进程调度实验报告
一、 实验目的
用高级语言编写和调试一个进程调度程序,以加深对进程的概念及进程调度算法的理解。
二、实验内容和要求
编写并调试一个模拟的进程调度程序,采用“简单时间片轮转法”调度算法对五个进程进行调度。
每个进程有一个进程控制块( PCB)表示。进程控制块可以包含如下信息:进程名、到达时间、需要运行时间、已运行时间、进程状态等等。
进程的到达时间及需要的运行时间可以事先人为地指定(也可以由随机数产生)。进程的到达时间为进程输入的时间。 进程的运行时间以时间片为单位进行计算。
每个进程的状态可以是就绪 W(Wait)、运行R(Run)两种状态之一。
就绪进程获得 CPU后都只能运行一个时间片。用运行时间加1来表示。
如果运行一个时间片后,进程的已占用 CPU时间已达到所需要的运行时间,则撤消该进程,如果运行一个时间片后进程的已占用CPU时间还未达所需要的运行时间,也就是进程还需要继续运行,此时应分配时间片给就绪队列中排在该进程之后的进程,并将它插入就绪队列队尾。 每进行一次调度程序都打印一次运行进程、就绪队列、以及各个进程的 PCB,以便进行检查。
重复以上过程,直到所要进程都完成为止。
三、实验主要仪器设备和材料
硬件环境:IBM-PC或兼容机
软件环境:C语言编程环境
四、实验原理及设计方案
1、进程调度算法:采用多级反馈队列调度算法。其基本思想是:当一个新进程进入内在后,首先将它放入第一个队列的末尾,按FCFS原则排队等待高度。当轮到该进程执行时,如能在该时间片内完成,便可准备撤离系统;如果它在一个时间片结束时尚为完成,调度程序便将该进程转入第二队列的末尾,再同样地按FCFS原则等待调度执行,以此类推。
2、实验步骤:
(1)按先来先服务算法将进程排成就绪队列。
(2)检查所有队列是否为空,若空则退出,否则将队首进程调入执行。
(3)检查该运行进程是否运行完毕,若运行完毕,则撤消进程,否则,将该进程插入到下一个逻辑队列的队尾。
(4)是否再插入新的进程,若是则把它放到第一逻辑队列的列尾。
(5)重复步骤(2)、(3)、(4),直到就绪队列为空。
五、流程图


 是
是
是
六、结果过程及截图
初始化队列

输入所有进程后的进程信息如下:

按Y键继续运行进程:
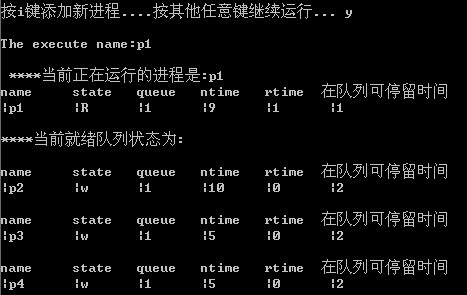
按Y键继续运行进程:
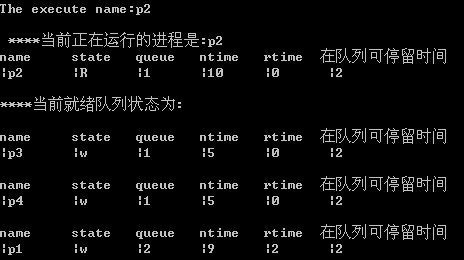
运行若干次后的状态:
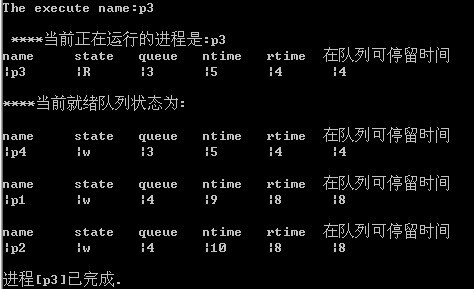
添加新的进程:

七、所遇困难的解决以及心得体会
在这个多级反馈的实验中,我采取了用一条实际上的链表队列来模拟多个逻辑上的队列,通过维护几个链表的状态信息来找到每个进程运行完后应该插入的地方,还有一个标志位Fend用来表明新插入的队列的位置。虽然实验原理很简单,但是在编写代码的过程中遇到了不少的问题,在两个小时之内已经完成的大体代码的编写,但是之中存在不少的问题,导致了用了差不多四个小时的时间去调试才把它弄好,这主要归咎于在开始设计代码的不太合理,在后期使得代码结构有些混乱,使得调试更加的麻烦,以及对编程的不熟悉。通过这个实验不仅使我对进程的调度算法有了更深的认识,使得理论知识得到的实践,也使我的编程能力得到了进一步提高。
八、源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define getpch(type) (type*)malloc(sizeof(type))
#define NULL 0
#define TIME 2//时间片长度
typedef struct pcb{//进程管理块
char name[10];//进程名字
char state; //进程状态
int queue; //进程所在的队列
int ntime; //进程需要运行的时间
int rtime; //进程已经运行的时间
int etime; //进程在本队列可运行的时间片
struct pcb *link;
}PCB;
