英语口译课程总结
As a bridge between different languages and cultures, interpretation has become a principal part in our language study. From the course of interpretation, I’ve learned some fundamental interpreting skills we require to be a competent interpreter. They are summed up as followings:
First, considering the extraordinary flexibility of interpretation, before performing interpreting work we have to make good preparations, including linguistic preparations and psychological preparations.
As for linguistic preparations, in the first place, we should be equipped with good hearing, speaking, writing and reading abilities. We should have a good command of a large quantity of vocabulary of the language. In addition, we should accumulate abundant knowledge and information about different kinds of fields, such as politics, science, business, laws, history and so on. Moreover, to be quite familiar with the two languages’ characteristics, similarities and differences is necessary.
In relation to psychological preparations, staying confident and relaxed plays an important role in interpreting work. Such mental qualities are crucial especially when we encounter some emergent situations in which we are faced with unacquaintance with the topic and the obscurity of the speaker’s words, which occur constantly in real life. And in this perspective, psychological preparations are effective supplements of linguistic preparations.
Second, we’re supposed to be familiar with the general process of the interpretation, which will guide our actions from beginning to end. We should focus on four aspects: listening, memorizing, processing, and delivering. Listening is an input and the first important part. So we should listen and sometimes should see carefully. We should remember the information using the top-down memory method and then try their best to translate what the speaker has said. After translating, delivering, output, is last part of the interpreting. We should speak out loudly, properly and clearly.
Third, regarding the specific interpreting tactics, how to take notes proficiently is no doubt the key to good interpretation. Most of us are unable to do interpreting work well without taking notes because our short-term memory is not capable enough. Whoever has some interpreting experiences must have thought about the skills of notes taking. In the course of interpretation, teachers remind us that we should note down the main points instead of the original sentences, and some abbreviations of the words and special marks are used frequently.
All in all, the course of interpretation allows us to grasp the basic interpreting strategies in not only the preparations but also the process of interpretation. However, interpreting is by no means an easy job and only by putting those strategies into practice can we really enhance our interpreting abilities. Just as the saying goes, practice makes perfect, practice is the best way to improve our interpretation. Apart from accomplishing the interpreting tasks in school, we can take part in different kinds of social activities that involve interpretation. Furthermore, we can utilize the Internet to provide