中国汽车研究报告-英文版

China Aims to Reach the Level of Advanced Countries in 2010
by Promoting Reorganization of Companies
Under the New Automobile Industry Development Policy
Outline of China's new auto policy and Chinese business plans
by automakers worldwide
In June 1, 2004, the Chinese government officially announced and enforced the Automobile Industry Development Policy (new auto policy), which replaces the Industrial Policy for the Automobile Industry
(formulated in 1994) as a new signpost and policy for development of the automotive industry. The new auto policy does not change the current move toward the expansion of a partnership with foreign automakers. The new policy aims to make China join with major auto producing countries by the standards of developed countries in 2010 using a partnership with foreign capital as the driving force.
In line with the announcement of the new auto policy and Auto China 2004 (the 8th Beijing Motor Show), which opened on June 9th, the announcement of Chinese business plans was successively made by
automakers worldwide. The scale of Chinese business by major global automakers, including plans already revealed by each automaker, will amount to more than 7.3 million a year in several years.
→
■China, focusing on the balance of development, aims to take a place among major auto producing countries by 2010
China's vehicle production surpassed 3.2 million (including 1.15 million passenger cars), the production target for 2005 under the Tenth Five-Year Plan (2001-2005) for the Automotive Industry in China, which was announced in June 2001. The production volume amounted to 4.44 million in 2003 (including 2.19 million passenger cars).
Against the backdrop of rapid growth and under the Automobile Industry Development Policy (issued in June 2004), which serves as guidance for China's automobile policy, the following objective has been set: The fostering of China's automotive industry into a core industry of the national economy by 2010, the
forming of industry into an exporting industry including, as the subject of the policy, cooperative development with related industry and transportation infrastructure and the fostering of a sound automobile consumer market while preventing severe maladjustment from occurring due to a rapid growth.
■China's Output of Automobiles (10,000 units)
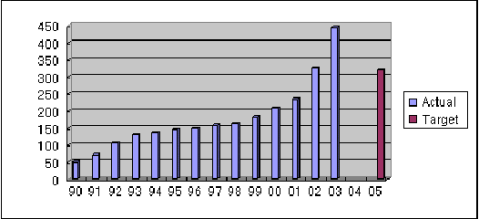
Note: The target figure for 2005 is 3.2 million under the Tenth Five-Year Plan
(2001-2005) for the Automotive Industry in China (which was compiled in
2001). Output went beyond 3.2 million to a total of 3.25 million in 2002.
Output amounted to 4.44 million in 2003. Output totaled 1.35 million in
1994, when Industrial Policy for the Automobile Industry was formulated
as China's first industrial policy.
■Objectives by 2010 under China's Automobile Industry Development Policy

■Fostering a large automobile corporate group with a market share of more than 15% and an independent management plan
As a principle of policy operation, integration is maintained of a basic role of resource allocation based on market mechanisms and macroeconomic adjustment by the government. One of the policies that bring the principle into shape is mandatory formulation of a development plan by a large-scale automobile corporate group, which mutually complements a medium- and long-term development plan that National Development & Reform Commission designs. Large-scale automobile groups themselves formulate their own
development plans based on the medium- and long-term plan and carry out the plan independently as it wins approval from National Development & Reform Commission.
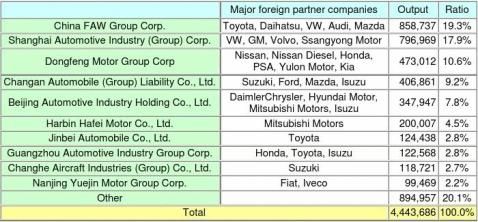
One of the requirements to become a large-scale corporate group is having a 15% share of the market in China; currently two groups, China FAW Group Corp. (FAW Group) and Shanghai Automotive Industry (Group) Corp. (SAIC Group) have a marketshare of 15%. The new auto policy supports automakers
developing into large-scale automobile corporate groups in the form of resource restructuring or encourages an automaker to form an alliance by complementing each company's advantage and sharing resources. Participation by foreign capital into such reorganization is also encouraged. The new auto policy supports
large auto corporate groups jointly in foreign auto groups consolidating/reorganizing automakers inside and outside of China, thus expanding their business range. In such a case, the restriction that limits the number of foreign shareholders to as many as two is not applied.
