硕士生管理经济学作业
硕士生管理经济学作业
1、试述微观经济学的逻辑结构
微观经济学是研究个体选择的理论,即研究某个特定消费单位或某个生产单位所做出的决策的问题。其研究的中心问题是价格问题,研究商品和劳务以及生产要素的相对价格可以影响个体经济单位的经济行为,从而调节资源的配置与产品的产量。并且通过可证伪条件、实证与规范分析方法、假设和模型、优化和均衡方法、成本收益分析方法等5种方法对以上问题进行研究。
2、张先生和吴先生在电影院看电影。但是他们二人都不是很喜欢这场电影。张对吴说:们应该留下来继续看,因为我们已经付了们付了6元钱,而是因为我们没有其他更好的事情可以做。为什么?
吴的观点更正确.是机会成本。张的观点,情,可能会有更大的收益,电影,也无其它事情可做,所以即使电影不好看也留下继续观看才成为了他们的正确选择。
3、公共汽车有着比较低的需求价格弹性,但是需求的服务弹性却很高(过对等待时间的敏感程度,便利性程度等)汽车的数量和减少线路来降低成本。这样做对吗?谈谈你的理由。
不对。降低成本的最终目的是为了利润的最大化,利润等于收入减去成本。单纯考虑降低成本而不考虑收入是不正确的。且减少汽车数量和线路,提升价格即可完成对这部分需求的调节,润。
4、解释为什么在肯德基软饮料的利润率比汉堡的利润率更高。
首先根据成本与定价,使消费者在购买汉堡的同时,时也降低了可乐的价格弹性。配汉堡,导致可乐的需求也高于汉堡。最终导致可乐的利润率高于汉堡。
5、一些音像商店往往给消费者提供一些选择方案。会员资格,这时每次租用为每张VCD每天支付间)。分别描述每一种方案背后的经济含义
对于不成为会员,为每张格的定价方法属于一级价格歧视。已经付的6元钱是沉没成本,未考虑机会成本,因此张的观点是不正确的。。为了平衡预算,当地的公共汽车部门作出了一个决策,通过消减而采取减少汽车数量和线路的方式,相当于通过外部因素抑制正常需求,可乐的利润比汉堡高很多。也会一同消费可乐,而汉堡的替代品较多,VCD的价格是3元。当然也可以支付VCD每天支付
6元钱:”。吴却说:”他们二人的观点哪一个更正确,不能改变。如果不看电影,利用电影播放的时间去做其它事吴的观点考虑了机会成本,根据价格与需求的关系,而可乐的销售策略一般采取套餐形式,这样就有效的降低了可乐的交易成本,消费者不会因为为了购买可乐而同时搭例如,消费者可以支付1元钱。另外消费者也可以不成为会员,但是需要300元然后免费观看(当然规定一点的观看时. 3元的顾客的方案,这种对每个消费者收取保留价“我即使不看 而通过同40元来购买一个“我们应该留下来不是因为我而为了看电影而放弃的时间
势必会降低收入。进一步对车数和线路进行优化。才能最大化扩大利
对于支付40元购买会员资格,然后每次租用VCD价格为1元的方案,所对应的消费者对观看VCD有固定的需求,但是随着观看数量的增多,其需求也是相应下降的,因此音像店对其对相同商品的不同消费量索取不同价格,这种定价方式属于二级价格歧视。
对于支付300元然后免费观看的消费者,针对的是对价格弹性敏感度高的消费者,这种方案是将不同的消费者划分为不同的市场,对不同的消费者收取不同的价格,这种方法属于三级价格歧视。
而整体来看,商家采取了两步定价法的方式来制定价格,会员资格相当于其中的固定费用。
第二篇:管理经济学作业一答案
Managerial Economics
Name:
Class:
Student #:
(Due day: Next class)
Part 1:
1. A perfectly competitive market has:
a) many buyers and sellers.
b) several large buyers.
c) a meeting place for buyers and sellers.
d) a) and b)
e) a) and c)
Choose: a) There must be numerous small buyers and sellers for a market to be perfectly competitive. A meeting place is unnecessary.