ourselves with ample interpreting opportunities. For instance, we can watch videos of simultaneous interpretation of News Conference Live and play the role of interpreters. Certainly we can learn a lot from the real interpreters who have high-level interpreting abilities and appropriate manner as well. Anyway, we should initiatively practise our interpreting skills both in and out of school, and always keep in mind that interpreting is an endless work and we still have a long way to go.
第二篇:《英语口译》课程教学大纲(三号加黑)
《英语口译》课程教学大纲(三号加黑)
一、课程名称:英语口译 E-C and C-E Interpretation
二、课程编码: 11031010
三、学时与学分: 68学时/4学分
四、考核方式:考试
五、先修课程:基础英语(1-4)、英语听力(1-3)、英语口语(1-3)
六、适用学科专业:英语专业
七、课程总体教学目的
(以上标题小四加黑;单倍行距,每个条目之间空一行;以下文本除了标题以外,均不加黑,1.5倍行距,小四号字体; 全文均为宋体)
1. 掌握口译的概念、历史、性质、特点、标准、过程、类型及译员必备
的素质。
2. 了解口译与笔译的相同点和不同点,把笔译技能灵活地应用到口译中
去。
3. 理解培养短时记忆的重要性并自觉地训练自己的短时记忆能力,达到
一次性精确地记忆30-50个汉字或英文单词所构成的文本意义的水平。
4. 能听懂每分钟150个词的英文材料,相当于VOA标准英语或BBC广
播节目的新闻播音速度。能精确地听懂英语国家人士的会议发言或学术讲座。
5. 掌握口译笔记的基本原则和技巧,能用常见的符号和中英两种文字一
次性记下600-800个汉字或英语单词的文本的程度。
6. 通过训练,能听懂常见的非标准英语,如非洲英语、阿拉伯英语、日
本英语、印度英语等等。
7. 掌握口译的基本原则和技巧,如旅游文本口译的原则与技巧、对外宣
传资料口译的原则与技巧、国际关系和国际政治文本口译的原则与技巧、饮食文化文本口译的原则与技巧等。
1
8. 初步了解同声传译的核心技巧和常用技巧。
八、总体教学要求:(第一句话写明该课程的性质,如专业必修课或选修课、公共必修课、任意选修课等;第二句话可说明使用的教材)
英语口译是英语专业的专业必修课,使用的主体教材为梅德明编著的《高级口译教程》和《中级口译教程》,由上海外语教育出版社出版。该课旨在培养熟练掌握口译技巧、能较好地承担生活接待、导游、一般性会议和商务洽谈等口译任务的英语人才。要胜任口译工作,译员必须在听说读写译五个方面全面发展,五种能力缺一不可。只有这五项技能平衡发展、达到较高水准,才能成为合格的口译工作者。考虑到英语专业高年级同学的具体情况,口译课主要通过训练学生的短时记忆能力、综合概括能力、记笔记能力等来综合提高学生听和口译的能力。通过一学年68学时的训练之后,学生应该能在笔记的帮助下一次性记住600-800个单词左右的文本并用地道的中文或英语进行口译。
本课程的测试要着重考核学生的口译能力。鉴于口译课程的特殊性,考试以主观题为主。因为不可能在期末一次考试中考察出学生的真实口译能力,所以平时成绩占的比例要相应提高,如40%-50%,包括学生的即兴演讲、模拟现场口译、网上查阅资料等方面的成绩,期末考试以口试为主。
教学中需要注意的几个问题
重视学生的听力水平的不断提高,在整个口译课程讲授过程中,要提醒学生在课后加强听力训练。没有坚实的听力基础,口译课将成为无源之水。
在口译课初始阶段,一定要学生打好短时记忆和记笔记的基础,否则本课程将无法进行下去。
要不断补充新材料,利用多媒体教学手段给学生提供可供学习、观摩的真实口译案例,提高学生的学习兴趣。
要通过即兴演讲、模拟现场口译等办法培养学生良好的口译风范,包括站立的姿态、说话声音的大小、音调的高低、表情、与公众的交流等等。
鉴于口译课每周只有两节课,教师必须给学生布置足够数量的课后作业,教材基本用于学生自学,教师一定要严格要求学生,定期检查学生课后作业的 2
完成情况,并作好记录,不得丝毫马虎。课堂上尽量给学生提供新的材料,经典的旧材料也可以。
九、基本教学安排
本课程的总学时为68学时,持续两个学期,每周2个学时。安排在第5 和第6个学期。教学进度安排如下:
第5学期:
Unit 1: A brief introduction to interpretation(教学目标和教学要求在每个章节或单元的开头;重点难点和习题在每个章节或单元的末尾)
Teaching objective: let ss grasp definition of interpretation, differences
between interpretation and translation, types of interpretation and qualities of an interpreter and essence of interpretation; make it clear to ss about
requirements of this course
Teaching requirements: T must demonstrate the essence of
interpretation—deverbalization, i.e., convey the information instead of words or expressions.
1. Definition of interpretation
2. Differences between interpretation and translation
3. Types of interpretation
4. Qualities of an interpreter
5. Requirements
What is interpretation?
1. Teacher’s demonstration: what is interpretation?
2. SS’ demonstration: what is interpretation?
3. T’s summary: essence of interpretation
The main points: Differences between interpretation and translation
Homework: Read p3—p15; p27—p28;
Unit 2: How to listen in interpretation?
Teaching objective: let ss differentiate active listening and passive listening and know about the difference of active listening in interpretation.
