup nodes and backup information of super-node to the new backup node.
Secondly, do restoration of ineffective node, the process is similar to node update in Chord Model. Exchange super-node’s subsequent to its own by precursor node, and inform the subsequent node to change the precursor to its own.
Finally, update super-node routing by ordinary nodes in group.
Based on the Chord routing protocol in-depth study, in the view of the logic of Chord topology and physical topology phase separation resulting in large routing delay and the "disturbance" in the system overhead caused by large and inefficient routing to improve both aspects. A structured hierarchical P2P model TChord. The new model will be a network node in accordance with the node's IP address is divided into different groups, groups constitute the interconnection between the distributed P2P network. TChord will be approaching a physical network routing algorithm organically into the Chord routing algorithm, in the next hop node to the logic of distance and physical distance between the value of a balanced selection, which can be at the routing table and neighbor table Choose the best hair the next Jump. At the same time, through the introduction of the strategy group of the first node cache mechanism, making Tchor not only reduce the number of cross-group search, but also reduces the routing overhead positioning, resulting in improved search efficiency.
附录B 外文翻译 -译文部分
P2P对等网络资源定位技术的研究
随着网络技术的飞速发展和个人计算机性能的增强,对等计算模式得到快速发展,互联网的计算模式正经历着从C/S模式向P2P(Peer-to-Peer)模式的转变。P2P技术被视为21世纪计算机技术的热点技术之一。对等网络架构去除了服务器端与客户端的明显区别,网络的互通使得网络中的各个节点能够彼此协作,提高了网络中资源、带宽的利用率,增强了网络的可扩展性、可靠性。
与传统系统不同,P2P系统具有规模巨大和动态性强等特点,这些特点给P2P资源搜索技术带来了巨大挑战。要想充分地利用网络中的各种资源,前提条件是能够有效地搜索到资源。资源定位问题是P2P网络的核心问题之一,也是P2P网络当前研究的热点。P2P的资源定位模型,按拓扑结构的不同可分为结构化对等网络和非结构化对等网络。与非结构化对等网络比较,结构化对等网络具有查找效率高和查找确定性等优点。路由算法是结构化对等网络资源定位的核心,它的路由效率、可扩展性和容错性对对等网络有着很重要的意义。本文就P2P对等网络中有关高效资源搜索(定位)的问题展开研究,下面通过对Chord路由协议的分析,针对其存在的不足之处展开讨论并提出改进办法。
Chord协议的拓扑结构(topology structure):Chord采用一维的环形拓扑结构,通过一致性哈希变换 (Consistent Hashing),通常使用哈希函数SHA-1,给每一个节点和文档都赋予一个m位的标识符key,节点的标识符(Nid)是通过对节点的IP地址进行哈希变换得到的,文档的标识符(Kid)是通过对文档的内容进行哈希变换得到的,节点标识符和文档标识符共同存在的一个一维离散环形空间。