PCB *ready = NULL, *pinsert = NULL, *pfend = NULL,*p =NULL; //就绪队列,进程插入位置的变量
int geti() //使用户仅能输入整数
{
char ch;
int i = 0;
fflush(stdin);
ch = getchar();
while(ch == '\n'){
printf("\tf输入不能为空..请重新输入\n");
fflush(stdin);
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch != '\n'){
if(ch > '9' || ch < '0'){
printf("\t输入有误!!输入只能为正整数,请重新输入...\n");
fflush(stdin);
i = 0;
ch = getchar();
}else{
i = i*10 + (ch - '0');
ch = getchar();
}
}
return i;
}
void findpos()//更新状态量
{
PCB *ps = pfend;
if(!ps || !ps -> link || (ps-> link->queue - ps->queue) > 1)
pinsert = ps;
else{
while (ps->link && ps ->link->queue != (pfend ->queue +2))
ps = ps->link;
pinsert = ps;
}
}
void insert()//插入进程
{
if(!ready ){
ready = p;
pfend = p;
pinsert = p;
}else if(ready ->queue == 1){//第一队列存在
p->link = pfend->link;
pfend->link = p;
pfend = p;
findpos();
}
else{
p->link = ready;
ready = p;
findpos();
}
}
void input()/*建立进程控制块函数*/
{
int i,num;
printf("\n请输入进程的个数?");
num = geti();
for(i=0; i < num; i++)
{
printf("\n进程号No.%d:\n",i+1);
p=getpch(PCB);
printf("\n输入进程名:");
scanf("%s",p->name);
printf("\n输入进程运行时间:");
p ->ntime = geti();
printf("\n");
p->rtime=0;
p->state='w';
p->queue =1;
p->etime = TIME;
p->link=NULL;
insert();/*调用insert函数*/
}
}
void disp(PCB *pr)/*建立进程现实函数,用于显示当前进程*/
{
printf("\nname\t state\t queue\t ntime\t rtime\t在队列可停留时间\t \n");
printf("|%s\t",pr->name);
printf(" |%c\t",pr->state);
printf(" |%d\t",pr->queue);
printf(" |%d\t",pr->ntime);
printf(" |%d\t",pr->rtime);
printf(" |%d\t",pr->etime);
printf("\n");
}
void check()/*建立进程查看函数*/
{
PCB *pr;
printf("\n ****当前正在运行的进程是:%s",ready->name);/*显示当前运行的进程*/
disp(ready);
pr= ready ->link;
printf("\n****当前就绪队列状态为:\n");/*显示就绪队列状态*/
while(pr!=NULL)
{
disp(pr);
pr=pr->link;
}
}
void sort()//调整进程队列
{
if(!ready->link ||ready->queue < ready->link->queue) return;