Teaching requirements: T must demonstrate how to prompt active listening
1. Active listening and passive listening
2. Do exercise: key words given—guess—listen to the original text and compare ss’ guesswork and the original text
Prompting passive memory
1. T’s demonstration: how to prompt passive memory
SS’ demonstration: how to prompt passive memory
The main points: transferrence from passive listening to active listening
Homework: pair work: student A chooses an English text about 300 words and select 3
the key words of the text. Student A asks student B to form the whole text on the basis of guesswork. Student B listens to the text and find out how good his guesswork is.
Unit 3: Interpreting ceremonial speeches
Teaching objective: let ss know why memory is so important in interpretation; let ss grasp the components of a toast, a welcoming address, an address for thanks, goodwill and congratulation and learn to interpret them
Teaching requirements: T must introduce to ss the methods of memorizing in interpretation
1. how to interpret a toast: components of a toast, a welcoming address, an address for thanks, goodwill and congratulation
2. ss interpret groups of sentences on expressing one’s welcome, thanks, goodwill and proposing a toast
3. ss interprets ceremonial speeches
the main points: components of a toast, a welcoming address, an address for thanks, goodwill and congratulation
homework: Listen to the four passages in unit 3 sentence by sentence and do interpretation. Pay attention to those idiomatic expressions of extending welcome, thanks and congratulations.
Unit 4: note-taking principles and skills (I)
Teaching objective: let ss have a rough idea about the overall principles of note-taking Teaching requirement: T must explain clearly about the principles of note-taking.
1. the overall note-taking principles and skills
2. introduce the use of Chinese characters and English abbreviations
3. demonstration of note-taking
4. what is decent interpretation manner?
the main points: the overall note-taking principles and skills / decent interpretation manner
homework:
1. Study the possible uses of Chinese characters and English capital letters in interpretation note-taking by using Chinese dictionary and group discussion. Report to the class next time.
2. Listen to the four passages of unit 4 of your textbook paragraph by paragraph. Take notes by using common symbols and signals. Do interpretation.
Unit 5: note-taking principles and skills (II)
Teaching objective: equip ss with the common symbols and signals used in interpretation note-taking; let ss be familiar with the usual symbols and signals used in interpretation note-taking and learn to invent their own signal and symbols by pair work or group work
Teaching requirement: T must remind ss that if they want to catch up with the speed of the original text, they must work hard to practise note-taking; T must remind ss that note-taking in interpretation is quite individual and the most important thing is that ss 4
must use appropriate means to represent logical relations in the ST.
1. introduce the use of short-hand signals, punctuation in interpretation note-taking
2. ss’ demonstration of note-taking
3. check ss’ homework. Ask ss to do impromptu interpretation on ceremonial speeches
4. practice listening and memory: contrastive analysis
T divides the class into two groups: one group of ss listen to a short text with note-taking. Another group of ss listen to it with memory. Ss write the message they’ve got from listening. T compares their writing.
The main points: use of symbols and signals in note-taking
Homework: SS are asked to work in groups and write a ceremonial speech in E or in
C and interpret it into C or E. T selects one from one group and asks the students of another group to do impromptu interpretation.
Unit 6: principles and skills of interpreting tourist text and publicizing texts (I)
Teaching objective: let ss grasp the basic principles and skills of interpreting tourist texts
Teaching requirement: T must emphasis on the differences of the stylistic features between C and E tourist texts and lead ss to thinking why we need to make great adjustments when we do C-E interpretation on tourist texts.
1. introduce the use of Arabic numerals, Roman numerals, signals taken from other systems or languages
2. introduce self-taught methods of note-taking
3. practice note-taking: the second passage of unit 5
4. principles and skills of interpreting tourist text and publicizing texts (I)
5. listen and memorize: contrastive analysis: questions before listening and questions after listening and no questions
the main points: principles and skills of interpreting tourist text and publicizing texts (I)
homework:
1. search articles on tranlation or interpretation of tourist texts and publicizing texts and report to the class next time.
