合肥工业大学编译原理实验报告(完整代码版)

计算机与信息学院
专 业 班 级
学生姓名及学号
课程教学班号
任 课 教 师
实验指导教师
实验地点
2015 ~2016 学年第 二 学期
实验1 词法分析设计
一、 实验目的
通过本实验的编程实践,使学生了解词法分析的任务,掌握词法分析程序设
计的原理和构造方法,使学生对编译的基本概念、原理和方法有完整的和清楚的
理解,并能正确地、熟练地运用
二、 实验要求
1、编程时注意编程风格:空行的使用、注释的使用、缩进的使用等。
2、将标识符填写的相应符号表须提供给编译程序的以后各阶段使用。
3、根据测试数据进行测试。测试实例应包括以下三个部分:
全部合法的输入。
各种组合的非法输入。
由记号组成的句子。
4、词法分析程序设计要求输出形式:
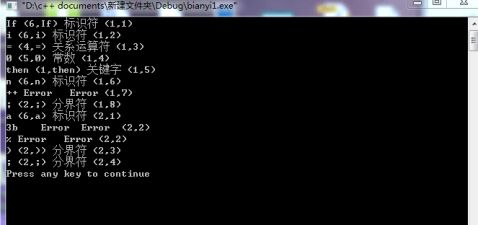
例:输入VC++语言的实例程序:
If i=0 then n++;
a﹤= 3b %);
输出形式为:
单词 二元序列 类 型 位置(行,列) (单词种别,单词属性)
for (1,for ) 关键字 (1,1) i ( 6,i ) 标识符 (1,2) = ( 4,= ) 关系运算符 (1,3) 12
0 ( 5,0 ) 常数 (1,4) then ( 1,then) 关键字 (1,5) n (6,n ) 标识符 (1,6) ++ Error Error (1,7) ; ( 2, ; ) 分界符 (1,8) a (6,a ) 标识符 (2,1) ﹤= (4,<= ) 关系运算符 (2,2) 3b Error Error (2,4) % Error Error (2,4) ) ( 2, ) ) 分界符 (2,5) ; ( 2, ; ) 分界符 (2,6)
三、 实验内容
用 VC++/VB/JAVA 语言实现对 C 语言子集的源程序进行词法分析。通过输
入源程序从左到右对字符串进行扫描和分解,依次输出各个单词的内部编码及单
词符号自身值;若遇到错误则显示“Error”,然后跳过错误部分继续显示 ;同时
进行标识符登记符号表的管理。
以下是实现词法分析设计的主要工作:
(1)从源程序文件中读入字符。
(2)统计行数和列数用于错误单词的定位。
(3)删除空格类字符,包括回车、制表符空格。
(4)按拼写单词,并用(内码,属性)二元式表示。(属性值——token的机内 表示)
(5)如果发现错误则报告出错 7
(6)根据需要是否填写标识符表供以后各阶段使用。
四、实验步骤
1、根据流程图编写出各个模块的源程序代码上机调试。
2、 编制好源程序后,设计若干用例对系统进行全面的上机测试,并通过所设计 的词法分析程序;直至能够得到完全满意的结果。
3、书写实验报告 ;实验报告正文的内容:
功能描述:该程序具有什么功能?