As for a recent actual example, GM and SAIC (1) will jointly purchase the former Daewoo Motor's
production facility in Shandong Province and (2) plan to bring Jinbei GM Automobile under the umbrella of Shanghai GM. A wide variety of similar potentials have opened for other companies that have expanded into China.
Note: As a measure to expand the range of independent management, a notification system was introduced into a portion of investment that was required to win approval. For instance, in the case of production of a new model which is required to receive authorization from multiple government agencies, companies, if they meet the requirements, are able to obtain approval through notification and the government's announcement in a shorter time than before.
Investments that are stipulated as subject to the notification system are as follows: (1) Investment in expansion of production capacity and increases in a variety of similar products by self-financing (2) Investment in motorcycles and motorcycle engines (3) Investment in vehicles, and parts for agricultural vehicles and motorcycles.
■To streamline the structure of the industry by promoting selection and
reorganization and by tightening conditions on the establishment of new
automakers
After 2000, when vehicle production in China surpassed 2 million, the number of companies that had
entered into the field of vehicle production by taking over slumping automakers and other means increased rapidly; an accumulated total of those companies has amounted to 24 since 2000. Including those new
entrants, more than one third of the 117 automakers were reported to be suffering from a deficit at the end of 2002.
Under the new auto policy, a system that leads corporate realignment is introduced to expand the scale of companies and profit, to increase concentration of industry, and to prevent small automakers where production and management capability is lower from proliferating.
Authorization of production to automakers had previously been referred to as permanent qualifications, but the new auto policy makes clear provisions for the shut down of automakers. In concrete terms, names of automakers that fail to sustain management are made public and those companies are prohibited from transferring qualification of production to non-automobile companies. In addition, companies whose names are made public are encouraged to shift into production of specialty vehicles and automotive parts, or to reorganize with other automakers.
Proliferation of automakers that are lacking in the technological base is restricted by other aspects. The new auto policy sets mandatory requirements for technologies including automobile safety, environmental protection, fuel saving, and anti-theft at the level that is compliant with mandatory requirements in the
international standard for vehicle technologies, thus establishing a certification system for automakers and products.
Companies and products that fail to meet conditions for certification are eliminated from notification; therefore, business activities of those companies are virtually terminated. Moreover, under the new auto policy, requirements for approval for production by companies include requirements for capability for design and development, production facility, stability of production and quality control capability, capability for sales and after-sales service.
Conditions for the establishment of a new automaker are tightened. Clearly indicated conditions include the attachment of R&D facilities with an investment of more than 500 million RMB, a total investment of more than 2 billion RMB, and self-financing of more than 800 million RMB. Companies that enter into production of passenger cars and heavy-duty trucks are also required to manufacture their engines.
In addition, the lowest annual production volume is clearly indicated for companies that manufacture passenger cars and heavy-duty trucks from scratch.
■Conditions of approval for a new investment in the new auto policy
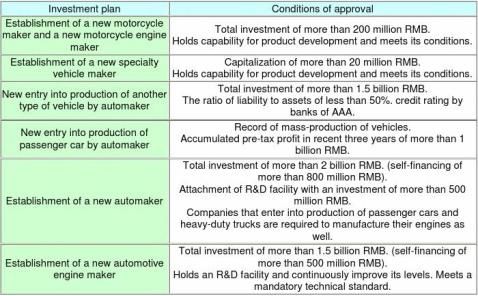
Note: The lowest annual production volume is clearly indicated as part of conditions regarding production of
passenger cars and heavy-duty trucks.
Four-cylinder engine passenger cars: 30,000. 6-cylinder engine passenger cars: 50,000. Heavy-duty trucks: 10,000.
■The new auto policy succeeds in restrictions on vehicle production by foreign capital while restrictions are not applied to investment in the establishment of an export base
The new auto policy succeeds in restrictions on foreign automakers concerning the number of Chinese joint venture partners to two companies in terms of passenger cars and commercial vehicles (two
companies in terms of motorcycle as well), respectively, and also to a restriction of ownership stake of 50% or less. The new policy makes it clear that foreign automakers that are tied through management rights are regarded as the same company.
