国际会议论文格式范本
Special Seminar: Assessing Emergent Business IT Using the Web of System Performance
Brian Whitworth1, CheiknaSylla2,Elizabeth Whitworth3
1Institute of Information and Mathematical Sciences, Massey University (Albany), New Zealand
2School of Management, New Jersey Institute of Technology, USA
3Psychology Department, Carleton University, Canada
2345@public.wh.hb.cn
[The title of the paper should be written in bold in 14 point font, centered on the top of the paper. The first letter of every word in the title should be capitalized. Leave one line, the authors’ names and their affiliations, following the title, must be 11 point font.]
Abstract: [9pt, bold, the first letter should be capitalized] Businesses must often decide whether to purchase emergent technology in various states of maturity. Purchasing immature technology can have serious consequences for a business, but equally not purchasing new technology can invoke intangible opportunity losses that are equally costly in the long term. Businesses that don’t upgrade their IT can go out of business, but upgrading every time can be equally disastrous. [9pt]
Keywords: keyword1, keyword2, keyword3, keyword4 [9pt]
[Every paper should include an abstract within 500 words. At the end of the abstract, skip a line and then type “Keywords:” (NOT bold, italic, and followed by a colon) followed by 3 to 8 words that describe the focus and contribution of the paper. ]
1. INTRODUCTION[10pt, capitalized, bold]
The use of information technology (IT) has become a primary survival factor for business organizations in a global competitive environment. However just as IT can make money for business, it can also lose money, as IT has become a major corporate expenditure.……
[This document has been prepared using the required format (Microsoft Word version 6.0 or later). Using this document as a template is highly recommended as it gives the best input for the final publications. ]
[Body of the paper: The whole paper should be written in “Times New Roman” font. Except the title of the paper that is in 14-font size and authors’ names with their affiliations in 11-font size, the whole paper should be written in 10 fonts. ]
[Do not use multiple columns. The line spacing should be single line. Every paper should be less than or equal to 6 pages. Set the page to A4 with margins of 2.54cm all around. Do not use headers and footers, do not use end notes and do not put page numbers. Microsoft Word file is strongly preferred. ]
2. WHY A NEW THEORY OFINFORMATION SYSTEMPERFORMANCE? [10pt, capitalized, bold]
[Headings are numbered and capitalized. All major headings are centered in bold in 10 fonts. Do not put a period after the text of the heading. There should be no more than three levels of heading. ]
In the infancy of software development, designers held functionality (what the system does to the world) as the primary goal of software development. This is because at that time, software was just a tool, as say a hammer is a tool. As information systems developed however, they not only became more complex, but also less passive and more active systems in their own right. IS today works with the user not just for the user, and now enables a virtual online society that could span the globe. Hence functionality has become an insufficient indicator of information system performance. The main battle against functionality as the prime directive of system designers was carried out by the proponents of usability, human-factors and human-computer interaction, supported by theoretical frameworks such as the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). These views presented ease of use as equal to usefulness in determining user acceptance of a system[1], e.g. if a web site performs well functionally, but users don’t like it and click on to other sites, then it is a failure. Functional failure and usability failure it was noted have the same effect – the system does not run!
3. WHAT IS A SYSTEMS APPROACH? [10pt, capitalized, bold]
Nearly forty years ago Bertalanffy noted that certain mathematical formulas repeated across many disciplines like chemistry, physics and biology [2], which used the same formulae to describe completely different things. Hence was borne the idea of studying a “system” without referencing what type of system it was.
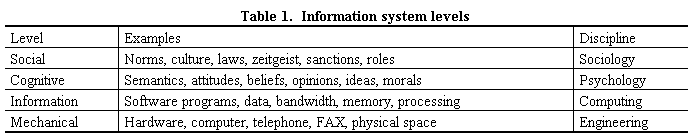
Computer systems seem systems in a general sense [3], so a hardware computer system of chips and circuits is also a software system of information exchanges, and today also the human-computer combination [4], e.g. a plane is mechanical, its computer controls are informational, but the plane plus pilot is also a system – a human-computer system. Human-computer interaction (HCI) sees computers as more than just technology (hardware and software). Table 1 summarizes the four computer system levels, matching the idea of an information system (IS) as hardware, software, people, and business processes[5]. The levels are different views of the same system not different systems, and match disciplines of Engineering, Computing, Psychology and Sociology, respectively.