p = ready ->link;
ready ->link = pinsert ->link;
pinsert ->link = ready;
pinsert = ready;
ready = p;
if (ready && ready -> queue == pinsert ->queue){
findpos();
}
}
void addnew()//添加新的进程
{
if(ready ->queue != 1){
(ready -> queue)++;
ready->etime *= 2;
ready -> state='w';
sort();/*调用sort函数*/
input();
}
else{
input();
}
}
void destroy()/*建立进程撤销函数(进程运行结束,撤销进程)*/
{
printf("\n进程[%s]已完成.\n",ready->name);
p = ready;
ready = ready->link;
free(p);
if (ready && ready -> queue == pinsert ->queue)
findpos();
}
void running()/*建立进程就绪函数(进程运行时间到,置就绪状态)*/
{
(ready -> rtime)++;
ready ->etime --;
if(ready->rtime == ready->ntime){
destroy();
return;
}else if(ready ->etime == 0){
int time = 2;
(ready -> queue)++;
for(int i = 2; i != ready->queue; ++i)
time *= 2;
ready->etime = time;
ready -> state='w';
sort();/*调用sort函数*/
}
}
void main()
{
char ch;
input();
while(ready != NULL)
{
printf("\nThe execute name:%s\n",ready ->name);
ready ->state = 'R';
check();
running();
printf("\n按i键添加新进程....按其他任意键继续运行...");
fflush(stdin);
ch = getchar();
if (ch == 'i'|| ch=='I')
addnew();
}
printf("\n\n 进程已经完成\n");
getchar();
}
第二篇:5种进程调度算法实验报告
操作系统教程
——进程调度算法
进程调度算法的模拟实现
● 实验目的
1.本实验模拟在单处理机情况下的处理机调度问题,加深对进程调度的理解。
2.利用程序设计语言编写算法,模拟实现先到先服务算法FCFS、轮转调度算法RR、最短作业优先算法SJF、优先级调度算法PRIOR、最短剩余时间优先算法SRTF。
3.进行算法评价,计算平均等待时间和平均周转时间。
● 实验内容及结果
1.先来先服务算法
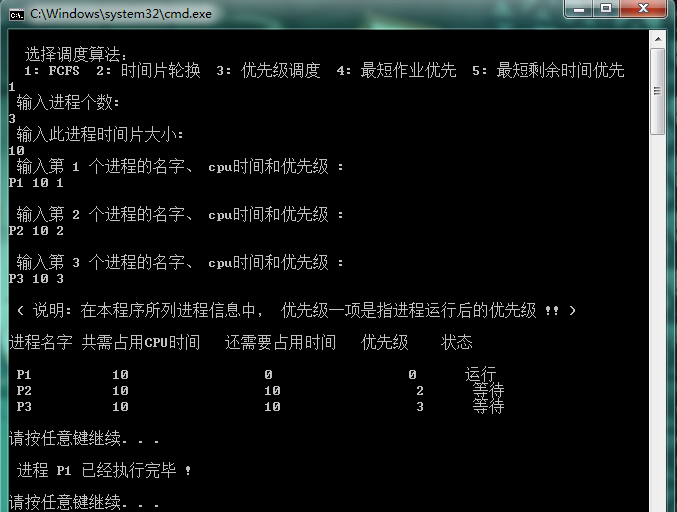


2.轮转调度算法
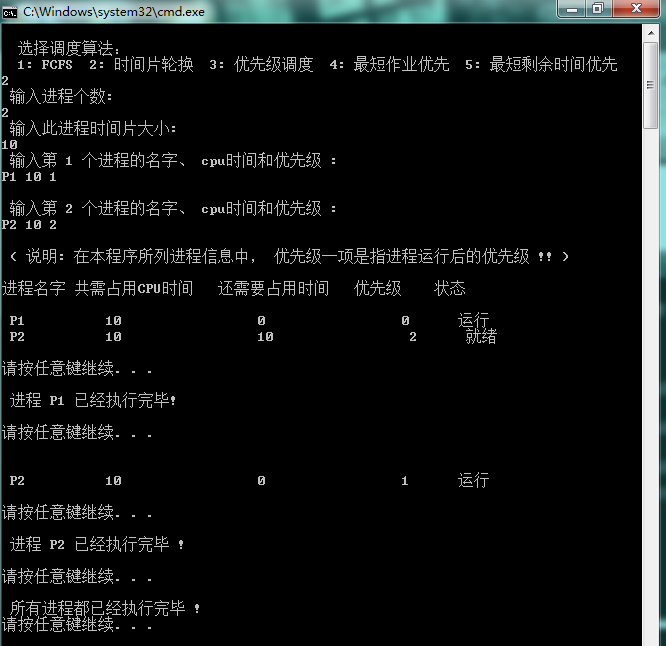
3. 优先级调度算法
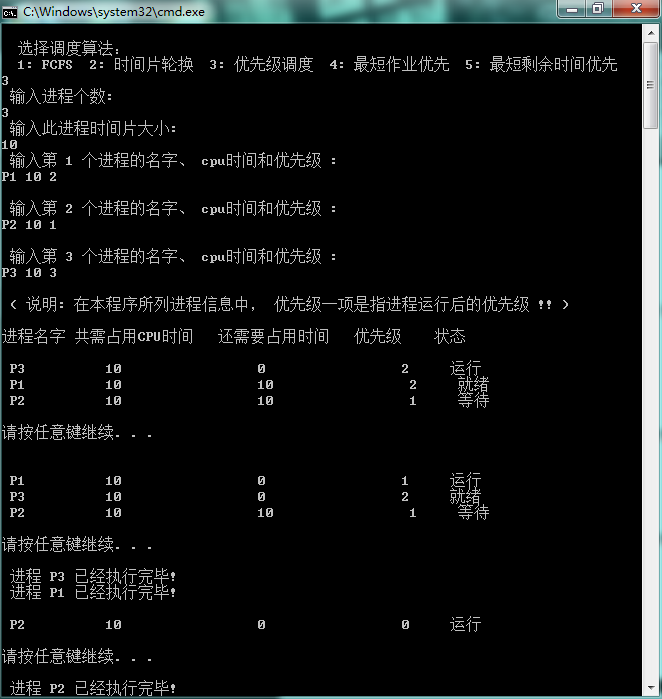
4. 最短时间优先算法
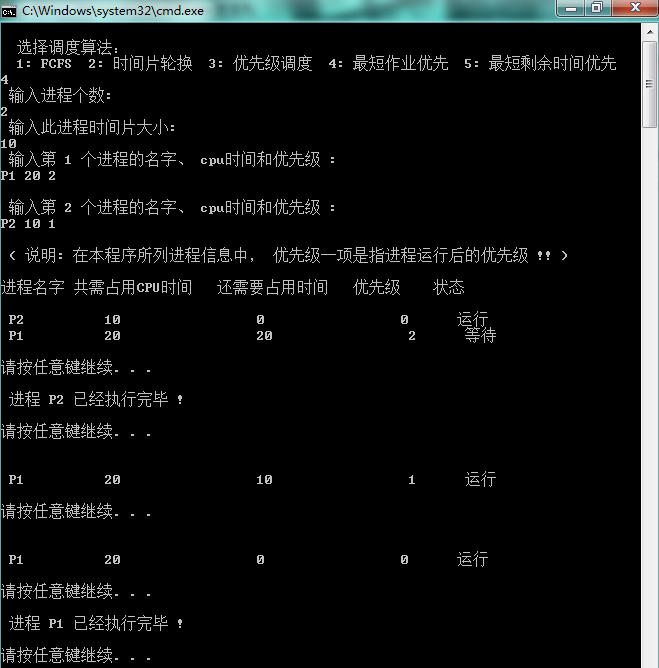
5. 最短剩余时间优先算法
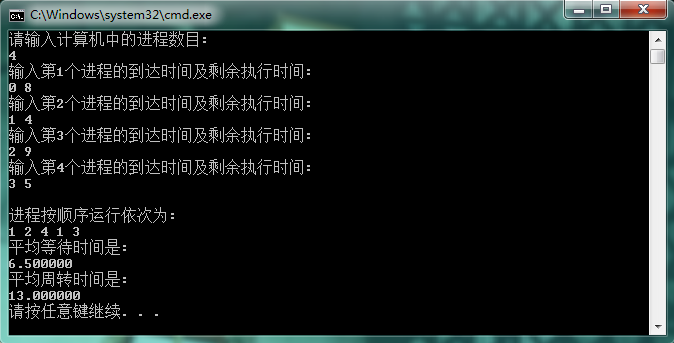
● 实验总结
在此次模拟过程中,将SRTF单独拿了出来用指针表示,而其余均用数组表示。
● 完整代码
【Srtf.cpp代码如下:】
//最短剩余时间优先算法的实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef struct
{
int remain_time; //进程剩余执行时间