2. Listen to the third and the fourth passage of unit 5. Take notes. Do intepretation. T will check whether ss have done the homework.
Unit 7: Principles and skills of interpreting tourist texts and pulicizing texts (II)
Teaching objective: let ss be more farmiliar with the principles and skills of interpreting tourist texts and let ss know about the qualifications of a guide interpreter Teaching requirement: T must emphasis on the cultural differences’ influence on C-E tourist texts’ interpretation
1. T goes on introducing principles and skills of interpreting tourist text
5
2. SS are asked to do interpretation on reception
3. T explains the qualities of being a guide interpreter
4. SS are asked to demonstrate note-taking on tourist text.
The main points: Principles and skills of interpreting tourist texts and pulicizing texts/ note-taking speed
Homework:
1. Listen to the four passages of unit 6. Take notes and do interpretation.
2. SS are divided into groups and write tourist text to introduce a scenic spot or a historical interest and interpret it into TT. Next time, T chooses one text to ask ss from another group to do impromptu interpretation.
Unit 8: Note-taking intensive training and interpretation accessment Teaching objective: let ss know about how interpretation is evaluated and learn to regulate their interpretation by keeping them in mind
Teaching requirements: T must evaluate ss’ interpretation according to the sheet in the classroom and ask ss to comment on their own interpretation.
1. Simulation 2: ss are asked to do impromptu interpretation on tourist text. T cameras it and play it and comment on it.
2. Manner of interpreting
3. Evaluation sheet of interpreting
4. SS are asked to have model test and T gives them evaluation
according to the evaluation sheet
5. T explains the principles and skills of interpreting texts on catering
6. T introduces the skills of interpreting Chinese food menu
7. Listening strategy:
Listen and memorize: listen to get the first sentence and the last sentence of a short text.
8. T explains what is summary interpretation?
9. Note-taking exercise: lengthen the unit of listening from 1 minute to 2 minute, take notes and do interpretation of unit 3 and unit 7
homework: Listen to the 8 passages in unit 11 and 12. Take notes and do interpretation. T ask ss to come to the board to demonstrate their note-taking by only listening to the text for one time.
Unit 9: Final examination
6
第6学期:
Unit 10: Interpreting texts on catering
Teaching objective: let ss grasp the principles and skills of interpreting texts on catering and emphasize the importance of interpreting C food menu
Teaching requirement: T must systematically introduce the methods to interpret
C food menu
1. introduce the principles and skills of interpreting texts on catering
2. introduce the principles and skills of interpreting chinese food menu
3. ss are asked to work out a menu in English to treat foreign guests.
4. SS are asked to simulate how to treat foreign guests to dinner
The main points: the principles and skills of interpreting texts on catering
Homework:
1. Listen to the two texts of Unit 11 in your textbook. Take notes and do
interpretation
3. Work in groups and prepare for a simulation on a welcoming banquet
Unit 11: Interpreting numbers (I)
1. skills of interpreting numbers
2. T demonstrates how to take notes when listening to a text which contains numbers
3. ss are asked to take down numbers in Arabic numerals
4. ss are asked to interpret C numbers into E or Engish numbers into C.
5. ss are asked to interpret texts which contains numbers
Simulation: ss are asked to present their simulation on a welcoming banquet The main points: skills of interpreting numbers
Homework:
1. Work in pairs and listen to numbers, take notes and do interpretation
2. Finish interpreting unit 6 of your textbook.
Unit 12: Interpreting numbers (II)
Teaching objective: let ss grasp the skills of numbers’ note-taking and interpretation Teaching requiremnt: T must introduce field skills of numbers’ note-taking and interpretation and emphasize that ss should have a great amount of practice if they want to interpret numbers well
More practice on taking down numbers and interpreting numbers
Impromptu interpretation: ss asked to do impromptu interpretation on a text which contains a great amount of numbers
Review: Principles and skills of interpreting tourist texts and publicizing texts Tips on interpreting culturally-loaded texts
The main points: skills of interpreting numbers
Homework:
1. Finishing listening the four texts in unit 3 of your textbook.
2. Work in groups and simulate publicizing a city, a scenic spot, or a kind of product 7
3. More practice on taking down numbers and interpreting numbers
T introduces principles and skills of interpreting idioms
Ss are asked to practice on idioms’ interpreting
Unit 13: Interpreting idioms and quotations
Teaching objective: let ss command the overall principles and skills of interpreting idioms and quotations
Teaching requirement: T should stress on the cultural differences’ influence on idoms and quotations’ interpretation
1. T explain the principles and skills of interpreting idioms and quotations
2. SS practise interpreting idioms and quotations
The main points: the principles and skills of interpreting idioms
Homework:
1. Read the textbook from p424 to p434
2. Listen to Premier Wenjiabao’s news conference and pay special attention to
idioms and quotations’ interpretation. Comment on the interpreters’ interpretation on idioms and quotations
Unit 14: Interpreting coping tactic 1—paraphrasing
Teaching objective: let ss know about the first coping tactic in interpretation—paraphrasing
Teaching requirement: T must be able to differentiate paraphrasing in interpretation and paraphrasing in other general English courses
1. T explains what is linear approach in interpretation?
2. T explains what is paraphrasing?
3. T explains the differences between linear approach and paraphrasing
4. Ss are asked to use linear apporach and paraphrasing to interpret the same sentence
4. Interpreting texts on science and technology and using paraphrasing when encoutering technical terms you’ve difficulty to deal with
The main points: the skills of paraphrasing
Homework:
1. Finish listening to unit 10 and learn to use paraphrasing
2. practise paraphrasing difficult sentences
Unit 15: Interpreting coping tactic 2—parrot-speaking
Teaching objective: let ss know about the second coping tactic—parrot-speaking to help them to go through difficulties in authentic interpretation
Teaching requirement: T must explain very clearly about the circumstances where we can use parrot-speaking
1. T explains what is parrot-speaking?
2. T demonstrates how to use parrot-speaking in interpretation
3. Interpreting texts on information technology and cultural exchanges by using parrot-speaking and paraphrasing together.
8
The main point: skills of using parrot-repetition
Homework:
1. Finish listening to unit 13 of your textbook
2. Work in groups and prepare for a simulation on cultural exchanges
Unit 16: the core skill of simultaneous interpretation
Teaching objective: let ss know about the core skill of SI—chopping sentences first and then interpreting by using the linear approach
Teaching requirement: T should demonstrate first how we chop sentences and do SI
1. Simulation : impromptu interpretation on cultural exchanges
2. Interpreting coping tactic 3—skipping and asking
3. Ss are asked to use skipping and asking in interpretation
4. T introduces the core skill of SI—linear approach
5. SS practice chopping sentences
6. Interpreting texts on foreign affairs and international relationship
The main point: the core skill of SI—linear approach
Homework: Practising chopping sentences by using unit 14 of your textbook. Work in pairs.