Chord协议的路由算法(Routing Algorithm):根据Chord关键字的分配方法,任何一个关键字都是只能出现在相应的后继节点上,而且这个后继节点是唯一的。路由算法就是用来查询某个关键字是否存在于Chord环中的某个节点之上,这个特定的节点上如果存在该关键字就返回找到消息,如果没有就返回环中无该关键字的消息。路由过程如下:
1) 节点发出查询请求,首先在本地是否保存查询关键字的索引,如果有则返回,否则转向下一步。
2) 查找本地节点路由表信息,找到最接近关键字key并且小于关键字key的节点,直接向该节点发送查询请求,节点接到查询请求后重复该步骤,直到搜索到目标节点。
Chord存在的问题:
① 路由延时:Chord是一种工作在应用层的网络,它是通过哈希函数将节点和文档索引映射到统一的逻辑空间,按照自己的机制自组织成一个覆盖网。然而通过映射之后,节点的位置信息全都被破环了,对等节点的物理位置与逻辑标识符之间的哈希散列关系,使得两者之间不存在任何联系,这就使得逻辑空间中节点的关系并不能对应实际网络中的关系,即覆盖网中相邻的节点可能在底层物理网络中相隔很远。这样就造成了相当大的网络延迟,路由效率不高。
② 节点异构性:在P2P网络中,基于负载均衡的角度考虑,节点的地位是平等的。但这种平等是不现实的,事实上,P2P网络中的各节点存在普遍的差异性,包括每个网络中节点在存储能力、CPU能力、网络能力以及节点活动时间长短等很多方面都存在差异。然而在Chord等覆盖网中模型中均没有考虑这些节点之间的差异。
新模型——TChord资源定位系统:
针对当前路由模型存在的信息,现提出一种基于群组的覆盖网络资源定位模型TChord。第一,根据节点的异构性,TChord采用充分考虑到“节点的综合性能”,基
于节点在线的异构性,我们利用相对稳定的所谓超级节点使之成为Chord中某区域的群首节点,采用自适应两层结构P2P模型网络,上层由超级节点组成一种自适应的结构化Chord网络,下层普通节点以本组超级节点为中心服务器形成群组。上层超级节点网络在节点加入或离开的时候不维护整个网络逻辑拓扑的一致,只简单更新节点前驱、后继节点路由表,另外在超级节点转发消息时动态地调整本地路由缓存使得网络逻辑拓扑结构趋向于一致,从而保证查询效率。下层节点保留本组超级节点备份,在超级节点失效的时候重新选择生成新的超级节点。
第二,针对节点的位置信息,为了实现改进后的Chord覆盖网(即TChord)的拓扑结构与其参与结点的物理网络拓扑结构之间的一致关系,在上层超级节点中引入了物理邻居表Proximity Table。
TChord路由算法描述:
邻居表的构建:在TChord系统的超级节点中使用了Proximity Table来反映节点的物理位置信息,邻居表是用于存放收集到的邻近节点信息的。每一项邻接表记录是一个二元组<NodeID,NodeAddress>包含邻近节点ID值和邻近节点的IP两个部分。邻接表的信息采集是利用界标簇(landmark binning)算法和往返延迟(RTT,RoundTrip Time)测量技术收集。其基本原理是首先在Chord网络中设置几个公开的全局的界标节点(landmark node),界标节点的地理位置尽量要求分散。每个节点和全局已知的几个界标节点进行延时测量,然后把延时按照某种顺序(升序或降序)进行排列,具有相同界标顺序的节点被认为在物理上是同一区域的。然后利用往返延迟测量技术把落在同一个区域中的节点进行进一步的区分。当测量到区域内某个节点延迟时间小于一个特殊阀值时就将该节点加入到自己的邻居表中来,当邻居表节点数量达到最大值时则删除该邻居表内物理距离最远的节点。以下是构建邻居表算法的过程:
为保证邻居表中节点的有效性,TChord的维护是通过周期性的“心跳”(heartbeat)算法来进行的。每一个TChord的超级节点只要通过“心跳”算法探测到其邻居节点集中的一个节点已经离开覆盖网时,就从当前节点的ProximityTable中删除该已失效的邻居节点。另外,如果TChord节点发现了新的邻居节点时,两节点会交换自己的Proximity Table的邻居节点,将对方节点的ProximityTable中存在而自己的Proximity Table没有的邻居节点加入到本地的ProximityTable中来。同时由于TChord超级节点的Proximity Table仅被用来优化路由效率,而路由的正确性仍然需要由节点的Successor状态保证。因此,Proximity Table的心跳周期和节点的Finger Table的维护周期应相同。
超级节点缓存策略:
为了加速TChord系统的资源定位,减少查询的跳数(hops),使得一个群组内的不同节点的重复查询可以在本群组内部完成,减少跨群组重复查找的次数,本模型采用了超级节点缓存管理的策略。主干网上的每个超级节点都有一定的内存空间用于资源查询的Cache(缓存)。
具体的缓存管理策略是:为群组中的普通节点每个查询的资源设置的一个计数器,当普通节点的中发布一个新资源时就将该对应的数据初始化为1,该资源被查询次数就由该计数器记录。如果节点中某个资源被访问的次数达到一个阀值,则认为该关键字为过热关键字,网络中多个节点在一段时间内都会连接该节点进行数据传输。
