初中英语八种时态归纳
初中英语八种时态归纳
时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,广大初中学生在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,下面我们就归纳复习一下这几种时态。
1、一般现在时:概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:
Always( 总是), usually(通常), often(经常), sometimes(有时候), every week (day, year, month?), once a week, on Sundays ,etc.
基本结构:
当主语是第三人称单数时
肯定句 主语 + 动词单三 + 其他
否定句 主语 +doesn't+ 动词原形 + 其他
一般疑问句 Does+ 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他
肯定回答 Yes ,主语 +does
否定回答 No ,主语 +doesn't
当主语不是第三人称单数时
肯定句 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他
否定句 主语 +don't+ 动词原形 + 其他
一般疑问句 Do+ 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他
例句:
I never get up early on Sundays.
特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词(when,where,who,how ,etc.)+一般疑问句
2、一般过去时:
概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month?), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
基本结构:
主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他
否定形式 did+not+do+ 其他 ;
一般疑问句 did+ 主语 +do+ 其他?
例句:
I went to Italy .I visited museums and sat in public gardens
3、现在进行时 :
概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
时间状语:now, at this time( 在这一刻 ), these days, etc.
基本结构:am/is/are+doing
否定形式: am/is/are+not+doing.
一般疑问句:把 be 动词放于句首。
4、过去进行时:
概念: ( 1 )表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
( 2 ) 表示一个动作正在进行时,另一个动作突然发生了。
时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time (在那一刻)或以 when 、 while 引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
基本结构:was/were+doing
否定形式: was/were + not + doing.
一般疑问句:把 was 或 were 放于句首。
While 与 when
(1) 用 while 连接( while 只接 doing )
例 :My mother was cooking while I was doing my homework.( 可以持续动作时态一致 )
(2 ) when 表示( when 可以接 doing 或 did , when 后动作时间长,用 doing ,时间短,用 did )
例 :I was doing my homework when my mother came in.( 间接表达了具体时间 )
例句 :
I was having breakfast when the telephone rang
5、现在完成时:
概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
时间状语: recently, lately, since( 自从 )?,for (长达) ?,in the past few years, etc.
基本结构:
主语 +have/has+ 过去分词 (done)
①肯定句:主语 +have/has+ 过去分词 + 其他 .
②否定句:主语 +have/has+not+ 过去分词 + 其他 .
③一般疑问句: Have/Has+ 主语 + 过去分词 + 其他 .
④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词或词组 + 一般疑问句( have/has+ 主语 + 过去分词 + 其他)?
例句:
I have just received a letter from my brother.
6、过去完成时:
概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即 “ 过去的过去 ” 。
时间状语: after,when, as soon as(一...就...), until, before, by the end of(到?为止) last year(term, month?),etc.
基本结构:主语 +had+ 过去分词 (done)
①肯定句:主语 +had+ 过去分词 + 其他 .
②否定句:主语 +had+not+ 过去分词 + 其他 .
③一般疑问句: Had+ 主语 + 过去分词 + 其他 ?
肯定回答: Yes, 主语 +had.
否定回答: No, 主语 +had not .
例句:
The children ran away after they had broken the window.
As soon as the sun had set we returned to our hotel.
I had not understood the problem until he explained it .
7、一般将来时:
概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year?),soon, in a few minutes, by?,the day after tomorrow, etc.
基本结构:①am/is/are/going to + do ; ②will/shall + do.
否定形式: ①was/were + not; ② 在行为动词前加 didn't ,同时还原行为动词。
一般疑问句: ①be 放于句首; ②will/shall 提到句首。
例句:
I will meet him at the harbour early in the morning.
注:将来进行时 will be doing 将来某时刻正在进行。
( 用将来进行时提问更加客气,礼貌。能用 will be doing 都能换成 will do 表达。但语气、含义稍有不同 )
例句:
Tomorrow evening they will be singing at the workers’ Club.