程序结构描述:函数调用格式、参数含义、返回值描述、函数功能;函数 之间的调用关系图。
详细的算法描述(程序总体执行流程图) 。
给出软件的测试方法和测试结果。
实验总结 (设计的特点、不足、收获与体会)。
五、实验截图
先创建salaryfile.txt文件
输入
If i=0 then n++;
a<= 3b %);
六、核心代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
const char* salaryfile="salaryfile.txt";
const int max=40;
string id[max]={"do","end","for","if","printf","scanf","then","while"};//关键字表
string
s[max]={",",";","(",")","[","]","+","-","*","/","<","<=","=",">",">=","<>"};//分界符表 算数运算符表 关系运算符表
string k[max];// 标识符
string ci[max];// 常数
int fjfpoint=5;//分界符表尾
int mathpoint=9;//算数运算符表尾
int cipointer=0;//常数表尾
int idpointer=0;//关键字表尾
int kpointer=0;//标识符表尾
int fjf;//0 不是分界符 1是
int rowy=1;//识别输入行位置
int rowx=1;//识别输入列位置
int outkey=0;//打印控制 0为数字后有字母 其他可以
void searcht(int i,string m)//根据已识别的首字母识别字符串
{
// cout<<"enter searcht!!"<<endl;
int x;
if(i==0)//首字符是字母识别关键字
{
// cout<<" a word!!"<<endl;
for(x=0;x<max;x++)
{
if(id[x]==m)
{
cout<<"(1,"<<id[x]<<")"<<" 关
("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
break;
}
}
if(x==max)//不是关键字再识别标识符
{
for(x=0;x<max;x++)
{
if(k[x]==m)
{ 键字
cout<<"(6,"<<m<<") "<<"标识符 ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
break;
}
}
if(x==max)//标识符表没有时插入标识符
{
cout<<"(6,"<<m<<") "<<"标识符 ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
k[kpointer]=m;
kpointer++;
}
}
}
if(i==1)//识别常数
{
// cout<<" a number!!"<<endl;
for(x=0;x<max;x++)
{
if(ci[x]==m)
{
cout<<"(5,"<<x<<")"<<endl;
break;
}
}
if(x==max)
{
cout<<"(5,"<<m<<") 常数 ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl; ci[cipointer]=m;
cipointer++;
}
}
if(i==2)//识别 分界符 算数运算符 关系运算符
{
// cout<<" a signal!!"<<endl;
for(x=0;x<max;x++)
{
if(s[x]==m)
break;
}
// x--;
if(x<6)
{
fjf=1;
}
if(x>5&&x<10)
{
if(outkey==1)
{
cout<<"(3,"<<s[x]<<") 算数运算("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
outkey=0;
}
fjf=0;
}
if(x>9&&x<max-1)
{
if(outkey==1)
{
cout<<"(4,"<<s[x]<<") 关系运算("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
outkey=0;
}
fjf=0;
}
if(x==max)
{
if(outkey==1)
{
cout<<"Error Error ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl; outkey=0;
}
fjf=0;
}
}
};
void wordlook(char t,string sn)//识别首字符,分类识别字符串 {
if(t>=48&&t<=57)
searcht(1,sn);
else
{ 符 符
if((t>64&&t<91)||(t>96&&t<123))
searcht(0,sn);
else searcht(2,sn);
}
};
void split(string s)//分割字符串
{
// cout<<s<<endl;
string now[max];
string sn;
int nowpointer=0;
int i=0;
int x;
int sign=2;//非法数字标志
int diannumber=0;//数中点的个数
for(x=0;x<s.length();x++)
{
if((s[x]>64&&s[x]<91)||(s[x]>96&&s[x]<123)||(s[x]>=48&&s[x]<=57)||(x>0&&s[x]==46&&sign==1))//判断数字后跟字母还是字母后有数字
{
if(i==0)
{
if(s[x]>=48&&s[x]<=57)