Although standards for management rights are not made public, if we set a standard at one third of the total share, Mazda is regarded as being the same company as Ford and Nissan is regarded as the same as Renault. In the meantime, as it was reconfirmed that foreign automakers are able to establish a tie up with two Chinese companies, a joint venture with Guangzhou Automotive Industry by Toyota, which is currently forming an alliance with China FAW, is expected to win approval at an early date.
The new auto policy was also designed to respond to the agreement in 2002, when China joined the WTO. The limit on the ownership stake of 50% is a restriction accepted when the country joined WTO. There are no provisions including balance of foreign currency on investment by foreign companies, balance of import and export, requirements for nationalization (in an investment in automobile production, a local-content ratio of auto-parts of 40% or over was required before), and requirements for export.
Incidentally, though standards for approval for production of vehicles to be exported and of automotive engines in the export and machining area are not made clear, nor are restrictions on the number of joint venture partners and the ratio of ownership stake applied. There is a greater potential for business
development using China as an export base; like the example of Honda's specialized export plant, Honda Automobile (China) Co., Ltd., which began production in Guangzhou City (65% owned by Honda, 10% by Dongfeng Motor Corp., and 25% by Guangzhou Automotive Industry).
Note: Outline of the agreement in the field of automobiles in 2002, when China joined the WTO is as follows:
(1) Lowering of tariffs: Import tariffs on passenger cars will gradually be lowered to 25% by July 1,
2006. The tariffs on buses will also be reduced to 25% by 2005. Those on trucks will be lowered to 15, 20, 25% between 2004 and 2005 (the ratio is different by GVW and the type of fuel).
(2) Quantitative restriction on imports: It will be completely abolished in 2006, until such a time when the import quota will gradually be expanded.
(3) Compliance with TRIM agreement (Agreement on Trade-Related Investment Measures): Balance of foreign currency, balance of import and export, demand for nationalization, and demand for export will be eliminated from requirements of approval for investment plans from abroad.
(4) Liberalization in the field of distribution: Restrictions on entry by foreign capital into wholesale/retail sale of automobiles will completely be abolished in three years.
(5) Entry into auto financing by non-bank financial institutions: Restrictions will be eliminated at the same time as the entry into the WTO.
■A new restriction on the import of auto-parts is introduced, requesting automakers
to spin off their auto-parts divisions
Though the standard for a local-content ratio in terms of vehicle production was abolished, import controls were introduced to foster auto-parts industry and suppliers.
In such a case where automakers manufacture finished vehicles by importing core components, the
automakers need to report to customs house as well as to the Ministry of Commerce of the P. R. China and National Development & Reform Commission. It is stipulated that if the ratio of import of core parts goes beyond a certain standard the products is regarded as an import of finished vehicles and that import tariffs on finished vehicles will be applied to imports of automotive parts. In effect, this is a regulation which requires that more than several kinds of parts by assembled vehicle be manufactured in China. It can be said that it is a system that designates nationalization of parts which adopts a selection system.
Note: Incidentally, the import of used cars and used parts, and scrapping/assembling used cars and used parts imported as scrapped products are prohibited as before.
■Cases in which tariffs on finished vehicles are imposed on imported parts

drive axle assembly, non-drive axle assembly, main frame assembly, steering assembly and brake system.
2. Import of components of assembly sets and component module parts of assembly sets and
systems is also regarded as import of assembly parts.
Moreover, to foster the auto-parts industry and companies that have a specialized field and hold
capabilities for mass-production and supply of modules a specialized development program for parts will be made by classifying the respective auto-parts. Automakers are obliged to gradually foster their auto-parts manufacturing division in-house to independent specialized suppliers for external companies.
Suppliers are urged to make efforts to expand into the global market by aggressively participating in the product development process of their customers to enhance their capabilities for system development in the core parts field and their capabilities for development/production of advanced products in the general parts field. In addition, it is stipulated that the government will preferentially provide support to suppliers which can respond to OEM supply to multiple independent automakers and to global procurement by
automakers/suppliers worldwide.
It is also stipulated that that focus will be on improvement of quality level of products and market
competitiveness in the field of material and supporting products which Automobile Industry Development Policy requires. It is written clearly that among such fields major support will be provided to the supply of sheet steel for passenger cars and to the development of design capabilities for vehicle dies.