8、过去将来时:
概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
时间状语:the next day(morning, year?),the following month(week?),etc. 基本结构:①was/were/going to + do ; ②would/should + do.
否定形式: ①was/were/not + going to + do;②would/should + not + do. 一般疑问句: ①was 或 were 放于句首; ②would/should 提到句首。 一般过去将来时常用在间接引语中
例句: She said that Mr.Jones would see you now.
他说过琼斯先生现在要见你。
特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词(when,where,who,how ,etc.)+一般疑问句
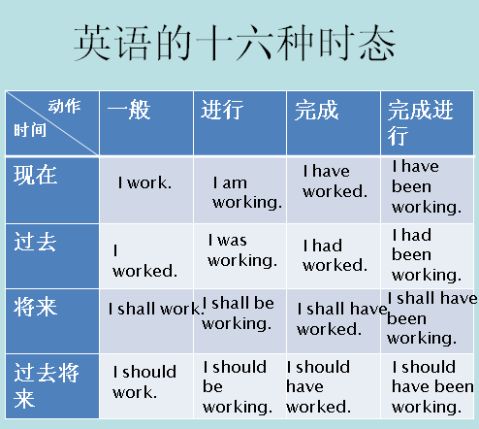
Ⅱ. 几种常见时态的相互转换
英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
一、 一般过去时与现在完成时的转换
在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能。
I have bought a car.
I have had the car for 3 weeks
I haven’t bought anything for 3 months
但是,可用别的表达方式: ① 瞬间动词用于 “ 一段时间 + ago” 的一般过去时的句型中; ② 瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用; ③ 瞬间动词用于 “It is + 一段时间 + since + 一般
过去时 ” 的句型中,表示 “ 自从 ?? 以来有 ?? 时间 ” 的意思,主句一般用 it is 来代替 It has been;④ 瞬间动词用于 “Some time has passed since + 一般过去时 ” 的句型中。请看:
A. He joined the League [li:ɡ] 联盟 two years ago.
B. He has been in the League for two years.
C. It is two years since he joined the League.
D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
二、 一般现在时与现在进行时的转换
在一般现在时中, at 加上名词表示 “ 处于某种状态 ” ,如 at work (在工作) , at school (上学、上课)等。此短语可与进行时态转换。请看: Peter is at work, but Mike is at play.
Peter is working, but Mike is playing.
三、 现在进行时与一般将来时的转换
在现在进行时态中 go, come, leave, start, arrive 等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作。如: I am coming, Mum! 意为 “ 我就来,妈妈! ” 请看:
The train is leaving soon.
The train will leave soon.
四、 “be going to+ 动词原形 ” 与 “will(shall)+ 动词原形 ” 结构的转换
“be going to+ 动词原形 ” 、表示打算、计划要做的事;将来时
“will(shall)+ 动词原形 ” 结构在书面语中,当主语为第一人称时,常用助动词 shall 。在口语中,所有人称都可以用 will 。请看:
We are going to visit the Great Wall next Sunday.
We shall visit the Great Wall next Sunday.
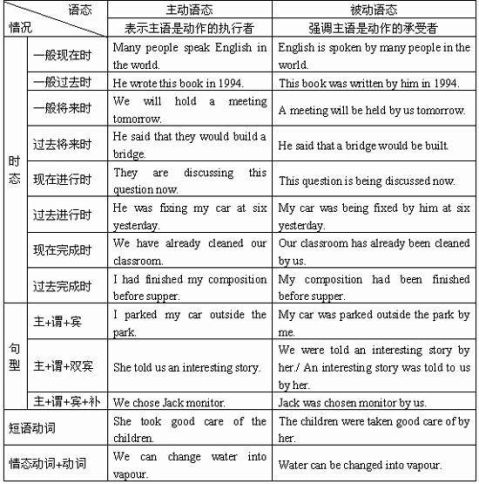
动词时态考点分析
一、根据时间状语确定时态的原则
1. Hurry up! The play for ten minutes.
A. has begun B. had begun C. has been on D. began
[ 析 ] 1. since 后接时间的起点, for 后接时间段,主句动词用现在完成时,应注意瞬间动词与延续性动词的使用。
二、特殊疑问句 2.How staying? for five days.
