linux实验报告

“Linux操作系统”课程
实验报告

实验名称: linux操作系统实验1--4
姓 名: 王威青
学 号: 2011080432104
专 业: 计算机科学与技术
编制时间: 20##-4-27
指导教师: 孙悦
北京联合大学-信息学院编制
实验一 Linux基本操作............................................................................................... 1
一、 实验目的....................................................................................................... 1
二、 实验内容....................................................................................................... 1
三、 实验环境....................................................................................................... 2
四、 实验过程与结果分析............................................................................ 2
简单命令.......................................................................................................... 3
五、 实验总结................................................................................................ 5
实验二 vi文本编辑器.................................................................................................. 6
一、 实验目的................................................................................................ 6
二、 实验内容................................................................................................ 6
三、 实验环境................................................................................................ 6
四、 实验过程................................................................................................ 6
五、 实验总结................................................................................................ 7
实验三 操作系统接口及Shell命令.......................................................................... 7
一、 实验目的................................................................................................ 7
二、 实验内容................................................................................................ 7
三、 实验环境................................................................................................ 8
四、 实验过程及结果.................................................................................... 8
五、 实验总结.............................................................................................. 11
实验四 进入VI编辑器......................................................................................... 11
一、 实验目的.............................................................................................. 11
二、 实验内容.............................................................................................. 11
三、 实验环境.............................................................................................. 11
四、 实验过程.............................................................................................. 11
五、实验总结................................................................................................ 16
实验一 Linux基本操作
一、实验目的
1、掌握linux操作系统的登录与其他基本口令
2、掌握linux操作系统的基本命令
二、实验内容
1、linux命令的格式
2、Linux命令的输入、修改、执行、分类、联机帮助
3、Linux文件操作
三、实验环境
安装有Fedora操作平台的计算机一台
四、实验过程与结果分析
一、linux口令
1、登录过程:
Login:cherry
Password:(输入口令,不显示)
Last login: Sat May 12 15:50:56 on :0
You have mail.
$_
2、修改口令:
$Passwd
Change password gor user cherry.
(current) UNIX password:(输入原来的口令,无显示)
New password:(输入新的口令,无显示)
Retype new password:(重复输入新的口令,无显示)
Passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
$_
3、退出:
Ctrl+d
4、系统的关闭与重启:
#shutdown now
#reboot
二、linux命令
1、命令的格式:
命令名 [选项1] [选项2] [参数1] [参数2]...
2、命令的修改与输入:
常用的Shell命令行编辑键

4、命令的执行
常用的Shell命令运行控制键

5、命令的分类:
·文件、目录操作
·文本编辑与处理
·备份与压缩
·网络通信
·其他
简单命令
1、who命令
功能:显示已登录的用户
$who
root tty1 May 25 11:28
zhao tty2 May 25 09:12
cherry pts/0 May25 08:45
$who -q
root zhao cherry cherry
$who am i
cherry pts/0 May25 08:45(:0.0)
$_
2、ehco命令
功能:显示命令行中的参数字符串
$echo Hello!
Hello!
3、date命令
功能:显示、设置系统日期和事间
$date
Mon May 26 20:19:34 CST 2009
$ date '+Today is %D,now is %r'
Today is 04/25/36,now is 08:14:36 PM
$_
4、cal命令
功能:显示月份和日历
$ cal
4月 2012
日 一 二 三 四 五 六
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11 12 13 14
15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 2 26 27 28
29 30 31
四、文件和访问权限及表示

如:目录一:drwxr-x--x
文件1:-rwxr-xr-x 目录的属主可删除
五、目录操作命令
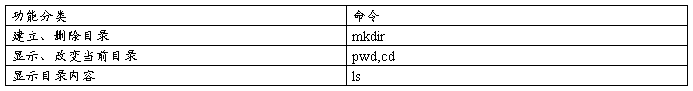
1、pwd命令
功能:显示当前目录的绝对路径
$ pwd
/home/cherry
$_
2、cd命令
改变当前目录为指定路径
$cd/user/bin
$pwd
/user/bin
3、ls命令
功能:显示指定文件或指定目录中的所有文件的信息
$ ls -l
drwxrwxr-x 2 cherry faculty 4096 Oct 14 12:50 book
4、创建与删除目录
mkdir命令 建立目录
$mkdir wang
$ls
book memo project wang
rmdir命令 删除目录
$ ls wang
book memo project wang
$ rmdir wang
cat命令 显示文件
$ cat
This is the 1st line
This is the 1st line
5、文件的复制、移动与删除
cp命令 复制文件
rm 命令 删除文件
mv 命令 移动文件、重命名文件
6、改变文件属性
chmod 命令 改变文件或目录的存取权限
六、实例
在当前用户下建立两个目录file1和file2,在file1中建立一个文本文档,复制到目录file2中,删除目录file1中的文件。
$mkdir file1
$cd file1
$pwd
/user/file1
$ vi wang.txt
Hello word!