■Establishment of R&D facilities is supported and hybrid DE technologies are stipulated as priority issues
However, models introduced from overseas partners accounted for 88% of the increased passenger car production of 2.19 million in China in 2003. It is necessary to develop advanced practical technologies by holding intellectual property rights through independent development to achieve a target of exporting
products in large numbers as one of the major auto producing countries. Yet, the principle of encouraging aggressive development of partnership with overseas companies and of combining introduction of foreign capital and independent development of products will be firmly maintained.
Support for build up of creativity for products and fostering of independent development capability by establishing R&D facilities for products are written clearly in the new auto policy. With respect to
independent development, there are various adoptable forms; such as exclusive development, joint
development, and outsourced development. The target is to secure competitiveness in the global market and to deal with problems in terms of safety and environment/energy.
Acquisition of technology for auto body development, development of technology in the product
manufacturing process, and capability for development of chassis and engines are cited as priority issues for automakers. It is also stipulated that support will be offered for companies that carry out such challenges - a large automobile corporate group or an auto-parts manufacturer.
Development of new engines and vehicles with new fuel is a challenge that the new auto policy
encourages. Among such new challenges, technologies for a hybrid vehicle and diesel engines for
passenger cars are regarded as priority issues. Regarding fuel economy of automobiles, it is written clearly that the average fuel economy of new passenger cars will be improved by more than 15% by 2010 from 2003 and that disclosure of information about fuel economy will be established as a system.
Promotion of R&D for new material for automobiles such as lightweight material, recyclable material, eco-friendly material and support for the automotive electronic industry are stated clearly. The bottom line for the ratio of material recycling will be set on a timely basis.
■Output of passenger cars in China by location of partner companies
(10,000 units)
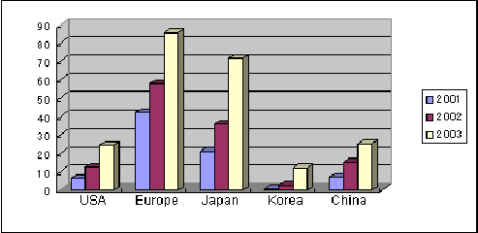
Note: Production models that are based on models of foreign automakers
are summed up by region - USA, Europe, Japan, and Korea. In 2003, the
number of models introduced from European automakers including VW
totaled 860,000, accounting for 40% while that of models introduced from
Japanese automakers has recently increased to 720,000. The number of
models from the USA totaled 240,000 while that from Korea numbered
120,000. The figures of China represent proprietary models by Chinese
automakers, which include models updated by each Chinese automaker,
which were manufactured through a tie-up with foreign automakers
before. In 2003, output of such models totaled 250,000, accounting for
12% of the total output of passenger cars of 2.19 million. Incidentally,
Beijing Jeep's Cherokee and Changan Ford Automobile's Mondeo are
included in USA.
■A brand system will be introduced. Establishment of a sound automobile
consumer market is set as the objective of the policy
Industrial Policy for the Automobile Industry, a former policy formulated in 1994 covered only the
automotive industry whereas the new auto policy also covers the service fields including sales, financing, and repair/maintenance as well as transportation infrastructure. Build-up of a sales network based on a brand system and support for formation of the used car market will be supported.
The brand system will be introduced to protect the legal rights of automobile consumers and to provide good service when the consumers purchase and use automobiles. Companies that sell automotive products which they themselves manufacture are required to establish sales and service networks for its own brand vehicles as early as possible.
Though no conditions are indicated so far, the combined sales of Chinese-made and imported vehicles are considered feasible. Major automakers will be able to sell full lineups through combined sales of those vehicles.
The brand system will be introduced in 2005. Automakers, motorcycle makers, engine and auto-parts suppliers have to register their own product brands and service brand and indicate the brands on all China-made vehicles and assembly parts starting in 2005. Dealers are also required to display the service brand of all manufacturers at their dealerships.
In addition, an exclusive sales system will be introduced for passenger cars made independently by each company in 2005 and all vehicles and parts in 2006. Providing products is not permitted for dealers who are not given authority for brand sales and who do not meet operating conditions.
For the establishment of the brand system, companies are required to aggressively develop products in which they hold intellectual property rights as well as to focus on protection of those rights and to make efforts at the enhancement of brand values. At the same time, it is stipulated that sales of products that violate intellectual property rights are prohibited.