sign=1;
else sign=2;
}
else
{
if(sign==1)
{
if(s[x]>=48&&s[x]<=57||s[x]==46)
{
if(s[x]==46)
{
if(diannumber==0)
diannumber++;
else sign=0;
}
}
else sign=0;
}
}
i++;
if(x==(s.length()-1))
{
sn=s.substr(x-i+1,i);
if(i>0)
{
// cout<<sn<<" i="<<i<<endl;
cout<<sn<<" ";
if(sign==0)//数字后有字母的情况
cout<<" Error Error ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
else //字母开头的字符串
{
// cout<<" true"<<endl;
wordlook(sn[0],sn);
rowx++;
}
}
}
}
else
{
if(x>0&&(s[x-1]>64&&s[x-1]<91)||(s[x-1]>96&&s[x-1]<123)||(s[x-1]>=48&&s[x-1]<=57))//遇到分界符运算符 如果前面是数字或字母
{
sn=s.substr(x-i,i);
if(i>0)
{
// cout<<sn<<" i="<<i<<endl;
cout<<sn<<" ";
if(sign==0)
cout<<" Error Error ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl; else
{
// cout<<" true"<<endl;
wordlook(sn[0],sn);
rowx++;
}
}
i=0;
}
string ll=s.substr(x,1);//判断是运算符还是分界符
wordlook(s[x],ll);
if(fjf==0)//是运算符
{
i++;
if((s[x+1]>64&&s[x+1]<91)||(s[x+1]>96&&s[x+1]<123)||(s[x+1]>=48&&s[x+1]<=57))//如果后面是数字或字母
{
sn=s.substr(x-i+1,i);
// cout<<sn<<"运算符 i="<<i<<endl;
cout<<sn<<" ";
outkey=1;
wordlook(sn[0],sn);
rowx++;
i=0;
}
}
if(fjf==1)
{
if((s[x-1]>64&&s[x-1]<91)||(s[x-1]>96&&s[x-1]<123)||(s[x-1]>=48&&s[x-1]<=57))//如果前面是数字或字母
{
}
else if(i>0)
{
sn=s.substr(x-i,i);
// cout<<sn<<"运算符 i="<<i<<endl;
cout<<sn<<" ";
outkey=1;
wordlook(sn[0],sn);
rowx++;
i=0;
}
cout<<s[x]<<" (2,"<<s[x]<<") 分界符 ("<<rowy<<","<<rowx<<")"<<endl;
rowx++;
/* if(ll==";")
{
rowy++;
rowx=1;
}
*/
}
}
}
};
int main()
{
int x;
string instring;//读入一行
string sn;
/*
getline(cin,sn);// string带空格输入 cout<<sn<<endl;
char t=sn[0];
if(t>=48&&t<=57)
searcht(1,sn);
else
{
if((t>64&&t<91)||(t>96&&t<123)) searcht(0,sn);
else searcht(2,sn);
}
*/
ifstream inputfile;//in file stream inputfile.open(salaryfile);
// inputfile>>noskipws;
if(!inputfile)
{
cout<<"no file"<<endl; }
string pp;
while(!inputfile.eof())
{
getline(inputfile,pp);
istringstream istr(pp);
string ppword;
while(istr>>ppword)//按照空格分割字符串
{
split(ppword);
}
/*
int begin = 0;//去掉字符串的所有空格
begin = pp.find(" ",begin); //查找空格在str中第一次出现的位置 while(begin != -1) //表示字符串中存在空格
{
pp.replace(begin, 1, ""); // 用空串替换str中从begin开始的1个字符
begin = pp.find(" ",begin); //查找空格在替换后的str中第一次出现的位置
}
*/
// cout<<"good "<<pp<<endl;
// rowx++;
rowy++;//换行
rowx=1;
}
return 0;
}
七、实验总结
通过本次试验使我不仅对词法分析器有了更深的了解,而且提高了编程能力,希望在以后的学习中可以解决词法分析更多的问题。
实验2 LL(1)分析法
一、实验目的
通过完成预测分析法的语法分析程序,了解预测分析法和递归子程序法的区
别和联系。使学生了解语法分析的功能,掌握语法分析程序设计的原理和构造方
法,训练学生掌握开发应用程序的基本方法。有利于提高学生的专业素质,为培
养适应社会多方面需要的能力。
二、实验要求
1、编程时注意编程风格:空行的使用、注释的使用、缩进的使用等。
2、如果遇到错误的表达式,应输出错误提示信息。
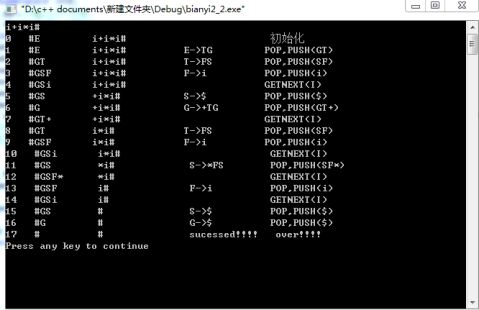