2. Boeing Corporation and Airbus Industries are the only two producers of long-range commercial aircraft. This market is not perfectly competitive because:
a) Each company has annual sales over $10 billion.
b) Each company can significantly affect prices.
c) Airbus receives subsidies from the European Union.
d) Airbus cannot sell aircraft to the United States government. e) All of the above.
Choose: b) The character of monopoly market is each firm can affect prices.
3. If the real price of a college education has risen during a period
of inflation:
a) its nominal price has not changed.
b) its nominal price has risen slower than a general index of prices. c) its nominal price has risen faster than a general index of prices. d) its current dollar price has not changed.
e) None of the above is correct.
Choose: c) When the nominal price of a college education rises faster than the
rate of inflation, the real price of a college education will rise.
4. The constant dollar price of a good:
a) is the same as its real price.
b) is the same as its nominal price.
c) adjusts for inflation in the overall price level.
d) b) and c)
e) a) and c)
Choose: e) By definition, the constant dollar price is equal to the real price, and
both adjust the nominal price for the effects of the inflation.
5. The price of a sandwich was $0.29 in 1970 and $0.99 in 1993. The CPI was 38.8 in 1970 and 144.0 in 1993. The 1993 price of a sandwich in 1970 dollars is:
a) $0.08.
b) $0.27.
c) $0.34.
d) $3.67.
Choose: b) 0.99/x=144/38.8 x=0.27
6. Which of the following would shift the demand curve for new textbooks to the right?
a) A fall in the price of paper used in publishing texts.
b) A fall in the price of equivalent used text books.
c) An increase in the number of students attending college.
d) A fall in the price of new text books.
Choose: c) non-price demand-determining variables
7. Plastic and steel are substitutes in the production of body panels for certain automobiles. If the price of plastic increases, with other things remaining the same, we would expect
a) the price of steel to fall.
b) the demand curve for steel to shift to the right.
c) the demand curve for plastic to shift to the left.
d) nothing to happen to steel because it is only a substitute for plastic.
e) the demand curve for steel to shift to the left.
Choose: b) the definition of substitutes
8. Last month you sold 10,000 stereos nationwide at $400 each. The month before that you sold 9,000 stereos at $410 each. Next month, you are thinking of cutting the price even further to $389.99. Assuming that (i) the market demand for your product is linear, and (ii) all else remains equal, what is your prediction for next month’s sales?
a) 10,100 units.
b) 11,000 units.
c) 11,001 units.
d) 11,051 units.
e) 12,000 units.
Choose: c) Using the two data points, find the slope and intercept of the demand curve: (9,000-10,000)/(410-400)=-100 and 10,000=a-100(400), or a=50,000. Thus, the equation of the line is Q=50,000-100P. When P=$389.99, Q=11,001.
The next 9-11questions refer to the following demand and supply curves:
QD = 189 – 2.25P
QS = 124 + 1.5P
Your answers should be correct to two decimal places.
9. The equilibrium price is:
a) $84 b) $82.67 c) $17.33 d) $150 e) None of the above is correct.
Choose: c) Setting QS =QD, we obtain 124 + 1.5P = 189 – 2.25P. Collecting
terms, 3.75P = 65, or P = $17.33.
10. The equilibrium quantity sold is:
a) 65 b) 150 c) 313 d) 84 e) None of the above is correct Choose: b) Using P =17.33 (from above), QS =124 +1.5(17.33) = 150.
11. At the market equilibrium, the price elasticity of demand equals:
a) -2.25 b) +2.25 c) -0.26 d) -0.17 e) None of the above is correct.
Choose: c) EP = -bP/Q = -2.25(17.33)/150 = -0.26.