A.long they will be B.they will be
C.long will they be D.long they be
[ 析 ] 特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词(when,where,who,how ,etc.)+一般疑问句
三、根据上下文已有时态信息点确定时态的原则
3. –When this kind of computer ?
--Last year.
A. did; use B. was; used C. is; used D. are; used
[ 析 ] 此例由下句的时间状语推断出一般过去时态,并且要考虑到被动语态。 利用上下文语意确定时态的原则
4. –Hi! Lin Tao. I didn’t see you at the party. --Oh, I ready for the maths exam.
A. am getting B. was getting C. got D. have got
[ 析 ] 此例由 didn’t, at the party 推断出应用过去进行时。
第二篇:初中英语八种时态归纳复习 详解
Ⅰ. 初中英语八种时态归纳复习
英语时态是一种表示动作或状态发生的时间的动词形式,而汉语动词没有时态形式。
一、一般现在时:
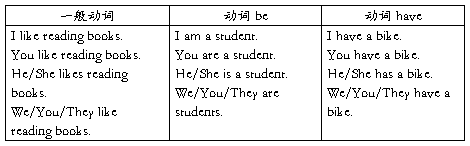
1. 概念:表示经常性的习惯动作,现在的特征或状态,和普遍真理的时候,谓语动词用一般现在时。
2. 构成:一般现在时主要由动词原形构成,但第三人称单数后要加词尾-s, 另外 动词be 和 have 有特殊的人称变化形式。
列表如下:
3.在词尾加-s时要注意:
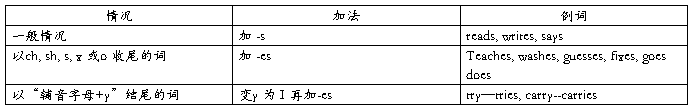
4.词尾-s 的读音,与名词复数词尾-s读音一样:

6. 与一般现在时经常搭配的时间状语:
always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc.
例句:I go to school every day.
7. 否定形式:①动词be: am/is/are+not;②行为动词:在其前加don't, 如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,助动词后动词一概用原形。
例句:Jerry is not a student. Sally doesn’t like animals.
8. 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
例句: Is Jerry a student? Does sally like animals?
9. 实用一般现在时句型:

二、一般过去时
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态,现在已经不再继续;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
2.构成:一般过去时由动词的过去式表示,
1) 动词be 有 was, were 两个过去式,was 用于第一、第三人称, were 用于第二人称和第一、二、三人称的复数形式。

2) 行为动词过去式的构成规则:
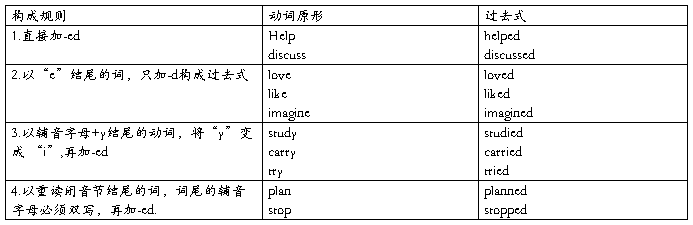
3)还有一些动词的过去式变化时不规则的,如:have-had, come-came, buy-bought等,此类动词请参照不规则动词表。
读音规则:

3. 与一般过去式经常搭配的时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
4.否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加助动词didn't,助动词后加动词原形。
5.一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,助动词后用动词原形。
6.实用句型:

三、现在进行时
1. 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。
2. 构成:动词be+v-ing, 动词be加现在分词构成。
现在分词的构成:

有一些动词的现在分词变化比较特殊,参照不规则动词表,如 die—dying, lie—lying.
3. 经常与现在进行时搭配的时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.