3、对下列文法,用 LL(1)分析法对任意输入的符号串进行分析:
(1)E->TG
(2)G->+TG|—TG
(3)G->ε
(4)T->FS
(5)S->*FS|/FS
(6)S->ε
(7)F->(E)
(8)

F->i
三、实验内容
根据某一文法编制调试 LL ( 1 )分析程序,以便对任意输入的符号串 进行分析。
构造预测分析表,并利用分析表和一个栈来实现对上述程序设计语言的分
析程序。
分析法的功能是利用 LL(1)控制程序根据显示栈栈顶内容、向前看符号
以及 LL(1)分析表,对输入符号串自上而下的分析过程。
四、实验步骤
1、根据流程图编写出各个模块的源程序代码上机调试。
2、 编制好源程序后,设计若干用例对系统进行全面的上机测试,并通过所设计 的 LL(1)分析程序;直至能够得到完全满意的结果。
3、书写实验报告 ;实验报告正文的内容:
写出 LL(1)分析法的思想及写出符合 LL(1)分析法的文法。
程序结构描述:函数调用格式、参数含义、返回值描述、函数功能;函数 之间的调用关系图。
详细的算法描述(程序执行流程图) 。
给出软件的测试方法和测试结果。
实验总结 (设计的特点、不足、收获与体会)。
五、实验截图
六、核心代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string pp;//输出字符串
string hh="\r\n";//换行
const int max=50;
int endfu[max];//终止符序号表
int endfupointer=8;
char endfureal[max]={'+','-','*','/','(','i',')','#'};
int unendfu[max];
int unendfupointer=5;
char unendfureal[max]={'E','G','T','S','F'};
string
makemath[max]={"E->TG","G->+TG","G->-TG","G->$","T->FS","S->*FS","S->/FS","S->$","F->(E)","F->i"};
//0 E->TG,1 G->+TG,2 G->-TG,3 G->$,4 T->FS,5 S->*FS,6 S->/FS,7 S->$,8 F->(E),9 F->i
//$代表空串
string behavior[max]={"初始化","POP"};
int smarttable[max][max];//分析表
int checkendfu(char fu)//查终结符序号 {
int x;
for(x=0;x<endfupointer;x++) {
if(endfureal[x]==fu)
{
break;
}
}
if(x<endfupointer)
return x;
else return -1;
};
int checkunendfu(char fu)//查非终结符序号 {
int x;
for(x=0;x<unendfupointer;x++) {
if(unendfureal[x]==fu)
break;
}
if(x<unendfupointer)
return x;
else return-1;
};
string checkmakemath(int x)//查产生式表 {
return makemath[x];
};
int checksmarttable(int x,int y)//查分析表 {
return smarttable[x][y];
};
class smartbox
{
public:
smartbox()
{
box[0]='#';
box[1]='E';
boxpointer=1;
}
void push(char fu)
{
boxpointer++;
box[boxpointer]=fu;
}
char pop()
{
char a=box[boxpointer];
if(a!='#')
{
// cout<<"pop: "<<boxpointer<<" "<<a<<endl; // stringstream oss;
/*
pp=pp+"pop: ";
char buffer[max];
sprintf(buffer,"%d",boxpointer);
string s=buffer;
pp=pp+" ";
pp=pp+s;
pp=pp+hh;
*/
boxpointer--;
return a;
}
}
void check()
{
if(checkendfu(box[boxpointer])!=-1)
{
char a;
// cout<<box[boxpointer]<<checkendfu(box[boxpointer])<<" //char buffer[max];
//sprintf(buffer
// pp=pp+box[boxpointer];
// pp=pp+checkendfu(box[boxpointer]);
// pp=pp+" ";
a=pop();
// cout<<"out "<<a<<endl;
}
}
char box[max]; ";
int boxpointer;
};
int main()
{
// TODO: Add extra validation here
// pp=pp+"步骤 分析栈 剩余输入串 所用产生式 动作"+hh; /*
string s1="sdsfs \r\nsdfsds";
string s3="aaaaaaaaaaaaa";
s3=s3+s1;
CString s2(s3.c_str());
// CString s2=CString(s1);
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT2,s2);//用SetDlgItemText(文本框ID,字符串),将文本框的内容设置为字符串的内容.