int arrive_time; //进程到达时间
int Tp; //进入就绪队列的时间
int Tc; //进入执行队列的时间
int To; //进程执行结束的时间
int number; //进程编号
}Process_Block; //定义进程模块
typedef struct _Queue
{
Process_Block PB;
struct _Queue *next;
}_Block,*Process; //定义一个进程模块队列中结点
typedef struct
{
Process head; //队列头指针
Process end; //队列尾指针
}Process_Queue; //进程队列
Process_Queue PQ; //定义一个全局队列变量
int t; //全局时间
Process Run_Now; //当前正在运行的进程,作为全局变量
void InitQueue(Process_Queue PQ)
{
PQ.head ->next = NULL;
PQ.end ->next = PQ.head;
}/*初始化队列*/
int IsEmpty(Process_Queue PQ)
{
if(PQ.end->next == PQ.head)
return 1; //队列空的条件为头指针指向尾指针并且尾指针指向头指针
else
return 0;
}/*判定队列是否为空队列*/
void EnQueue(Process_Queue PQ,Process P)
{
Process temp =(Process)malloc(sizeof(_Block));
temp = PQ.end;
temp->next->next = P;
PQ.end->next = P;
}/*插入队列操作*/
Process DeQueue(Process_Queue PQ)
{
if(IsEmpty(PQ))
return NULL;
Process temp = PQ.head->next;
PQ.head->next= temp ->next;
if(PQ.end->next == temp)
PQ.end->next = PQ.head;
return temp;
}/*出列操作*/
Process ShortestProcess(Process_Queue PQ)
{
if(IsEmpty(PQ)) //如果队列为空,返回
{
if(!Run_Now)
return NULL;
else
return Run_Now;
}
Process temp,shortest,prev;
int min_time;
if(Run_Now) //如果当前有进程正在执行,
{
shortest = Run_Now; //那么最短进程初始化为当前正在执行的进程,
min_time = Run_Now->PB.remain_time;
}
else //如果当前没有进程执行,
{
shortest = PQ.head->next; //则最短进程初始化为队列中第一个进程
min_time = PQ.head->next->PB.remain_time;
}
temp = PQ.head;
prev = temp;
while(temp->next)
{
if(temp->next->PB.remain_time
{
shortest = temp->next; //则保存当前进程,
min_time = shortest->PB.remain_time;
prev=temp; //及其前驱
}
temp=temp->next;
}
if(shortest == PQ.end->next) //如果最短剩余时间进程是队列中最后一个进程,
PQ.end->next = prev; //则需要修改尾指针指向其前驱
prev->next = shortest->next; //修改指针将最短剩余时间进程插入到队头
return shortest;
}/*调度最短剩余时间的进程至队头*/
void Run()
{
Run_Now->PB.remain_time--; //某一时间运行它的剩余时间减
