中南大学算法实验报告



实验一 分治
—最近点对
一.问题
Problem
Have you ever played quoit in a playground? Quoit is a game in which flat rings are pitched at some toys, with all the toys encircled awarded.
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
Assume that all the toys are points on a plane. A point is encircled by the ring if the distance between the point and the center of the ring is strictly less than the radius of the ring. If two toys are placed at the same point, the radius of the ring is considered to be 0.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. For each case, the first line contains an integer N (2 <= N <= 100,000), the total number of toys in the field. Then N lines follow, each contains a pair of (x, y) which are the coordinates of a toy. The input is terminated by N = 0.
Output
For each test case, print in one line the radius of the ring required by the Cyberground manager, accurate up to 2 decimal places.
二.分析思路
题目是给n个点的坐标,求距离最近的一对点之间距离的一半。第一行是一个数n表示有n个点,接下来n行是n个点的x坐标和y坐标。
首先,假设点是n个,编号为1到n。找一个中间的编号mid,先求出1到mid点的最近距离设为d1,还有mid+1到n的最近距离设为d2。如果说最近点对中的两点都在1-mid集合中,或者mid+1到n集合中,则d就是最小距离了。但是还有可能的是最近点对中的两点分属这两个集合,若存在,则把这个最近点对的距离记录下来,去更新d。这样就得到最小的距离d了。
三.源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define N 1000010
struct point
{
double x;
double y;
}p1[N],p2[N];
double dis ( point a , point b )
{
return sqrt( pow (a.x-b.x,2) + pow ( a.y-b.y,2 ) );
}
double min ( double a , double b )
{
return a<b?a:b;
}
bool cpx ( point a , point b )
{
return a.x < b.x ;
}
bool cpy ( point a , point b )
{
return a.y < b.y ;
}
double mindis ( int l , int r )
{
if( l + 1 == r )
return dis ( p1[l] ,p1[r] );
if( l + 2 == r )
return min ( dis ( p1[l] , p1[l+1] ) , min ( dis ( p1[l+1] , p1[r] ) , dis ( p1[l] , p1[r] ) ) );
else
{
int mid , count=0 ;
double mini;
mid = ( l + r) /2 ;
mini = min ( mindis ( l , mid ) , mindis ( mid+1 , r ) );
for( int i = l ; i <= r ; i++ )
{
if ( fabs ( p1[i].x - p1[mid].x ) <= mini )
p2[count++]=p1[i];
}
sort ( p2 , p2+count , cpy );
for ( int i=0 ; i < count ; i++ )
{
for ( int j = i+1; j < count ;j++)
{
if ( p2[j].y-p2[i].y>=mini)
break;
else
if(dis (p2[j],p2[i])<mini)
mini=dis(p2[j],p2[i]);
}
}
return mini;
}
}
int main()
{
int n ;
double dia ;
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1&&n)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf",&p1[i].x,&p1[i].y);
sort ( p1 , p1 + n-1 , cpx );
dia = mindis ( 0 , n-1 );
printf("%.2f\n", dia / 2 );
}
return 0;
}
四.运行结果
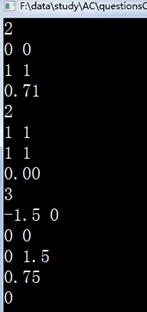
实验二 回溯
—堡垒问题
 一.问题
一.问题
Problem Description
Suppose that we have a square city with straight streets. A map of a city is a square board with n rows and n columns, each representing a street or a piece of wall.
A blockhouse is a small castle that has four openings through which to shoot. The four openings are facing North, East, South, and West, respectively. There will be one machine gun shooting through each opening.
Here we assume that a bullet is so powerful that it can run across any distance and destroy a blockhouse on its way. On the other hand, a wall is so strongly built that can stop the bullets.
The goal is to place as many blockhouses in a city as possible so that no two can destroy each other. A configuration of blockhouses is legal provided that no two blockhouses are on the same horizontal row or vertical column in a map unless there is at least one wall separating them. In this problem we will consider small square cities (at most 4x4) that contain walls through which bullets cannot run through.