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT2,s2);
*/
// MessageBox(str);
string str;
cin>>str;
int x,y;
for(x=0;x<max;x++) //初始化分析表 99为错误代号
for(y=0;y<max;y++)
smarttable[x][y]=99;
smarttable[0][4]=0;
smarttable[0][5]=0;
smarttable[1][0]=1;
smarttable[1][1]=2;
smarttable[1][6]=3;
smarttable[1][7]=3;
smarttable[2][4]=4;
smarttable[2][5]=4;
smarttable[3][0]=7;
smarttable[3][1]=7;
smarttable[3][2]=5;
smarttable[3][3]=5;
smarttable[3][6]=7;
smarttable[3][7]=7;
smarttable[4][4]=8;
smarttable[4][5]=9;
smartbox mark;
char fu;
char enterfu;
int endfunumber;
int unendfunumber;
string readyin;
string enter;
// cin>>enter;
//enter="i+i*i#";
enter=str;
//enter="(i)#";
int count=0;
//步骤
char buffer1[max];
sprintf(buffer1,"%d",count);
string s1=buffer1;
pp=pp+s1+" ";
//分析栈
for(int qq1=0;qq1<=mark.boxpointer;qq1++) {
pp=pp+mark.box[qq1];
}
for(qq1=0;qq1<10-mark.boxpointer;qq1++) {
pp=pp+" ";
}
//剩余输入栈
string jiequ1=enter.substr(0,enter.length()); pp=pp+jiequ1;
for(int t1=0;t1<20;t1++)
{
pp=pp+" ";
}
pp=pp+" 初始化"+hh;
for(x=0;x<enter.length();)
{
//步骤
count++;
char buffer[max];
sprintf(buffer,"%d",count);
string s=buffer;
pp=pp+s+" ";
//分析栈
for(int qq=0;qq<=mark.boxpointer;qq++) {
pp=pp+mark.box[qq];
}
for(qq=0;qq<10-mark.boxpointer;qq++) {
pp=pp+" ";
}
//剩余输入栈
string jiequ=enter.substr(x,enter.length()-x); pp=pp+jiequ;
for(int t=0;t<x+10;t++)
{
pp=pp+" ";
}
enterfu=enter[x];
// cout<<"enterfu: "<<enterfu<<endl;
mark.check();
fu=mark.pop();
// cout<<"fu: "<<fu<<endl;
if(fu=='#')//&&enterfu=='#')
{
// cout<<"sucessed!!!! over!!!!"<<endl; pp=pp+"sucessed!!!! over!!!!"+hh; break;
// // } unendfunumber=checkunendfu(fu); endfunumber=checkendfu(enterfu); cout<<unendfunumber<<endl; cout<<endfunumber<<endl; if(smarttable[unendfunumber][endfunumber]==99) { pp=pp+"error!!"; break; } readyin=makemath[smarttable[unendfunumber][endfunumber]]; pp=pp+readyin; for(int ddd=0;ddd<14-readyin.length();ddd++) { pp=pp+" "; } pp=pp+"POP,PUSH("; for(y=readyin.length()-1;y>2;y--) { pp=pp+readyin[y]; } pp=pp+")"+hh; // cout<<"readyin: "<<readyin<<endl; int firsttime=0; for(y=readyin.length()-1;y>2;y--) { // cout<<readyin[y]<<" "; if(readyin[y]!='$') { mark.push(readyin[y]); if(firsttime==0) { if(checkendfu(readyin[y])!=-1) { // cout<<"now x: "<<x<<" "; //步骤 count++; char buffer[max];
sprintf(buffer,"%d",count);
string s=buffer;
pp=pp+s+" ";
//分析栈
for(int qq=0;qq<=mark.boxpointer;qq++)
{
pp=pp+mark.box[qq];
}
for(qq=0;qq<10-mark.boxpointer;qq++)
{
pp=pp+" ";
}
//剩余输入栈
string jiequ=enter.substr(x,enter.length()-x);
pp=pp+jiequ;
for(int t=0;t<x+10;t++)
{
pp=pp+" ";
}
pp=pp+" GETNEXT(I)"+hh;
x++;