12. If the price elasticity of demand for coffee is estimated to be –0.25 in the
short of run, which is the most likely value of the long-run elasticity?
a) -0.10 b) -0.25 c) -0.40 d) -∞
e) None of the above the elasticity of demand in the long run is always
positive.
Choose: c) For most goods (except those that are durable), the long-run
elasticity is greater in absolute value than the short-run elasticity.
Part 2:
Suppose the table below lists the price and consumption levels of food and clothing during 1990 and 2000. Calculate a Laspeyres and Paasche index
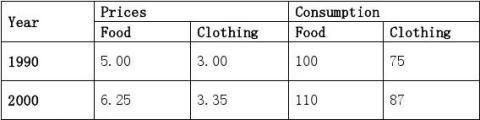
Solution:
The Laspeyres Index is calculated as follows:
FCP2000F1990?P2000C1990?6.25?100?(3.35)75876.25LI?F???1.209. C5100?375725PF?PC1990199019901990
The Paasche Index is calculated as follows:
FCP2000F2000?P2000C2000?6.25?110?(3.35)87978.95PI?F???1.207. C5110?387811PF?PC1990200019902000
Part 3:
This exercise uses the market data given in Table 1.1

a) Plot the supply and demand curve with quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
b) Derive the intercepts and slops for the demand curve QD = a – bP and the supply curve QS = c + dP.
c) Make sure that the equations you found are correct by plugging in P = $10 and P = $ 40 and verifying the quantities with Table 1.1. d) Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
Answer:
a)
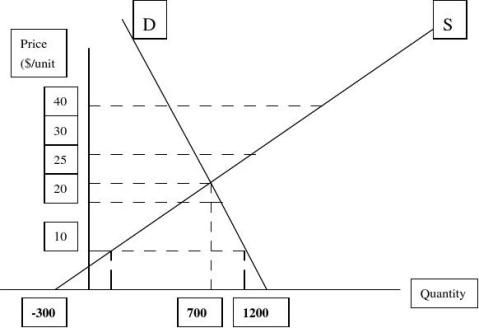
b) First, consider the supply curve. From point (Q1, P1) and (Q2, P2), we
can derive the slope: d = ΔQS/ΔP =(Q2 – Q1)/(P2 – P1) = (1,300 –900)/(40 –30) = 400/10 =40. The intercept c equals QS –dP =1,300 – 40(40) = -300. So, the supply curve is QS =-300 + 40P.
The slope of the demand curve is
b = ΔQD/ΔP = (Q5 –Q6)/(P5 – P6) =(800 –1,000)/(20 –10) = -200/10
=-20, so b =20. The intercept is a =QD +bP = 800 +20(20) =1,200. So, the demand curve is QD = 1,200 – 20P.
a) For supply, at P =10,QS = -300 + 40(10) = -300 + 400 = 100.
At P = 40, QS = -300 + 40(40) = 1,300.
For demand, at P = 10, QS = 1,200 – 20(10) =1,000.
At P =40, QD = 1,200 – 20(40) = 400.
d) Set QS = QD or –300 +40P =1200 – 20P. Combining terms we get, 60P
=1,500, or P =25. Substituting back into the supply curve, we obtain QS = -300 + 40(25) =700. As a check, substitute back into the demand curve to get QS = 1,200 – 20(25) =700. We have verified that P = 25 is the equilibrium price, since QS =QD =700 at that price.
Part 4:
The wheat market is perfectly competitive, and the market supply and demand curves are given by the following equations:
QD = 20,000,000 - 4,000,000P
QS = 7,000,000 + 2,500,000P,
where QD and QS are quantity demanded and quantity supplied measured in bushels, and P = price per bushel.
a) Determine consumer surplus at the equilibrium price and quantity. b) Assume that the government has imposed a price floor at $2.25 per bushel and agrees to buy any resulting excess supply. How many bushels of wheat will the government be forced to buy? Determine consumer surplus with the price floor.