$ls file1
Wang.txt
$mkdir file2
$cp ../file1/wang.txt ./file2
$cd ./
$ cd file1
$rm wang.txt
$_
五、实验总结
本实验主要练习Linux一些常用命令,Linux的命令功能都很强大,每个命令都有许多参。不过有一些命令使用起来还是比较方便的。
实验二 vi文本编辑器
一、实验目的
1、了解vi文本编辑器
2、会使用vi文本命令进行基本的文件操作
二、实验内容
1、vi的启动和退出
2、文本输入与删除
3、撤销与重做
4、文件操作与退出命令
三、实验环境
安装有Fedora操作平台的计算机一台
四、实验过程
1、Shell下输入vi命令后,便进入编辑环境,格式:vi[文件名]
编辑完成后,要用:wq 命令保存退出,或者:q不保存退出。
2、vi基本命令
(1)·文本输入:进入文本编辑界面后,执行插入命令,处于输入模式,屏幕底部显示“-插入-”提示,输入完成后按Esc键返回到命令模式。
·插入命令:
a、A 在光标位置后,行尾后开始插入
i、I 在光标前,行尾前开始插入
o、O 在光标所在行,光标所在行之前的新行开始插入。
(2)·文本的删除:
删除命令:
·x、X 删除光标处,光标前的字符
·dd 删除光标所在行
·D 删除光标右面的文本
·J 删除当前行尾的换行符
·d+定位符 删除从光标位置到指定位置范围内的字符
(3)文本的修改:
·cc 修改光标所在行
·C 修改光标处到行尾的文本
·c+定位符 修改光标达到指定位置范围内的字符
(4)字符串的替换:
·字符串替换使用S 命令
·S命令的一般格式为::[n1/,n2]s/p1/p2/[g][c]
(5)执行Shell命令:
·执行shell命令的格式是:
·!命令 执行指定的Shell命令
3、实例
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 main()
3 {
4 printf("Hello World!/n");
5 }
~
~
~
Hello.c test.c abc.c
执行:!ls*.c命令,列出文件
五、实验总结
Vi是一个全屏幕文本编辑器,具有文本编辑所需的全部功能。Vi 以高效和快捷著称。通过一节课的实训,我基本掌握了vi 命令的特征,及用法。为后面进一步的学习奠定基础。
实验三 操作系统接口及Shell命令
一、实验目的
1、了解linux系统的接口组成
2、了解Shell界面的组成
3、了解X图形窗口接口并掌握启动方式
4、掌握Shell的建立执行
二、实验内容
1、linux系统接口的组成
2、X图形窗口
3、Sell程序的建立执行
三、实验环境
装有Fedora操作系统的计算机一台
四、实验过程及结果
1、linux系统提供命令行和图形两种用户接口以及程序接口。
2、Shell功能
(1)、解析和执行命令
(2)、配置命令的运行环境
(3)、提供内部命令
(4)、支持Shell编程
3、X 图形窗口的启动与退出
startx命令
通常系统的默认配置是启动桌面环境(在Fedora中,启动的是GNOME桌面),按Ctrl+Alt+Backspace 键或退出桌面后X即停止。
4、Shell程序的建立与执行
Shell脚本的执行方式有3种:
(1)将脚本作为可执行文件执行:
$chmod a+x hello
$./hello
(2)启动一个Shell子进程来执行脚本文件
$ bash hello #或bash<hello
(3)让当前Shell进程执行脚本文件
$ .hello
5、命令执行控制符
(1)顺序执行
";"是顺序执行符
如:$ cd ..;pwd;ls
即转到上一级目录,显示目录的路径名和目录的文件列表
(2)条件执行
"&&"是逻辑与执行符
$ cp file1 file2 && rm file1
即将文件1复制到文件2,如成功则删除file1
(3)后台执行
"&"是后台执行符
$ yes>/dev/null &
即在后台运行yes命令,丢弃输出,
6、元字符的引用

7、Shell变量
(1)为变量赋值
A.变量名=字符串
如:$ nodehost=beijing.web
$user="zhang san"
B.用read命令即 read 变量名 [变量名...]