// cout<<"next x: "<<x<<" "<<endl;
firsttime=1;
}
}
}
}
mark.check();
// cout<<endl;
// pp=pp+hh;
}
cout<<pp;
return 0;
//CDialog::OnOK();
}
七、实验总结
通过本次试验使我不仅对ll(1)分析法有了更深的了解,而且提高了编程能力,希望在以后的学习中可以解决自动构造follow集的问题。
实验3 LR(1)分析法
一、实验目的
构造 LR(1)分析程序,利用它进行语法分析,判断给出的符号串是否为该文 法识别的句子,了解 LR(K)分析方法是严格的从左向右扫描,和自底向上的
语法分析方法。
二、实验要求
1、编程时注意编程风格:空行的使用、注释的使用、缩进的使用等。
2、如果遇到错误的表达式,应输出错误提示信息。
3、程序输入/输出实例:
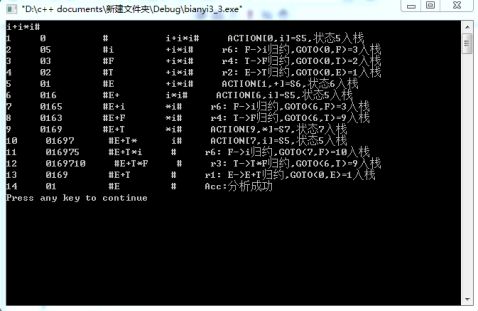
输入一以#结束的符号串(包括+*()i#):在此位置输入符号串 输出过程如下:
步骤 状态栈 符号栈 剩余输入串 动 作 1 0 # i+i*i# 移进
i+i*i 的 LR分析过程
步骤 状态栈 符号栈 输入串 动作说明
1 0 # i+i*i# ACTION[0,i]=S5,状态5入栈
2 05 #i +i*i# r6: F→i 归约,GOTO(0,F)=3 入栈
3 03 #F +i*i# r4: T→F归约,GOTO(0,T)=3 入栈
4 02 #T +i*i# r2: E→T归约,GOTO(0,E)=1 入栈
5 01 #E +i*i# ACTION[1,+]=S6,状态6入栈
6 016 #E+ i*i# ACTION[6,i]=S5,状态5入栈
7 0165 #E+i *i# r6: F→i 归约,GOTO(6,F)=3 入栈
8 0163 #E+F *i# r4: T→F归约,GOTO(6,T)=9 入栈
9 0169 #E+T *i# ACTION[9,*]=S7,状态7入栈
10 01697 #E+T* i# ACTION[7,i]=S5,状态5入栈
11 016975 #E+T*i # r6:F→i 归约,GOTO(7,F)=10 入栈
12 0169710 #E+T*F # r3: T→T*F归约,GOTO(6,T)=9 入栈 13 0169 #E+T # r1:E→E+T,GOTO(0,E)=1 入栈
14 01 #E # Acc:分析成功
三、实验内容
对下列文法,用 LR(1)分析法对任意输入的符号串进行分析:
(1)E-> E+T
(2)E->T
(3)T-> T*F
(4)T->F
(5)F-> (E)
(6)F-> i
四、实验步骤
1、根据流程图编写出各个模块的源程序代码上机调试。
2、编制好源程序后,设计若干用例对系统进行全面的上机测试,并通过所设计
的 LR(1)语法分析程序;直至能够得到完全满意的结果。
3、书写实验报告 ;实验报告正文的内容:
描述 LR(1)语法分析程序的设计思想。
程序结构描述:函数调用格式、参数含义、返回值描述、函数功能;函数 之间的调用关系图。
详细的算法描述(程序执行流程图) 。
给出软件的测试方法和测试结果。
五、实验截图
六、核心代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int count=1;
string pp;//输出字符串
string hh="\r\n";//换行
const int max=100;
char endfureal[max]={'i','+','*','(',')','#','E','T','F'};
int endfupointer=8;
string
creatword[max]={"E->E+T","E->T","T->T*F","T->F","F->(E)","F->i"};
//(0)E-> E+T(1)E->T (2)T-> T*F (3)T->F (4)F-> (E) (5)F-> i //注意rj时j应对应数组下标
int checkendfu(char fu)//查终结符序号
{
int x;
for(x=0;x<=endfupointer;x++)
{
if(endfureal[x]==fu)
{
break;
}
}
if(x<=endfupointer)
return x;
else return -1;
};
class actiongo//原子动作
{
public:actiongo()
{
// cout<<"eroor! wrong action or goto creat"<<endl; actype=4;
}
action(int i,int j)
{
actype=i;
number=j;
// cout<<i<<" "<<j<<endl;
}
int actype;//0=s 1=r 2=acc 3=goto表 4=wrong int number;
};
actiongo smarttable[max][max];
class stylebox//状态栈
{
public:
stylebox()
{
box[0]=0;
boxpointer=0;
}
void push(int style)
{
boxpointer++;
box[boxpointer]=style;
}
int pop()
{
int a=box[boxpointer];
boxpointer--;
// cout<<"pop now"<<endl;
return a;
}
int box[max];
int boxpointer;
};
class readybox//已归约栈
{
public:
readybox()
{
box[0]='#';
boxpointer=0;
}
void push(char fu)
{
boxpointer++;
box[boxpointer]=fu;
}
char pop()
{
char a=box[boxpointer];
boxpointer--;
return a;