return;
}/*运行函数*/
void Wait()
{
return ;
}
int sum(int array[],int n)
{
int i,sum=0;
for(i=0;i
sum+=array[i];
return sum;
}
int main()
{
PQ.head = (Process)malloc(sizeof(_Block));
PQ.end = (Process)malloc(sizeof(_Block));
Run_Now = (Process)malloc(sizeof(_Block));
Run_Now =NULL;
InitQueue(PQ);
int i,N,Total_Time=0; //Total_Time为所有进程的执行时间之和
printf("请输入计算机中的进程数目:\n");
scanf("%d",&N);
Process *P,temp;
P = (Process*)malloc(N*sizeof(Process));
int *wt,*circle_t;
wt =(int*)malloc(N*sizeof(int));
circle_t =(int*)malloc(N*sizeof(int));
for(i=0;i
{
P[i] = (Process)malloc(sizeof(_Block));
P[i]->PB.number =i+1;
P[i]->next =NULL;
wt[i] =0;
circle_t[i] =0;
printf("输入第%d个进程的到达时间及剩余执行时间:\n",i+1);
scanf("%d %d",&P[i]->PB.arrive_time,&P[i]->PB.remain_time);
}
for(i=0;i
Total_Time+=P[i]->PB.remain_time;
printf("\n进程按顺序运行依次为:\n");
i=0;
int k=0;
for(t=0;;t++)
{
if(Run_Now) //如果当前有进程正在执行
{
Run();
if(t == P[i]->PB.arrive_time) //如果当前时间正好有进程进入
{
if(P[i]->PB.remain_time < Run_Now->PB.remain_time)
{
temp = P[i];
P[i] = Run_Now;
Run_Now = temp; //则调度它至运行队列中,
Run_Now->PB.Tp=t;
Run_Now->PB.Tc=t;
wt[Run_Now->PB.number-1]+=Run_Now->PB.Tc-Run_Now->PB.Tp;
printf("%d ",Run_Now->PB.number);
}
EnQueue(PQ,P[i]); //并将当前运行进程重新插入队列中
P[i]->PB.Tp=t;
k++;
i=(i+1)>(N-1)?(N-1):(i+1);
}
if(Run_Now->PB.remain_time == 0) //如果当前进程运行结束,
{
Run_Now->PB.To=t; //进程运行结束的时间
circle_t[Run_Now->PB.number-1] +=t-Run_Now->PB.arrive_time;
free(Run_Now); //则将它所占资源释放掉,
Run_Now =NULL; //并修改Run_Now为NULL
Run_Now = ShortestProcess(PQ); //从就绪队列中调出最短剩余时间进程至队头,
if(!Run_Now) //如果队列为空,转为等待状态
{
if(IsEmpty(PQ) && k >= N) break;
Wait();
continue;
}
else
{
Run_Now->PB.Tc=t;
wt[Run_Now->PB.number-1]+=Run_Now->PB.Tc-Run_Now->PB.Tp;
printf("%d ",Run_Now->PB.number);
}
}
}
else //如果当前运行进程为空,那么
{