$ read usera userb
Joe zhao
$_
C.用for 命令
`for 变量[in 字符串列表]
do
命令列表
done
(2)引用变量
$ 变量名 或 $[变量名]
在命令中引用变量
$ dir= /home/cherry/cprogram
$ echo $dir #实际执行echo/home/cherry/cprogram
//home/cherry/cprogram
8、循环控制命令
(1)for命令
for 变量[in 字符串列表]
do
命令列表
done
(2)while命令
while 条件命令
do
命令列表
done
(3)until命令
·until 条件命令
·do
命令列表
·done
9、退出循环命令
(1)用break命令终止循环
例:$ cat break_test
while:
do
echo "continue?[y/n]:"
read reply
if [$replay =n]
Then break
fi
done
$break_test
Continue?[y/n]:y
Continue?[y/n]:y
Continue?[y/n]:n
(2)用continue命令跳过某轮循环
$ cat continue_test
`cd $1
`for file in *
`do
` if[-d $file]
` then continue
`fi
`ls -l $file
`done
$ continue_test /home/cherry
-rwxr-xr-x 1 cherry faculty 564 Jan 31 08:09 memo
$_
10、Linux C编程实例
Gcc 编译
$ ls
hello.c
$ cat hello.c
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
Printf("Hello world!\n");
}
$ gcc -o hello1 hello.c
$ ls
helllo1 hello.c
$ ./hello1
Hello world!
$_
五、实验总结
这节课包含的知识量较大,包括linux系统的接口组成,Shell界面的组成,X图形窗口接口并掌握启动方式,Shell的建立执行,虽然一节课下来都练习了一遍,但是有一些方面仍然不是很明白,课后通过请教同学终于弄明白了,尤其是linux C的掌握为下节课的进一步学习打好了基础。
实验四 进入VI编辑器
一、实验目的
1、了解Vi编辑器三种工作方式
2、掌握用vi编辑文件并进行编译
二、实验内容
1、用vi编辑器编辑下列文件,使用gcc编译器和gdb调试器,对下列程序编译运行,分析运行结果。要求至少完成3个程序。
三、实验环境
装有Fedora操作系统的计算机一台
四、实验过程
一、Vi编辑器三种工作方式:
1.编辑方式:进入VI 处于编辑方式
2.文本输入方式:在编辑方式下输入a ,进入追加方式,输入i,进入插入方式
3.命令方式:在输入方式下,按Esc 键,由文本输入转向编辑方式,输入冒号:进入命令方式
4.退出vi
: wq写文件退出
:w wenjianming 写文件
: q! 不写退出
:wq! 写退出
编译c文件
Gcc -o wenjianming.out wenjianming.c
运行文件:
./wenjianming.out
二、程序实例
(1) /* 父子进程之间的同步之例 */
#include <stdio.h>
main( )
{
int pid1;
if(pid1=fork()) /*create child1 */
{ if (fork()) /*create the child2*/
{printf (“parent’s context.\n”);
printf(“parent is waiting the child1 terminate.\n);
wait(0);
printf(“parent is waiting the child2 terminate.\n”);
wait(0);
printf(“parent terminate.\n”);
exit(0);
}
else
/* child2*/
printf(“child2’s context.\n”);
sleep(5);
printf(“ child2 terminate.\n”);
exit(0);
}
else { if(pid1==0)/* child1 */
{ printf(“child1’s context.\n”);
sleep(10);
printf(“child1 terminate.\n”);
exit(0);
}
}
}
分析: 上述程序是父进程首先创建一个子进程,若成功,再创建另一个子进程,之后三个进程并发执行。
结果:
child1’s context.
child2’s context.
parent terminate.
parent is waiting the child1 terminate.
child2 terminate.
parent is waiting the child2 terminate.
child1 terminate.
parent’s context.
(2)管道通信机制
通过使用管道实现两个和多个进程之间的通信。所谓管道,就是将一个进程的标准输出与另一个进程的标准输入联系在一起,进行通信的一种方法。同组进程之间可用无名管道进行通信,不同组进程可通过有名管道通信。
使用无名管道进行父子进程之间的通信
#include <sys/types.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int pipe( int filedes[2]);
char parent[]=”a message to pipe’ communication.\n”;
main()
{ int pid,chan1[2];
char buf[100];
pipe(chan1);
pid=fork();
if(pid<0)
{ printf(“to create child error\n”);
exit(1);
}
if(pid>0)
{ close(chan1[0]); /*父进程关闭读通道*/
printf(“parent process sends a message to child.\n”);
write(chan1[1],parent,sizeof(parent));
close(chan1[1]);
printf(“parent process waits the child to terminate.\n”);
wait(0);
printf(“parent process terminates.\n”);
}
else{
close(chan1[1]);/*子进程关闭写通道*/
read(chan1[0],buf,100);
printf(“the message read by child process form parent is %s.\n”,buf);
close (chan1[0]);
printf(“child process terminates\n”);
}
}
结果:
parent process sends a message to child.
parent process waits the child to terminate.
the message read by child process form parent is a message to pipe’ communication.
child process terminates.
parent process terminates.