[Figures and tables should be placed as close as possible to where they are cited. Captions should be Times New Roman 9-point, bold. Figures and Tables should be numbered separately and consecutively. Avoid color diagrams. Figure’s captions should be flush center below the figures, and Table captions should be in center above the table body. Initially capitalize only the first word of each caption. Table contents should be Times New Roman 9-point, no bold. ]
4. WHAT DOES THE FIGURE REPRESENT? [10pt, capitalized, bold]
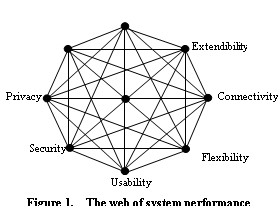 In the web of system performance (Figure1):
In the web of system performance (Figure1):
· Web area represents system performance in general, so a bigger the area means a greater system performance potential.
· Web shape represents the goal criterion weights, which vary with the environment, e.g. a threat environment may mean security has more weight.
· Web lines represent goal tensions, imagined as connecting rubber bands that can pull back one performance dimension as another increases.
5. HOW ARE THE DIMENSIONS EDFINED? [10pt, capitalized, bold]
5.1 Ideas seem similar to Alexander’s synthesis of form. [10pt, no capitalized, bold]
[Subheadings are flush left, in bold in 10point type, not be capitalized. There should be one line space before second-level heading. Keeping two space for third-Level heading that is also in bold in 10 point type, as shown in the subheading for this paragraph. ]
Yes, this model merely applies Alexander’s theory to IS. Over forty years ago Alexander noted the “tension” problems of physical world system design [5]. Since then, his architectural pattern theory has been applied to information systems (IS) and object orientated (OO) design. Design tensions arise when physical systems composed of parts have multiple contextual demands. For example, in a simple machine such as a vacuum cleaner, each part, like the engine, can be designed for its specific function by using the best materials. Specialized materials allow a powerful engine, with more suction, but this may also create more noise, heat and weight, making the vacuum harder to use. Part specialization may also mean more complex joints that fail easier, reducing reliability. Finally, customizing parts can increase manufacturing material diversity, raising costs.
[All equations should be placed on separate lines and numbered consecutively, with the equation numbers placed within parentheses and aligned against the right margin as shown in equation (1).
Min C = 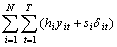 (1)
(1)
Be sure that the symbols in your equation have been defined before the equation appear or immediately following. ]
5.2 Is WOSP useful for system evaluation as well as system design? [10pt, no capitalized, bold]
Yes, it can be used as a process-oriented design framework for system developers, or a product-oriented evaluation framework for system users/buyers. The common concept of system performance connects the two fields: generally designers want to produce high performance systems, and likewise users want to buy them.
5.2.1 Reason A
Design then, is the art of synthesizing “forms” to reconcile contradictory contextual demands, e.g. vacuums that are both lightweight and powerful. “Patterns” are generic solutions to design conflicts that repeat: “Each pattern describes a problem which occurs over and over again in our environment, and then describes the core of the solution to that problem.” [6]. If problems repeat, it makes sense to re-use successful solutions. The logic applies as well to IS design as it does to physical design.
6. CONCLUSIONS[10pt, capitalized, bold]
Supply chain coordination has become the key strategic area that has direct impact over the success of any enterprise in today’s highly competitive business environment.
[Making sure author’s paper follows the guidelines for submissions. If there is a mismatch, the author(s) will be informed of needed corrections. ]
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT[10pt, capitalized, bold]
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 70572071.
[Use the singular heading even if you have many acknowledgments. Avoid expressions such as “One of us (S.H.C.) would like to thank ... .” Instead, write “F.A. Author thanks ... .”. Sponsor and financial support acknowledgments expressions such as “This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 123456”.]