if(t == P[i]->PB.arrive_time) //如果正好这时有进程入队
{
k++;
EnQueue(PQ,P[i]);
Run_Now = DeQueue(PQ); //则直接被调入运行队列中
Run_Now->PB.Tp=t;
Run_Now->PB.Tc=t;
printf("%d ",Run_Now->PB.number);
i=(i+1)>(N-1)?(N-1):(i+1);
}
else
{
Wait();
continue;
}
}
}
printf("\n");
printf("平均等待时间是:\n%f\n",((float)sum(wt,N))/N);
printf("平均周转时间是:\n%f\n",((float)sum(circle_t,N))/N);
return 0;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
【Process.cpp代码如下:】
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Process
{
public:
string ProcessName; // 进程名字
int Time; // 进程需要时间
int leval; // 进程优先级
int LeftTime; // 进程运行一段时间后还需要的时间
};
void Copy ( Process proc1, Process proc2); // 把proc2赋值给proc1
void Sort( Process pr[], int size) ; // 此排序后按优先级从大到小排列
void sort1(Process pr[], int size) ; // 此排序后按需要的cpu时间从小到大排列
void Fcfs( Process pr[], int num, int Timepice); // 先来先服务算法
void TimeTurn( Process process[], int num, int Timepice); // 时间片轮转算法
void Priority( Process process[], int num, int Timepice); // 优先级算法
void main()
{
int a;
cout<
cout<<" 选择调度算法:"<
cout<<" 1: FCFS 2: 时间片轮换 3: 优先级调度 4: 最短作业优先 5: 最短剩余时间优先"<
cin>>a;
const int Size =30;
Process process[Size] ;
int num;
int TimePice;
cout<<" 输入进程个数:"<
cin>>num;
cout<<" 输入此进程时间片大小: "<
cin>>TimePice;
for( int i=0; i< num; i++)
{
string name;
int CpuTime;
int Leval;
cout<<" 输入第"<< i+1<<" 个进程的名字、cpu时间和优先级:"<
cin>>name;
cin>> CpuTime>>Leval;
process[i].ProcessName =name;
process[i].Time =CpuTime;
process[i].leval =Leval;
cout<
}
for ( int k=0;k
process[k].LeftTime=process[k].Time ;//对进程剩余时间初始化
cout<<" ( 说明: 在本程序所列进程信息中,优先级一项是指进程运行后的优先级!! )";
cout<
cout<<"进程名字"<<"共需占用CPU时间 "<<" 还需要占用时间 "<<" 优先级"<<" 状态"<
if(a==1)
Fcfs(process,num,TimePice);
else if(a==2)
TimeTurn( process, num, TimePice);
else if(a==3)
{
Sort( process, num);
Priority( process , num, TimePice);