(3)Linux中的多线程编程threads.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 10
pthread_t thread[2];
pthread_mutex_t mut;
int number=0, i;
void *thread1()
{
printf ("thread1 : I'm thread 1\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
printf("thread1 : number = %d\n",number);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mut);
number++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mut);
sleep(2);
}
printf("thread1 :主函数在等我完成任务吗?\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *thread2()
{
printf("thread2 : I'm thread 2\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
printf("thread2 : number = %d\n",number);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mut);
number++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mut);
sleep(3);
}
printf("thread2 :主函数在等我完成任务吗?\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void thread_create(void)
{
int temp;
memset(&thread, 0, sizeof(thread)); //comment1
/*创建线程*/
if((temp = pthread_create(&thread[0], NULL, thread1, NULL)) != 0) //comment2
printf("线程1创建失败!\n");
else
printf("线程1被创建\n");
if((temp = pthread_create(&thread[1], NULL, thread2, NULL)) != 0) //comment3
printf("线程2创建失败");
else
printf("线程2被创建\n");
}
void thread_wait(void)
{
/*等待线程结束*/
if(thread[0] !=0) { //comment4
pthread_join(thread[0],NULL);
printf("线程1已经结束\n");
}
if(thread[1] !=0) { //comment5
pthread_join(thread[1],NULL);
printf("线程2已经结束\n");
}
}
int main()
{
/*用默认属性初始化互斥锁*/
pthread_mutex_init(&mut,NULL);
printf("我是主函数哦,我正在创建线程,呵呵\n");
thread_create();
printf("我是主函数哦,我正在等待线程完成任务阿,呵呵\n");
thread_wait();
return 0;
}
结果:
I'm the main function ,and I'm creating the thread.
thread 1 has been created
thread 2 has been created
I'm the main function ,and I'm waitting the ending the thread.
thread1: I'm thread 1
thread1: number=0
thread2: I'm thread 2
thread2: number=1
thread1: number=2
thread2: number=3
thread1: number=4
thread2: number=5
thread1: number=6
thread1: number=7
thread2: number=8
thread1: number=9
thread2: number=10
thread1: Does the main function waits for the task?
Thread1 has ended.
Thread2: Does the main function waits for the task?
Thread2 has ended.
[stu2@localhost~]$_
五、实验总结
这节课主要是练习使用vi编辑器编译c文件,并运行。根据运行结果分析其运行原理,从中能更好的理解掌握所学内容。
-
linux实验报告
实验二Linux常用命令使用一、实验目的1.掌握Linux一般命令格式。2.掌握有关文件和目录操作的常用命令。3.掌握有关进程操作…
-
Linux实验报告
Linux操作系统实验报告实验编号实验编号实验名称实验名称实验1Linux安装实验2掌握虚拟机的使用实验目的1熟练掌握Linux系…
-
Linux基础操作实验报告
实验项目名称Linux基础操作实验项目编号一学号组号上机实践日期20xx919上机实践时间2学时一目的本次实验所涉及并要求掌握的知…
-
Linux 实验报告(一)系 统 常 用 命 令
专业计算机科学与技术学号姓名Linux操作系统报告单名称系统常用命令任课教师专业计算机科学与技术班级姓名学号完成日期成绩12345…
-
linux实验报告
实验一Linux的基本操作命令一实验目的了解Linux的基本命令实现Linux的文件系统操作二实验内容1在Linux字符环境下练习…
-
linux 实验资料总结
Linux考试实验1修改运行级别,级别切换:(1)vi/etc/inittab将5改为3(2)reboot2修改root密码:进入…
-
linux实验报告
LINUX实验报告专业班级学号姓名实验一实验名称Linux基本命令的使用实验时间2学时实验目的熟练使用Linux字符界面窗口系统的…
-
Linux基础操作实验报告
实验项目名称Linux基础操作实验项目编号一学号组号上机实践日期20xx919上机实践时间2学时一目的本次实验所涉及并要求掌握的知…
-
linux实验报告
实验二Linux常用命令使用一、实验目的1.掌握Linux一般命令格式。2.掌握有关文件和目录操作的常用命令。3.掌握有关进程操作…
-
Linux实验报告
课程编号B080103040Linux操作系统实验报告东北大学软件学院实验一熟悉Linux环境实验内容一练习常用的Shell命令当…