Input
The input file contains one or more map descriptions, followed by a line containing the number 0 that signals the end of the file. Each map description begins with a line containing a positive integer n that is the size of the city; n will be at most 4. The next n lines each describe one row of the map, with a '.' indicating an open space and an uppercase 'X' indicating a wall. There are no spaces in the input file.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing the maximum number of blockhouses that can be placed in the city in a legal configuration.
二.分析思路
对于每个点,若能放置大炮则能选择放或者不放两种情况,若不能放置大炮则就只有一种情况。直接搜索,回溯的时候把点的状态恢复.
三.源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10
char map[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
int d[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
int N,cnt;
int ok(int x, int y)
{
if(map[x][y]!='.')
return 0;
int i,xx,yy;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
xx=x+d[i][0];
yy=y+d[i][1];
while(xx>=0 && xx<N && yy>=0 && yy<N && map[xx][yy]!='X')
{
if(map[xx][yy]=='o')
return 0;
xx+=d[i][0];
yy+=d[i][1];
}
}
return 1;
}
int search(int x, int y, int c)
{
int i,j;
for(j=y;j<N;j++)
if(ok(x,j))
{
map[x][j]='o';
search(x,j+1,c+1);
map[x][j]='.';
}
for(i=x+1;i<N;i++)
for(j=0;j<N;j++)
if(ok(i,j))
{
map[i][j]='o';
search(i,j+1,c+1);
map[i][j]='.';
}
if(c>cnt)
cnt=c;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i;
while(scanf("%d",&N)&&N)
{
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
scanf("%s",map[i]);
cnt=0;
search(0,0,0);
printf("%d\n",cnt);
}
return 0;
}
四.运行结果
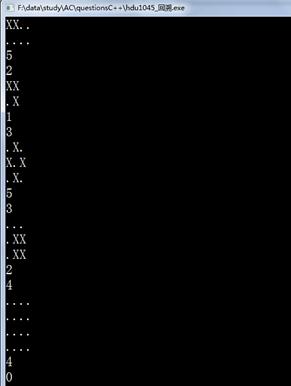
实验三 动态规划
—免费馅饼
一.问题
Problem Description
都说天上不会掉馅饼,但有一天gameboy正走在回家的小径上,忽然天上掉下大把大把的馅饼。说来gameboy的人品实在是太好了,这馅饼别处都不掉,就掉落在他身旁的10米范围内。馅饼如果掉在了地上当然就不能吃了,所以gameboy马上卸下身上的背包去接。但由于小径两侧都不能站人,所以他只能在小径上接。由于gameboy平时老呆在房间里玩游戏,虽然在游戏中是个身手敏捷的高手,但在现实中运动神经特别迟钝,每秒种只有在移动不超过一米的范围内接住坠落的馅饼。
为了使问题简化,假设在接下来的一段时间里,馅饼都掉落在0-10这11个位置。开始时gameboy站在5这个位置,因此在第一秒,他只能接到4,5,6这三个位置中其中一个位置上的馅饼。问gameboy最多可能接到多少个馅饼?(假设他的背包可以容纳无穷多个馅饼)
Input
输入数据有多组。每组数据的第一行为以正整数n(0<n<100000),表示有n个馅饼掉在这条小径上。在结下来的n行中,每行有两个整数x,T(0<T<100000),表示在第T秒有一个馅饼掉在x点上。同一秒钟在同一点上可能掉下多个馅饼。n=0时输入结束。
Output
每一组输入数据对应一行输出。输出一个整数m,表示gameboy最多可能接到m个馅饼。
二.分析思路
将所有的时间段和馅饼看成是一个矩阵,时间就是行数,掉馅饼的就是列数,则就是数字三角形问题,从最底层找一条路径,使得路径上的和最大。
状态转移方程为:dp[i][j]=max(dp[i+1][j-1],dp[i+1][j],dp[i+1][j-1])+pie[i][j]。pie[i][j]为时间i时在j位置掉的馅饼数目。
三.源代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX 100001
int pie[MAX][12];
int Max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