此时普通节点将该资源索引传送给该群组的超级节点。同时将该关键字索引发送给其物理邻居表中的超级节点成员以更新其缓存内容。当超级节点缓存超过最大值时可以采用缓存索引记录的替代算法进行更新,缓存索引记录的替代算法可以根据配置文件设定。常用的替代算法有FIFO,LRU和LFU等。
这种做法的好处在于,如果一个文件的被访问次数超过了我们预先设定的阀值,那么我们就认为这个文件是当前网络中流行的普遍受到欢迎的文件,一段时间之内会有很多用户查找这一文件。使用了缓存策略后,当超级节点收到其群组节点的查询请求时,超级节点都先查看自己的查询缓存,如果存在与查询ObjKey匹配的索引记录,就立即返回。只有查询结果不在超级节点的缓存时,才在主干网上发送资源查询请求。这样做使得网络中很大一部分查询可以在群组内部完成。由于缓存中存放的都是近期内热门资源的索引,可使得缓存查询的命中率大大提高,从而有效提高搜索效率,减少网络流量,降低了路由的存储开销和时间开销。
在路由算法中核心是逻辑下一跳的选择。和Chord不同,TChord主网路由在原Chord算法的基础上做了改进。改进后的TChord主网路由算法中选择下一跳的不仅由节点路由指针表(Finger Table)决定,同时也被邻居表(Proximity Table)信息所影响。同时该算法并非一味的用邻居表节点代替路由表节点来选择逻辑下一跳,而是在物理距离和逻辑跳数之间采取一个平衡策略来选取下一跳节点。
节点失效恢复处理:
在Chord中,当结点n失效时,所有在指针表中包括n的结点都必须把n替换成n的后继结点。另外,结点n的失效不能影响系统中正在进行的查询过程。在失效处理中最关键的步骤是维护正确的后继指针.为了保证这一点,每个Chord结点都维护一张包括r个最近后继的后继列表。
副本节点通过定时Ping超级节点,探测超级节点是否已失效。当确认超级节点失效后,节点失效处理步骤如下:
⑴ 备份节点会首先取代失效超级节点作为该群组的新超级节点,将失效超级节点备份的信息添加到自身。之后再从备份节点列表中选出一个综合评价性能最好的节点作为备份节点。备份节点列表和超级节点备份信息添加到新的备份节点上去。
⑵ 然后再进行节点失效修复工作,其过程Chord模型中的节点更新过程相仿。通知超级节点Chord环上的前驱节点更改其后继为自身,通知后继节点更改其前驱为自身。
⑶ 最后通过组内普通节点更新超级节点路由为自身。
本文通过对基于Chord路由协议的深入研究,针对Chord的逻辑拓扑和物理拓扑相分离导致路由时延大与“扰动”现象引起的系统开销大及路由低效两个方面问题进行改进。提出了一种分层的结构化P2P模型TChord。新模型将网络中的节点按照节点的IP地址划分为不同的群组,群组之间互连构成分布式的P2P网络。TChord将物理网络的临近路由选择算法有机地组合到Chord的路由算法中,在节点至下一跳的逻辑距离与物理距离之间选择一个均衡值,进而可在路由表和邻居表中选择最佳下一跳转发。同时通过引入群首节点缓存策略机制,使得TChor不仅减少跨群组搜索的次数,而且减少了路由定位开销,从而提高了搜索效率。
附录C 毕业设计需求说明和总体设计、详细设计文档 (需求说明、软件总体系统结构、模块划分、数据流图、E-R图、详细设计说明等内容)
。。。。。。。。。
-
毕业设计小结
经过四个月的努力我的毕业设计终于完成了,但是现在回想起来做毕业设计的整个过程,颇有心得,其中有苦也有甜,艰辛同时又充满乐趣,不过乐…
-
毕业设计心得
毕业设计感想光阴似箭,时光如梭,眼前止在紧张而义忙碌着进行着毕业设计,这项工作量大,具有挑战性的任务是对自己二年以来学习的检验,必…
-
毕业设计心得体会
毕业设计总结随着毕业日子的即将到来,我们的毕业设计也划上了圆满的句号。毕业设计是我们学业生涯的最后一个环节,不仅是对所学基础知识和…
-
毕业设计心得体会
20xx年的寒假,我就开始了我的毕业设计工作,时至今日,历时将近半年的时间,毕业设计基本完成。想想这段难忘的岁月,从最初的茫然,到…
-
毕业设计总结
时间过的很快,一晃大学三年的生活已接近了尾声在目,当初还是刚进大学的懵懂少年现在也长大了学到了很多,也懂得了很多。随着毕业日子的到…
-
毕业论文中期报告(改)
《代数方程组的MATLAB求解》中期报告专业、班级:数学与应用数学(师范)2班学号:20xx06034250报告人:蔡松廷1、前期…
-
毕业论文中期总结报告
毕业论文中期总结院系理学院化学系姓名吴琳学号08052222班级化学08-2班毕业论文中期总结1.论文题目:季戊四醇双缩酮的合成研…
-
毕业论文中期报告
齐齐哈尔大学毕业论文中期总结学院化学与化学工程学院专业班级化学063班学生姓名孙佳慧指导教师魏彦20xx年x月x日毕业论文中期总结…
-
20xx届本科毕业论文中期检查自查报告
20xx届本科毕业论文中期检查自查报告根据本学年度教务处和系部具体教学工作的安排,我系于20xx年x月x日组织了20xx届毕业论文…
-
20xx届毕业论文中期检查情况报告
各学院:为做好本科毕业论文(设计)工作,保证本科毕业论文(设计)质量,根据《沈阳农业大学本科毕业论文(设计)工作规范》的要求,学校…
-
毕业设计中期总结-完成
毕业设计(论文)期中总结土木与建筑工程学院系(院)20xx届题目阳明中学教学楼设计课题类型设计型课题来源自拟课题学生姓名李俊学号2…