The new auto policy demands that provisions by administrative bodies and local governments which violate the Chinese government provisions and the new auto policy be abolished at each level including new car registration, consumption, and disposition to protect consumer benefits. For example, local governments' restriction on issues of license plates conflict with the new auto policy and will be abolished.
■Chinese business plans by automakers worldwide add up to more than 7.3 million vehicles
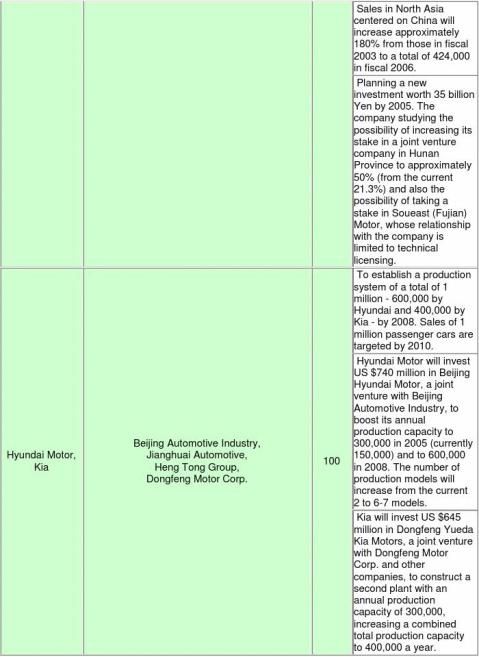
After the announcement of the new auto policy, Chinese business plans released by auto manufacturers worldwide are as follows: GM announced an investment plan in which it would invest a total of US $3 billion by 2007 to boost annual production capacity to 1.3 million. VW announced that it would build new engine plants with annual production capacity of 300,000 in Shanghai and Dalian within two to three years. Toyota announced establishment of exclusive dealers for its high-end brand model, the Lexus. Hyundai Motor released a plan to increase its annual production capacity to 600,000 with a total investment of US $740
million by 2007 (In May 2004, Kia, its subsidiary, released a plan to construct a new plant to boost the
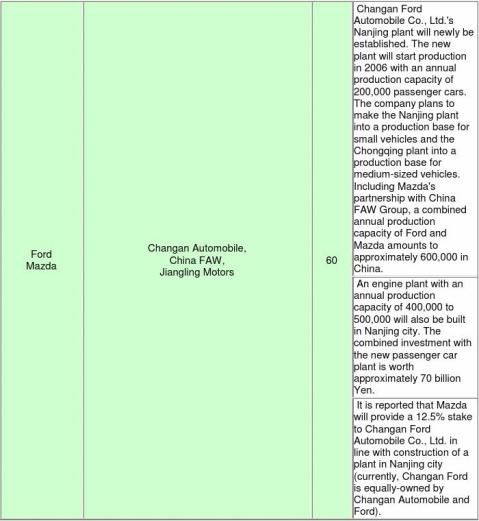
annual production capacity to 400,000). Ford and Mazda revealed progress of an investment plan in which a second passenger car plant and an engine plant of Changan Ford Automobile Co., Ltd. would be built in Nanjing. If the plan goes smoothly, the combined annual production capacity of Ford and Mazda in China will expand to 600,000.