}
char box[max];
int boxpointer;
};
int program(stylebox&style,readybox&ready,char fu,int icount,string ptr,int control)//返回是否需要移进信号
{
if(control==1)
{
//////////////////////////////
char ber[max];
sprintf(ber,"%d",count);
string st=ber;
pp=pp+st+" ";
count++;
////////////////////////////////////
//---------------------------------------------------------
pp=pp+" ";
for(int qq=0;qq<=style.boxpointer;qq++) {
char bss[max];
sprintf(bss,"%d",style.box[qq]); string st=bss;
pp=pp+st;
}
for(qq=0;qq<10-style.boxpointer;qq++) {
pp=pp+" ";
}
for( qq=0;qq<=ready.boxpointer;qq++) {
pp=pp+ready.box[qq];
}
for(qq=0;qq<10-ready.boxpointer;qq++) {
pp=pp+" ";
}
for(int dj=icount;dj<ptr.length();dj++) {
pp=pp+ptr[dj];
}
pp=pp+" ";
//---------------------------------------------------------
//////////////////////////////////////// }
int i=style.pop();//如果是s则状态还要入栈 // cout<<"现在状态"<<i;
int j=checkendfu(fu);
if(j==-1)
{
pp=pp+"error!!!";
return 4;//wrong!!!
}
// cout<<" 现在符号: "<<fu<<" "<<j<<endl; int checkstyle=smarttable[i][j].actype;//查表
if(checkstyle==4)
{
pp=pp+"error!!!";
return 4;//wrong!!!
}
if(checkstyle==0||checkstyle==3)
{
style.push(i);//如果是s则状态还要入栈
if(checkstyle==0)
{
//cout<<"ACTION["<<i<<","<<fu<<"]=S"<<smarttable[i][j].number<<",状态"<<smarttable[i][j].number<<"入栈"<<endl;
pp=pp+"ACTION[";
char buffer[max];
sprintf(buffer,"%d",i);
string s=buffer;
pp=pp+s;
pp=pp+",";
pp=pp+fu;
pp=pp+"]=S";
char buf[max];
sprintf(buf,"%d",smarttable[i][j].number);
s=buf;
pp=pp+s;
pp=pp+",状态";
pp=pp+s+"入栈"+hh;
}
if(checkstyle==3)
{
// cout<<i<<","<<endfureal[j]<<")="<<smarttable[i][j].number<<"入栈"<<endl;
char bf[max];
// //
sprintf(bf,"%d",i); string s=bf; pp=pp+s; pp=pp+","+endfureal[j]+")="; char bfff[max]; sprintf(bfff,"%d",smarttable[i][j].number); s=bfff; pp=pp+s+"入栈"+hh; } ready.push(fu); style.push(smarttable[i][j].number); cout<<style.box[style.boxpointer]<<endl; return 1;//移进 } if(checkstyle==1) { // string l=creatword[smarttable[i][j].number]; cout<<"r"<<smarttable[i][j].number+1<<": "<<l<<"归约,GOTO("; pp=pp+"r"; int dd=smarttable[i][j].number+1; char bfc[max]; sprintf(bfc,"%d",dd); string ss=bfc; pp=pp+ss+": "+l+"归约,GOTO("; // // char n;//pop用的 int x; cout<<l.length()<<endl; char sq=ready.pop(); for(x=0;x<l.length()-4;x++)//前面pop一次了 { n=style.pop(); n=ready.pop(); cout<<n<<endl; } cout<<l[0]<<endl; x=program(style,ready,l[0],icount,ptr,0);//识别非终结符
return 0;//归约
}
if(checkstyle==2)
{
return 2;//接受
}
}
int main()
{
// TODO: Add extra validation here string str;
cin>>str;