4. 现在进行时的三种形式:
1)肯定形式:am/is/are +doing。 如: He is doing his homework now.
2)否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing. 如: He is not doing his homework now.
3)一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。如:Is he doing his homework now?
5.实用句型:
1)What are you doing? 你正在做什么?
2) I am watching TV now. 我正在看电视。
3) My mother is cooking at this time. 我妈妈这个时候正在煮饭。
4) He is studying English these days. 他这些天一直在学英语
5) We are practising a new song now. 我们正在练习新的曲目。
6) The sun is shining. 太阳当空照。
7) It is raining. 现在正在下雨。
有时候一些动词的现在进行时有表达将来的意思。
8) The train is starting in five minutes. 火车五分钟后将开出。
9) I’m leaving for Beijing next week. 我下周去北京。
10) Where are you going? 你将要去哪里?
四、过去进行时:
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2. 构成:was/were+v-ing, 动词be 的过去式加现在分词。
3.常与过去进行时搭配的时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
4.过去进行时的三种形式
1)肯定形式:was/were+doing 如:I was doing my homework at this time yesterday.
2)否定形式:was/were + not + doing. 如: I was not doing my homework at this time yersterdy.
3)一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。如: Are you doing your homework at this time yersterdy?
5.实用句型:
1) I was tidying up my room last night. 昨晚我一直在整理房间。
2) When David’s father arrived home, David was playing computer games.当大卫的爸爸回到家时大卫正在玩电脑游戏。
3) Sally was practising music last night. 萨利昨晚一直练习音乐。
4) We were discussing this question when he came in.当我们正在讨论这个问题的时候,他进来了。
5) They were watching TV while there was a knock at the door.他们正在看电视,这时有人敲门。
6)What were you doing at six o’clock yesterday? 你昨天晚上六点在做什么?
7) I was working at my English at that time. 我那时候正在学英语。
8)Shirley was writing a book about China last year. 雪莉去年正在写一本关于中国的书。
9)He said he was working all day long on Sunday. 他说他周日的时候工作了一整天。
10)She told me she was studying English these days. 她跟我说她最近一直在学英语。
五、现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.构成:现在完成时态是由“助动词have(has)+过去分词”构成。
过去分词的构成,大部分的过去分词与动词的过去式是一样的,有些特殊变化的参照不规则动词表。

3.常与现在完成时搭配的时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,before,in the past few years, yet,etc.
4.现在完成时的三种形式:
1)肯定形式:have/has + done。 My father has warned me not to play games on his computer.
2)否定形式:have/has + not +d one. I haven’t done my homework yet.
3)一般疑问句:have或has开头。 Have you done your homework?
5.现在完成时与一般过去时的比较:现在完成时强调过去已经发生的事情对现在仍然造成影响,有时候有现在仍继续发生之意。一般过去时强调动作在过去发生,对现在已经没有影响,或不考虑对现在的影响,常与具体的过去的时间连用。
1)a. We have known each other for three years. 我们相识三年了。
b. We knew each other in 2008. 我们是在20##年相识的。
2) a. I have studied English for six years. 我学英语六年了。
b. I have studied English since two years ago. 我从两年前开始学了英语。
c. I sturdied English two years ago. 我两年前学了英语。
3)a. I have been to Guilin. 我曾到过桂林。
b. I went to Guilin last year. 我去年去了桂林。
c. He is not here right now. He has gone to Guilin. 他现在不在这里,他去了桂林。
4)a. I have had my breakfast. 我吃过早餐了。
b. I had my breakfast at 7 o’clock this morning. 我今早七点吃早餐。
6.现在完成时实用句子:
1)I have studied English for three years. 我学习英语三年了。
2)We have made a plan for summer holiday. 我们已经制定了暑假计划。
3)David has been to America. 大卫曾经到过美国。
4)I have just cleaned the classroom. 我刚刚打扫了教室。
5)I have read that book. It is very interesting. 我读过那本书,那本书很有趣。
6)I have never heard of that before. 我之前从未听说过那样的是。
7)She has left for 2 hours. 她离开有两小时了。
8)Where have you been? 你去了哪里?