In addition, the following companies announced their plan: VW plans to boost annual the production
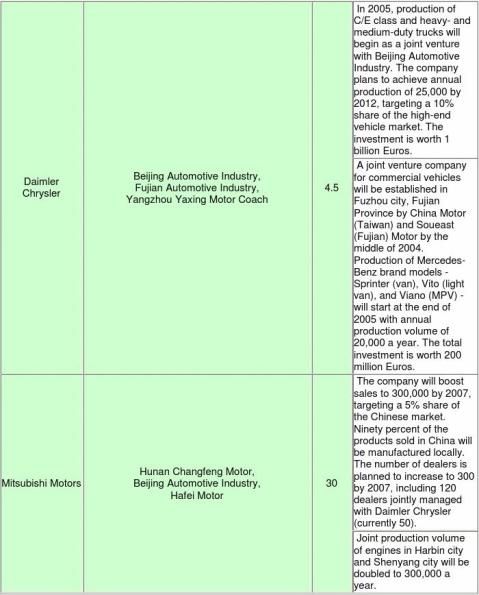
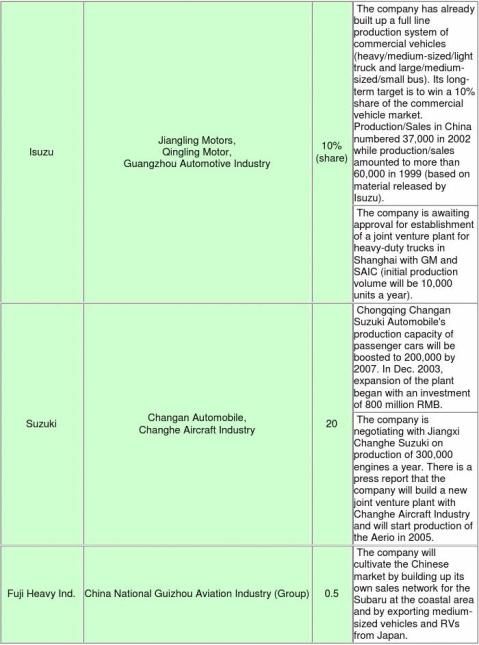
capacity to 1.62 million by 2008, Fiat plans to increase its capacity to 150,000 in 2006, and PSA to 300,000. DaimlerChrysler plans to manufacture 2.5 million C-class and E-class as well as 20,000 high-end light vans while BMW plans to boost its annual production capacity to 30,000. As for Japanese automakers, Toyota plans an annual production capacity of 600,000, Honda plans an annual production capacity of 500,000, and Suzuki 200,000. Nissan plans a sales volume of 620,000 in 2007 while Mitsubishi Motors plans 300,000. When we add such major automakers' plan, the scale of Chinese operations will amount to more than 7.3 million a year in a few years.
■Outline of production/sales plan in China by foreign major automakers
(Partner companies include companies whose relationship is limited to technical licensing. A simple
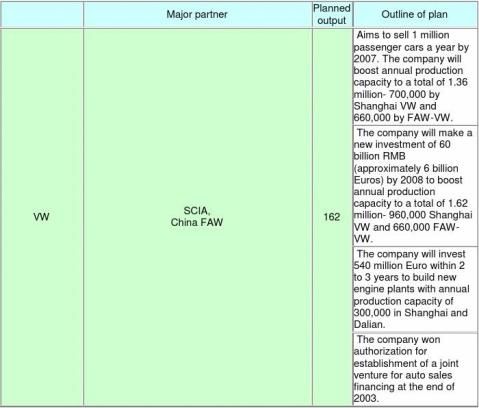
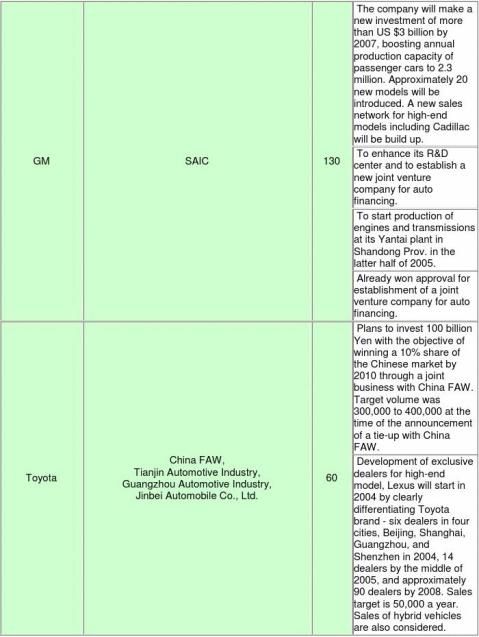