REFERENCES[9pt, capitalized, bold, centered]
[1] Bird R B, Stewart W E. (1960).Lightfoot E N. Transport Phenomena. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 75
[2] Henry R C, Lewis C W, Collins J F. (1994).Vehicle-related hydrocarbon source compositions from ambient data: the GRACE/SAFER method. Eniron Sci Technol, , 28(5): 823-832
[3] Ma Tingxi, Lu Xueshu. (1992).Computer aided analysis of the penetration of mounted tillage implement. In: Zhang Wei, Guo Peiyu, Zhang Senwen, eds. Agricultural Engineering and Rural Development: Vol I. Beijing: International Academic Publishers, 157-160(in Chinese)
[4] Young L C. (1974). The Application of Orthogonal Collocation to Laminar Flow Heat and Mass Transfer in Monolith Converters. Ms D Thesis. Washington: University of Washington,
[5] Larsen C E, Trip R, Johnson C R. (1995-01-25). Methods for Procedures Related to the Electrophysiology of the heart. US Patent 5 529 067.
[6] APHE. (1985). Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC,
[7] Xie Xide. (1998-12-25). Creating new way to study. People’s Daily, (10)
[8] Chescheir G M, Westerman P W. (1984). Rapid Methods for Determining Fertilizer Value of Livestock Manures. ASAE paper No.84-4082. Michigan: American Society of Agricultural Engineering
[9] Chaplin M. (2003). Guar gum. www.sbu.ac.uk/water/hygua.html,
[Number citations consecutively in square brackets [1]. The sentence punctuation follows the brackets [2]. Multiple references [2], [3] are each numbered with separate brackets [1]–[3]. When citing a section in a book, please give the relevant page numbers [2]. In sentences, refer simply to the reference number, as in [3]. Do not use “Ref. [3]” or “reference [3]” except at the beginning of a sentence: “Reference [3] shows ...”]
-
国际会议论文格式要求
国际会议论文格式要求:AuthorGuidelinesfor8.5x11-inchProceedingsManuscriptsAu…
-
国际会议论文格式范本
SpecialSeminarAssessingEmergentBusinessITUsingtheWebofSystemPerformanceBria…
-
20xx国际会议论文排版格式要求及样张
20xx管理科学与工程国际会议论文排版要求及格式样张LANHua1ZHAOShurong21SchoolofManagementH…
-
20xx国际会议论文排版格式要求及样张
20xx管理科学与工程国际会议论文排版要求及格式样张LANHua1ZHAOShurong21SchoolofManagementH…
-
国际会议论文格式(中文)
论文题目格式论文题目格式副标题如果有的话用副标题格式第一作者姓名第二作者姓名第一行部门名称第一行部门名称第二行组织名称缩写词第二行…
-
社会实践报告格式及范文
社会实践报告格式“社会实践报告”,它的体例、写法目前还无定论,可以参考“调查报告”的体例和写法。我个人认为,“社会实践报告”应该有…
-
会议论文模板
智能化电器与系统IntelligentElectricalApparatusandSystem西安交通大学作者1,作者2,??(X…
-
会议报告的格式
会议报告(一)会议报告标题。会议报告的标题有几种写法。综合性会议报告的标题一般采用“会议报告单位+会议报告时限+文种”,如《××大…
-
初中生社会实践报告格式和范文
初中生社会实践报告格式和范文作为学生练习写作用的“社会实践报告”,它的体例、写法目前还无定论,可以参考“调查报告”的体例和写法。我…
-
社会实践报告格式及范文
系部名称:专业:______-年级______班级:_________姓名:_____学号:____-实践单位:XXXX有限公司-…
-
第二届软实力国际会议开幕词及部分报告
“第二届(20xx)国际软实力学术研讨会”开幕式及大会报告专家演讲记录主持人:尊敬的各位领导,各位专家、学者、嘉宾,女士们、先生们…