9) I have been to the park. 我去了公园。
10)The boy has become my best friend. 那个男孩成了我最好的朋友。
11)I’ve listened to that programme. 我曾经收听过那个节目。
12)I have had my supper. I am not hungry now. 我吃过晚餐了。我现在不饿。
13)Daivid has become a successful young writer. 大卫成了一个成功的年轻作家。
14)I’ve heard that you play in your school orchestra. 我曾听说你在学校管弦乐队演奏。
15)Have you seen this movie before? 你曾读过这本书吗?
16)Have you met him recently? 你最近见到他吗?
17)Have you had your lunch? 你吃午饭了吗?
18)I’ve already done my homework. 我已经做完作业了。
19)My mother has bought me a new watch for my birthday. 妈妈给我买了一块新表作为生日礼物。
20)We have been friends since chilhood. 我们从小就是好朋友。
六、过去完成时
1. 概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。一般比较少用,常用在复合句中,句中一般有明确的过去时间,过去完成时的动词表示在过去某个明确的时间点之前已经完成的动作。
2. 构成:过去完成时由“助动词had+过去分词”构成。
3. 常与过去完成时搭配的时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc.
4. 过去完成时的三种形式:
1)肯定形式:had + done. She had studied English for six years before she entered junior high school.
2)否定形式:had + not + done. She had never studied English before she entered junior high school.
3)一般疑问句:had放于句首。Had she ever studied English before she entered junior high school?
5. 过去完成时与现在完成时的比较:
a. She has studied English for two years. 她已经学了两年的英语。(意指现在她还在学)
b. She had studied English for six years before she entered junior high school. 在进入初中之前她已经学了六年的英语。(强调动作在初中之前已经完成,有明确的过去的时间点,进入初中。)
6. 实用句型:
1)The rain had stopped by half past eight o’clock last night. 昨晚八点半雨已经停了。
2)When we arrived at the station, we learnt that the train had already gone. 当我们到达车站时,得知火车已经走了。
3)I did not go to the cinema because I had already seen the flim. 我没去看电影因为我已经看过这部影片了。
4)It was five years since she had been there. 那时她在哪里已经待了五年。
5)I knew that she had left for the South. 我知道她已经离开去了南方。
6)When I arrived, Ann had left. 当我到达时,安娜已经离开了。
7)He suddenly remembered that he hadn’t locked the door. 他突然记起他忘记锁门了。
8)She didn’t go to bed until she had finished her work. 她直到完成作业才去睡觉。
9)My mother asked me whether I had had my breakfast. 妈妈问我我是否吃了早餐。
10)David said that he had already finished his homework. 大卫说他已经做完了他的作业。
七、一般将来时
1.概念:表将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.构成:一般将来时由助动词shall或will 加动词原形构成,shall 用于第一人称,will 三个人称都可以用。
3. 常与一般将来时搭配的时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
4.一般将来时的三种形式:
1)肯定形式: will/shall + do. I shall go. We shall go. He will go. You will go. They will go.
2)否定形式:will/shall+ not+ do. I shall not go. We shall not go. He will not go. They won’t go.
3)一般疑问句: will/shall提到句首。Shall I go? Will you go? Shall we go? Will he go? Will they go?
5 实用句子:
1)When and Where shall we meet? 我们什么时候在什么地方见面?