}
else // 最短作业算法,先按时间从小到大排序,再调用Fcfs算法即可
{
sort1(process,num);
Fcfs(process,num,TimePice);
}
}
void Copy ( Process proc1, Process proc2)
{
proc1.leval =proc2.leval ;
proc1.ProcessName =proc2.ProcessName ;
proc1.Time =proc2.Time ;
}
void Sort( Process pr[], int size) //以进程优先级高低排序
{// 直接插入排序
for( int i=1;i
{
Process temp;
temp = pr[i];
int j=i;
while(j>0 && temp.leval
{
pr[j] = pr[j-1];
j--;
}
pr[j] = temp;
} // 直接插入排序后进程按优先级从小到大排列
for( int d=size-1;d>size/2;d--)
{
Process temp;
temp=pr [d];
pr [d] = pr [size-d-1];
pr [size-d-1]=temp;
} // 此排序后按优先级从大到小排列
}
/* 最短作业优先算法的实现*/
void sort1 ( Process pr[], int size) // 以进程时间从低到高排序
{// 直接插入排序
for( int i=1;i
{
Process temp;
temp = pr[i];
int j=i;
while(j>0 && temp.Time < pr[j-1].Time )
{
pr[j] = pr[j-1];
j--;
}
pr[j] = temp;
}
}
/* 先来先服务算法的实现*/
void Fcfs( Process process[], int num, int Timepice)
{ // process[] 是输入的进程,num是进程的数目,Timepice是时间片大小
while(true)
{
if(num==0)
{
cout<<" 所有进程都已经执行完毕!"<
exit(1);
}
if(process[0].LeftTime==0)
{
cout<<" 进程"<
for (int i=0;i
process[i]=process[i+1];
num--;
}
else if(process[num-1].LeftTime==0)
{
cout<<" 进程"<
num--;
}
else
{
cout<
process[0].LeftTime=process[0].LeftTime- Timepice;
process[0].leval =process[0].leval-1;
cout<<" "<
cout<
}
} // else
cout<
system(" pause");
cout<
} // while
}
/* 时间片轮转调度算法实现*/
void TimeTurn( Process process[], int num, int Timepice)
{
while(true)
{
if(num==0)
{
cout<<" 所有进程都已经执行完毕!"<
exit(1);
}
if(process[0].LeftTime==0)
{
cout<<" 进程"<
for (int i=0;i
process[i]=process[i+1];
num--;
}
if( process[num-1].LeftTime ==0 )
{
cout<<" 进程" << process[num-1].ProcessName <<" 已经执行完毕! "<
num--;
}
else if(process[0].LeftTime > 0)
{
cout<
process[0].LeftTime=process[0].LeftTime- Timepice;
process[0].leval =process[0].leval-1;
cout<<" "<
cout<
if(s==1)