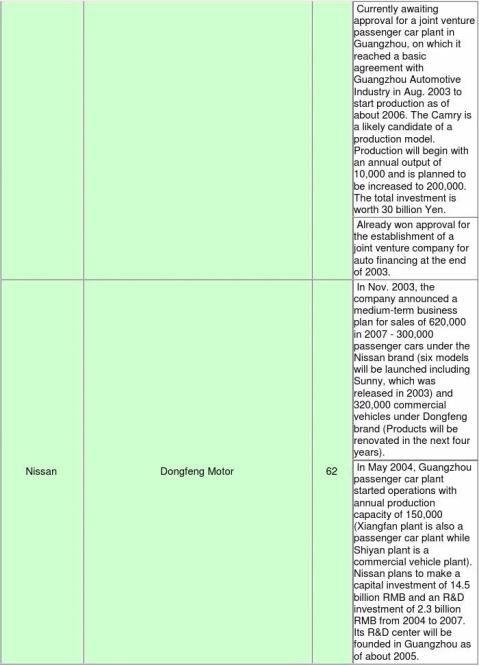
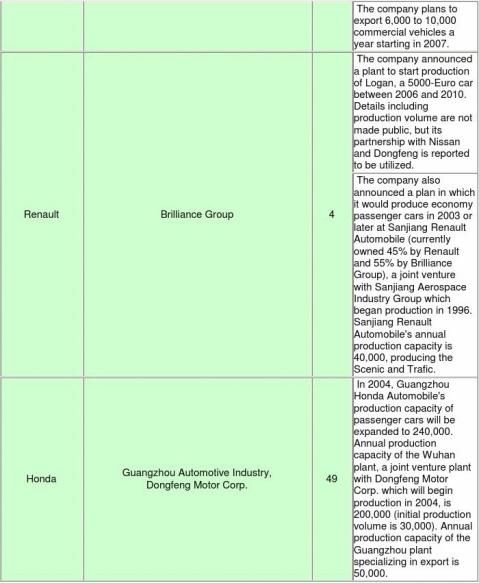
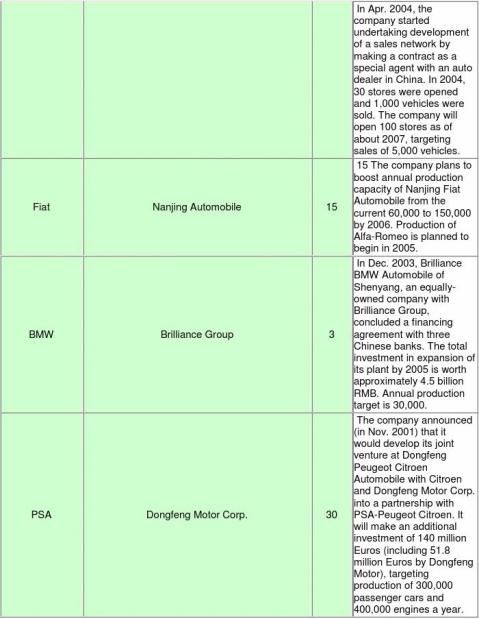

-
英语课题研究报告
TheApplicationOfchantToEnglishClassChant在小学英语教学中的魅力研究报告青神县实验小学英语组…
-
可行性研究报告(英文) - 副本
4000000tonslateritenickeloreProjectinIndonesiaFeasibilityStudyReport1Chapte…
-
可行性研究报告英文模板-实用版
TableofContentsContentsChapter1NameofProject...............................…
-
英语课题研究报告
创新多种活动方式激发英语学习兴趣课题研究报告仪阳中学英语课题组内容摘要英语学习兴趣是英语教学的生命一个成功的英语教师要在教学中有意…
-
外商投资企业可行性研究报告范本(英文)
FeasibleResearchReportTheprojectofcompanywhichisinvestedandheldbyCoLtdhasbe…
-
初中英语课例研究报告(正稿)
英语课例研究报告研究主题:初二英语听说课教学课目:Module7FeelingsandimpressionsUnit1教学年级:初…
-
英语课题研究报告
《语法课的实效性研究》课题研究报告报告课题组20xx、12、25《语法课的实效性研究》课题研究报告报告学校坚持以“为了每个学生的发…
-
可行性研究报告英文模板-实用版
TableofContentsContentsChapter1NameofProject...............................…
-
英语研究性学习结题报告范文
本次的实践活动我们班完成的十分好。我们在看英文电影的时候,不仅看到了精美的画面,同时也学到了不少。我认为看英文电影可以补充中国没有…
-
怎样做英文科技报告
1Introductions听众总是很挑剔应该说越来越挑剔他们会在很短的时间决定是否喜欢这个演讲者是否想听这个报告而这个决定是受到…
-
20xx年中国车市报告
20xx年中国车市的行业风向标20xx年的车市有点冷这对于已经过惯了好日子的汽车厂商和经销商来说是始料未及的据中国汽车工业协会发布…