Solution:
a. The first step is to determine the equilibrium price ?Pe? and
quantity ?Qe? by equating QD and QS.
20,000,000?4,000,000Pe?7,000,000?2,500,000Pe
13,000,000?6,500,000Pe
Pe?$2.00.
Substitute into QD or QS
Qe?20,000,000?4,000,000?2?
Qe?12,000,000.
To find consumer surplus, we must also determine the choke price
(PC). That is, the price at which quantity demanded is zero.
solve for P in terms of QD and QS.
0?20,000,000?4,000,000PC
4,000,000PC?20,000,000
P
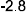
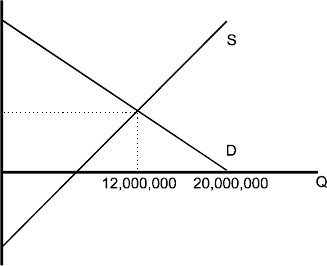
C?5.
CS?1?PC?Pe?Qe?0.5?5?2?12,000,000?18,000,000. 2
b.
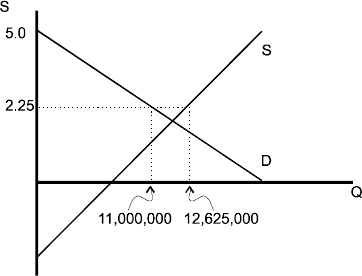
At price of 2.25
QD = 20,000,000 - 4,000,000(2.25)
QD = 11,000,000
QS = 7,000,000 + 2,500,000(2.25)
QS = 12,625,000
Excess supply is QS - QD.
12,625,000 - 11,000,000 = 1,625,000
Government should expect to buy 1,625,000 bushels.
Cs = (0.5)(Pc-$2.25)QD = (0.5)(5-2.25)(11,000,000)=15,125,000.
C.S. fell from 18,000,000 to 15,125,000
-
管理经济学学习心得
这学期我选择了管理经济学这门学科,刚刚开始有点不习惯,因为别的课程都是有书本的,而选修课却没有课本。并且,在我的认知中,文科都是比…
-
1102506003 管理经济学心得
华北电力大学MBA作业《管理经济学》学习心得课程名称:____管理经济学_____任课教师:班级代号:姓名:_______周程扬_…
-
管理经济学课程小结
经过这七周管理经济学课程的学习,让我们初步了解了微观经济学的基本观点与基本理论,同时让我们认识到管理经济学不仅是一门简单经济学理论…
-
管理经济学总结
管理经济学考试题一填空题1管理经济学研究的基本问题核心答管理经济学是研究如何把微观经济学的理论和经济分析方法应用于企业管理决策实践…
-
管理经济学有关概念归纳总结
管理经济学有关概念总结归纳第一章:管理经济学:管理经济学是一门研究如何把西方传统的微观经济学理论与方式应用于企业管理实践的基础理论…
-
管理经济学课程小结
经过这七周管理经济学课程的学习,让我们初步了解了微观经济学的基本观点与基本理论,同时让我们认识到管理经济学不仅是一门简单经济学理论…
-
管理经济学知识总结
管理经济学:是一门研究如何把传统经济学的理论和经济分析方法应用于企业管理决策实践的学科,是应用经济学的一个分支。企业行为的经济性:…
-
1102506003 管理经济学心得
华北电力大学MBA作业《管理经济学》学习心得课程名称:____管理经济学_____任课教师:班级代号:姓名:_______周程扬_…
-
管理经济学学习心得
这学期我选择了管理经济学这门学科,刚刚开始有点不习惯,因为别的课程都是有书本的,而选修课却没有课本。并且,在我的认知中,文科都是比…
-
管理经济学自考复习总结
第五章1、相关成本2、非相关成本3、增量成本4、沉没成本5、变动成本6、固定成本7、成本函数8、边际成本9、长期10、贡献11、盈…