cout<<" 就绪"<
else
cout<<" 等待"<
}
Process temp;
temp = process[0];
for( int j=0;j
process[j] = process[j+1];
process[num-1] = temp;
} // else
cout<
system(" pause");
cout<
} // while
}
/* 优先级调度算法的实现*/
void Priority( Process process[], int num, int Timepice)
{
while( true)
{
if(num==0)
{
cout<< "所有进程都已经执行完毕!"<
exit(1);
}
if(process[0].LeftTime==0)
{
cout<<" 进程" << process[0].ProcessName <<" 已经执行完毕! "<
for( int m=0;m
process[m] = process[m+1]; //一个进程执行完毕后从数组中删除
num--; // 此时进程数目减少一个
}
if( num!=1 && process[num-1].LeftTime ==0 )
{
cout<<" 进程" << process[num-1].ProcessName <<" 已经执行完毕! "<
num--;
}
if(process[0].LeftTime > 0)
{
cout<
process[0].LeftTime=process[0].LeftTime- Timepice;
process[0].leval =process[0].leval-1;
cout<<" "<
cout<
if(s==1)
cout<<" 就绪"<
else
cout<<" 等待 "<
}
} // else
Sort(process, num);
cout<
system(" pause");
cout<
} // while
}
-
进程调度实验报告[1]
实验一进程调度一实验题目1编写并调试一个模拟的进程调度程序采用最高优先数优先调度算法对五个进程进行调度2编写并调试一个模拟的进程调…
-
计算机操作系统进程调度实验报告
操作系统实验题设计一若干并发进程的进程调度程序一实验目的无论是批处理系统分时系统还是实时系统用户进程数一般都大于处理机数这将导致用…
-
操作系统进程调度实验报告
操作系统进程调度实验报告一实验目的用高级语言编写和调试一个进程调度程序以加深对进程的概念及进程调度算法的解进程调度时进程管理的主要…
-
进程调度算法实验报告
操作系统实验报告二实验题目进程调度算法实验环境C实验目的编程模拟实现几种常见的进程调度算法通过对几组进程分别使用不同的调度算法计算…
-
操作系统进程调度模拟程序实验报告
沈阳理工大学课程设计任务书1沈阳理工大学目录1课程设计目的32课程设计要求33相关知识34需求分析45概要设计56详细设计67测试…
-
计算机操作系统进程调度实验报告
操作系统实验题设计一若干并发进程的进程调度程序一实验目的无论是批处理系统分时系统还是实时系统用户进程数一般都大于处理机数这将导致用…
-
操作系统课程设计报告_进程调度算法
1实验目的通过优先权法和轮转算法的模拟加深对进程概念和进程调度过程的理解掌握进程状态之间的切换同时掌握进程调度算法的实现方法和技巧…
-
操作系统课程设计报告_进程调度算法
1实验目的通过优先权法和轮转算法的模拟加深对进程概念和进程调度过程的理解掌握进程状态之间的切换同时掌握进程调度算法的实现方法和技巧…
-
进程调度实验报告[1]
实验一进程调度一实验题目1编写并调试一个模拟的进程调度程序采用最高优先数优先调度算法对五个进程进行调度2编写并调试一个模拟的进程调…
-
进程调度算法实验报告
操作系统实验报告二实验题目进程调度算法实验环境C实验目的编程模拟实现几种常见的进程调度算法通过对几组进程分别使用不同的调度算法计算…
-
操作系统进程调度实验报告
操作系统进程调度实验报告一实验目的用高级语言编写和调试一个进程调度程序以加深对进程的概念及进程调度算法的解进程调度时进程管理的主要…