int Max(int a, int b, int c){
int max = (a>b) ? a:b;
return (max>c) ? max:c;
}
int MaxNumOfPie(int max_time){
int i, j, max;
for (i = max_time - 1; i >= 0; --i){
pie[i][0] = Max(pie[i+1][0], pie[i+1][1]) + pie[i][0];
for (j = 1; j < 10; ++j){
pie[i][j] = Max(pie[i+1][j-1], pie[i+1][j], pie[i+1][j+1]) + pie[i][j];
}
pie[i][10] = Max(pie[i+1][10], pie[i+1][9]) + pie[i][10];
}
return pie[0][5];
}
int main(){
int n,time,location;
int max_time;
while (scanf("%d",&n) != EOF && n != 0){
memset(pie, 0, sizeof(pie));
max_time = -1;
for (int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
scanf ("%d%d", &location, &time);
++pie[time][location];
if (max_time < time)
max_time = time;
}
printf ("%d\n", MaxNumOfPie(max_time));
}
return 0;
}
四.运行结果
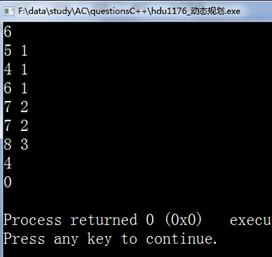
实验四贪心算法
/*
给定n种物品和一个背包。物品i的重量是Wi,其价值为Vi,背包的容量为C。
应如何选择装入背包的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?在选择物
品i装入背包时,可以选择物品i的一部分,而不一定要全部装入背包,1≤i≤n。
编程任务:
对于给定的n种物品和一个背包容量C,编程计算装入背包中最大的物品总价值。
Input
输入由多组测试数据组成。
每组测试数据输入的第1行中有2个正整数n和C。正整数n是物品个数;正
整数C是背包的容量。接下来的2行中,第一行有n个正整数,分别表示n个
物品的重量,它们之间用空格分隔;第二行有n个正整数,分别表示n个物
品的价值,它们之间用空格分隔。
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
double weight;
double value;
};
bool comp (Node a,Node b)
{
return a.value/a.weight > b.value/b.weight;
}
int main()
{
int n,i;
double c,w,v;
printf("请输入物品的种数和背包容量:");
while(scanf("%d%lf",&n,&c)!=EOF)
{
Node infor[2001];
printf("请输入物品的重量\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf",&infor[i].weight);
printf("请输入物品的价值\n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf",&infor[i].value);
sort(infor,infor+n,comp);
v = 0.0;
w = 0.0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(infor[i].weight + w <= c)
{
w += infor[i].weight;
v += infor[i].value;
}
else
{
v+=(c-w)/infor[i].weight * infor[i].value;
break;
}
}
printf("最优的解是:%.1lf\n",v);
}
return 0;
}
结果:
- 中南大学刚体转动惯量实验实验报告
- 中南大学--算法实验报告
-
中南大学自控实验报告
订装实验报告系姓名预定时间实验名称11典型环节的时域响应专业学号实验时间班授课老师实验台号彭涛订装2订装3订装4订装5订装6订装7…
-
中南大学数据库实验报告
中南大学数据库原理实验报告学生姓名学号专业班级指导教师盛津芳学院信息科学与工程学院完成时间20xx年1月实验一实验二一实验目的12…
-
中南大学数字信号处理实验报告
中南大学数字信号处理实验报告学生姓名学号指导教师学院专业班级完成时间2目录实验一实验二常见离散时间信号的产生和频谱分析3实验结果与…
- 中南大学刚体转动惯量实验实验报告
-
中南大学近代物理实验报告-光泵磁共振实验报告
近代物理实验报告实验名称光泵磁共振实验指导老师黄迪辉班级物理升华1301学号0801130117姓名黄佳清1实验目的1观察铷原子光…
- 中南大学x射线实验报告参考
- 电桥实验报告(中南大学)
-
中南大学近代物理实验报告-X射线衍射实验报告
近代物理实验实验报告实验名称所在学院物理与电子学院专业班级物理升华班学生姓名黄佳清学生学号指导教师黄迪辉1301080113011…
-
中南大学机电工程学院机械振动基实验报告
机械振动基实验报告机械0814中南大学1机械振动实验报告姓名学号0806081529成绩指导教师隆志力23机械振动实验报告姓名周菁…