Unit 17: other skills of Simultaneous Interpretation
Teaching objective: let ss have a rough idea about the other skills in SI—anticipation, shelving and correction
Teaching requirements: T should demonstrate to ss we have several ways in simultaneously interpreting the same sentence if we use different skills
1. T explains the other skills of SI—anticipation, shelving, correction
2. SS are asked to use these skills in SI
3. NAETI model test
4. self-taught methods in SI—single-tasking shadowing and multi-tasking
shadowing
The main point: the other skills of SI—anticipation, shelving, correction
Homework: Simultaneously interpreting unit 15 of your textbook
Unit 18: Final examination
9
附录1:(附录1和2均为小四宋体,两个附录必须单独分页,不得出现在同一个页面上)
教学课时分配表
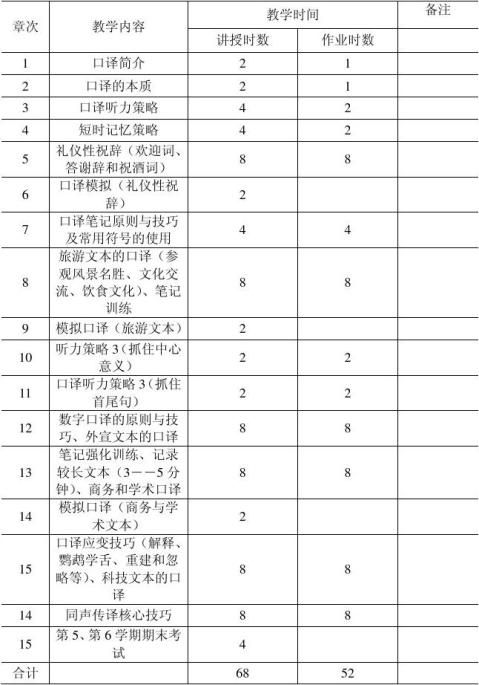
10
附录2:
主要参考书目
1、梅德明编著:《高级口译教程》,上海外语教育出版社20xx年版。
2、吴冰主编:《汉英口译教程》,外语教学与研究出版社,19xx年版。
3、张清平编:《英语口译基本技能》,对外经济贸易大学出版社19xx年版。
4、杨永平,周国强编:《高级听力教程》,上海外语教育出版社出版20xx年版。
5、梅德明编著:《英语口译实务》第三级,外文出版社20xx年版。
6、张建威编著:《出卖口译天机》,大连理工大学出版社20xx年版。
11
-
大学英语课程总结
《大学英语》课程总结20xx-20xx学年第二学期XXX20xx.7.1时光如梭,忙碌的一个学期又已经结束,回头看看这一学期的大学…
-
高二英语教学总结
高二英语教学工作总结蒋维本学期我担任高二(2)班的英语科教学。在教学中结合本校学生的实际情况,精心备课,积极听课、评课,认真有效上…
- 大学英语课程总结
-
英语课程总结
14152计算机科学与技术专业大学英语课程总结姓名高封学号20xx1103153时间第15周时光飞逝大二的第二学期要已经结束了回头…
-
英语特色课堂总结
特色英语课堂教学展示活动反思为了提高小学英语课堂教学质量,12月x日我来到鲁北实验小学参加特色英语课堂教学展示活动,9日上午,鲁北…
-
小学英语课外活动总结4
小学英语课外活动总结——王清红这学期开校不久,学校为了提高学生的综合素质,利用每天下午活动时间,成立了英语课外活动小组。感触颇深。…
-
20xx英语社团活动总结
实验小学英语社团活动总结社会的进步使得英语逐渐为人们所重视,本人在这学期担任英语社团指导老师。学生学习英语的兴趣浓厚。现将本学期英…
-
小学英语公开课活动总结
为了使老师进一步深化教学改革,优化课堂教学,全面提高教学水平。同时营造教师相互学习的氛围,不断提高教师自身的教育教学水平,乌当区高…
-
英语特色课堂总结
特色英语课堂教学展示活动反思为了提高小学英语课堂教学质量,12月x日我来到鲁北实验小学参加特色英语课堂教学展示活动,9日上午,鲁北…
-
英语主题活动总结1
英语主题活动总结安子岭学校***为了进一步丰富校园文化生活,营造积极向上的英语氛围,我校以“我参与,我快乐,EveryoneisN…
-
20xx——20xx学年第一学期三年级英语教学工作总结
20xx——20xx学年第一学期三年级英语教学工作总结本学期,我担任小学三年级英语教学工作。由于本人平时爱好英语,一直认为小学英语…