2)I will/shall arrive tomorrow. 我明天到。
3)We won’t free tonight. 我们今晚没有空。
4)If she becomes a star, her parents will be proud of her.如果她成为明星,她父母将为她骄傲。
5) If you tell him the truth, he’ll be angry with you.如果你告诉他真相,他会非常生你的气。
6) Sally will go to school next day. 萨利第二天将要去学校。
7)Our class will go to the park the day after tomorrow. 我们班后天要去公园。
8)The orchestra will play in the background. 管弦乐队将在后面弹奏。
9)If I study hard, I will get a good result in the exam. 如果我认真学习,我将会在考试中取得好成绩。
10)We will meet at seven o’clock at the gate of school. 我们七点钟将在学校大门见面。
6. 表示将来要发生的动作,除了一般将来时,有时候会用 be going+ 不定式 ,表示打算、准备做某事或即将发生某事,某事肯定要发生。
1)How are you going to spend your holidays? 假期你准备怎么过?
2)I think it is going to rain. 我看天要下雨了。
3)Sally is going to give an interview on Radio Beijing. 萨利将要去北京电台接受采访。
4)It’s going to be expensive to mend the computer. 修电脑将会很贵。
5)We are going to have a picnic this Sunday. 这个星期日我们打算去野餐。
八、一般过去将来时
1. 概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将要发生的事情,常用于宾语从句中。
2.构成:一般过去将来时由should 或 would 加动词原形构成, 第一人称用should, 其他人称用would, 第一人称也可以用 would.
3. 常与一般过去时搭配的时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
4. 一般过去将来时的三种形式
1)肯定形式: would/should + do. He said he would come the next day. 他说过他第二天回来。
2)否定形式 would/should + not + do. He said he would not come the next day. 他说他第二天不会来。
3)一般疑问句: would/should 提到句首。“Would he come the next day?”she asked.她问:“ 第二天他回来吗?“
5.实用句子:
1)He said he would come to the party. 他说过他会来派对。
2)I thought you wouldn’t come with us. 我以为你不会跟我们一起。
3) He didn’t expect that we should/would be there. 他没有想到我们会在那里。
4)They said they would help us. 他说他会帮助我们。
5)She told us everything would be all right. 她告诉我们一切都会顺利的。
6.除了一般过去将来时,表示过去将要发生的事情,还可以用was/were/going to + do。
1)He said he was going to try. 他说他准备试试。
2)The teacher said we were going to have a picnic on Sunday. 老师说我们星期天将要去野餐。
3)We didn’t know where we were going to spend our holiday. 我们不知道要去哪里度假。
-
初中英语语法总结(动词的时态)
初中英语语法总结(动词的时态)1.1一般现在时的用法1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every…,…
-
初中英语语法与时态语态总结表
初中英语时态语态总结表初中英语八种时态归纳复习时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容广大初中学生在实际运用时往往对时态总是倍感棘手下面…
-
初中英语语法时态总结
初中英语语法动词时态总结一一般现在时1经常性或习惯性的动作常与表示频度的时间状语连用时间状语everysometimesatonS…
-
初中英语语法八大时态
初中英语语法八大时态第一课时一般现在时的用法一概述一般现在时表示习惯性经常性反复性的动作或存在的状态习惯性经常性反复性是一般现在时…
- 初中英语语法总结(时态部分)
-
爱卫、创卫工作总结
********************公司20xx年爱卫、创卫工作总结20xx年以来,我公司在州、市政府及上级单位各级领导的领导…
-
20xx年创建平安医院工作总结
白沙县人民医院20xx年“平安医院”创建活动工作总结20xx年,我院在县委、县政府和县卫生局的统一领导下,在有关部门的协调配合下,…
-
吴窑镇江中小学预防疟疾工作总结
为了普及疟疾防治知识,提高小学生的疟疾防治意识,促进学校健康教育顺利进行,根据教育部体育卫生与艺术教育司《关于启动并实施第五轮中国…
-
普通话演讲比赛总结
大家下午好!我们都知道,普通话作为一种交流手段,其作用在现代社会中越来越重要,一个国家语言文字的普及程度和社会应用的规范水平是一个…
-
20xx年爱卫创卫工作总结
半年来,全体师生在学校党委行政的正确领导下,坚持以“xx大”精神为指导,以科学发展观为动力,严格执行中央、省、市关于城市创建工作的…