//0=i 1=+ 2=* 3=( 4=) 5=# 6=E 7=T 8=F smarttable[0][0].action(0,5); smarttable[0][3].action(0,4); smarttable[0][6].action(3,1); smarttable[0][7].action(3,2); smarttable[0][8].action(3,3); smarttable[1][1].action(0,6); smarttable[1][5].action(2,0); smarttable[2][1].action(1,1); smarttable[2][2].action(0,7); smarttable[2][4].action(1,1); smarttable[2][5].action(1,1); smarttable[3][1].action(1,3); smarttable[3][2].action(1,3); smarttable[3][4].action(1,3); smarttable[3][5].action(1,3); smarttable[4][0].action(0,5); smarttable[4][3].action(0,4); smarttable[4][6].action(3,8); smarttable[4][7].action(3,2); smarttable[4][8].action(3,3); smarttable[5][1].action(1,5); smarttable[5][2].action(1,5); smarttable[5][4].action(1,5); smarttable[5][5].action(1,5); smarttable[6][0].action(0,5); smarttable[6][3].action(0,4); smarttable[6][7].action(3,9); smarttable[6][8].action(3,3);
smarttable[7][0].action(0,5);
smarttable[7][3].action(0,4);
smarttable[7][8].action(3,10);
smarttable[8][1].action(0,6);
smarttable[8][4].action(0,11);
smarttable[9][1].action(1,0);
smarttable[9][2].action(0,7);
smarttable[9][4].action(1,0);
smarttable[9][5].action(1,0);
smarttable[10][1].action(1,2);
smarttable[10][2].action(1,2);
smarttable[10][4].action(1,2);
smarttable[10][5].action(1,2);
smarttable[11][1].action(1,4);
smarttable[11][2].action(1,4);
smarttable[11][4].action(1,4);
smarttable[11][5].action(1,4);
string enter=str;
int i;
int x;
stylebox st;
readybox ready;
for(i=0;i<enter.length();)
{
// cout<<"----------------enter: "<<enter[i]<<" x=program(st,ready,enter[i],i,enter,1); if(x==1)i++;
if(x==2)
{
// cout<<"Acc:分析成功"<<endl;
pp=pp+"Acc:分析成功"+hh;
break;
}
if(x==4)
break;
// cout<<endl;
// cout<<endl;
// pp=pp+hh; ----------------"<<endl;
}
cout<<pp;
// CDialog::OnOK();
}
七、实验总结
通过本次试验使我不仅对LR(1)分析法有了更深的了解,而且提高了编程能力,希望在以后的学习中可以解决LR(1)中确定化的问题。
-
大连理工大学实验报告模版
【大物实验】拉伸法测弹性模量http://hi.baidu.com/%CE%D2%B5%C4%D3%EE%D6%AE%D6%E6/…
-
RLC电流研究实验报告-大连理工大物实验
RLC串联电路特性的研究实验报告电阻、电容及电感是电路中的基本元件,由RC、RL、RLC构成的串联电路具有不同的特性,包括暂态特性…
-
大连理工大学 大物实验报告 温度传感技术
这个实验操作步骤比较简单,实验过程中主要就是等待,不难。老师是武震林,人特别好。报告为什么扣分,我也不太清楚,可能是数据点没用X表…
-
大连理工大学盘锦校区大学物理实验报告页
大连理工大学大学物理实验报告实验报告完成日期学号姓名班级实验准备时间第周周第节实验完成时间第周周第节实验名称大连理工大学大学物理实…
-
大工大物实验报告——低压气体直流击穿特性
低压气体直流击穿特性实验目的1研究低气压的实验和维持方法了解气压的测量原理2观测直流暗放电的脉冲现象研究电子碰撞引起雪崩电离的过程…
-
编译原理-语法分析实验报告
课程实验报告课程名称:编译原理(语法分析)专业班级:信息安全1001班学号:姓名:指导教师:报告日期:20XX/11/8计算机科学…
-
编译原理 语法分析 实验报告
编译原理实验报告编译原理实验报告1编译原理实验报告一实验内容设计编制并调式一个语法分析程序加深对语法分析原理的理解二实验目的及要求…
-
武汉理工大学编译原理实验报告
武汉理工大学学生实验报告书实验课程名称编译原理开课学院计算机科学与技术学院指导老师姓名饶文碧学生姓名学生专业班级软件20xx20x…
- 编译原理语法分析实验报告(含有源代码)
-
编译原理语法分析实验报告
目录一语法分析方法11判断为算符优先文法12求FirstVT集和LastVT集13根据FirstVT和LastVT集构造算符优先表…
-
江苏科技大学编译原理实验报告
实验一词法分析设计一实验目的通过本实验的编程实践使学生了解词法分析的任务掌握词法分析程序设计的原理和构造方法使学生对编译的基本概念…