《英语写作(二)》课程实训总结
外语教学综合实验中心实训课程学习总结
课程名称: 英语写作(二) 专业班级: 英语班
学生姓名: 学 号:
指导教师: 戴水姣 开课学期: 20##至2015 学年第2学期

第二篇:大二期末英语写作总结
? 1. Diction:
? Definition: Diction refers to the appropriate choice and use of the words when writing a
composition.
? 2. Types of words ? 2.1 Common words:
? Definition: common words form the core of English vocabulary, they are used in all kinds
of writing and speech. ?
? 2.2 Formal and technical words
Definition: words used by people of special professions of fields, on special occasions or for
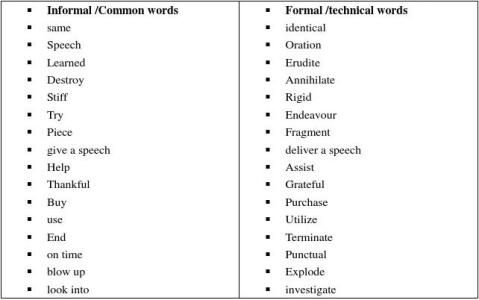
? Definition: used by people who are not well educated or by people of special groups, such
as region or age group. ? 2.3.1 Slang
? Definition: very informal words, phrases, etc commonly used in speech, esp. between
people from the same social group or who work together, not considered suitable for formal contexts and often not in use for long. E.g. Cop; buddy; guy; Baby-sitter. 2.3.2 Jargon
difficult for others to understand. E.g. 偶,9494,顶,东东,大虾,表,BF,GF,886,bridge(网桥: )broadband(宽带):DNS(域名系统):Download(下载):File Transfer Protocol (FTP) (文件传输协议):Gateway(网关):IP Address(IP地址):Upload(上载):Hypertext(超文本):Host(主机):Domain Name System(域名系统):
2.3.3 Dialect
? Definition: Dialect is a form of language used in a part of a country or by a class of
people. E.g. Goody mate; it’s my shout; how are you going?
2.3.4 Obsolete words
Definition: Obsolete words are the words that are out of date or no longer used. E.g. Thy; Thee; rouseabout; jumbucker
3. choice of words
?
? ?
? ?
?
?
?
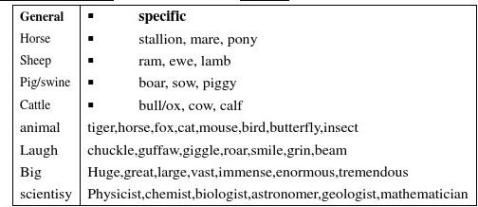
3.1 common or informal words 3.2 formal or nonstandard 3.3 Specific or concrete Specific or concrete words for details 3.4 general or abstract words 3.5 Idiomatic expressions and words
? are used in English writing; We should avoid combinations that are unidiomatic;
? Acquire knowledge; Get a job; Achieve success; Gain reputation; Attain one`s end;
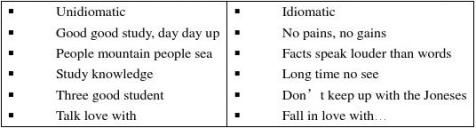

improve
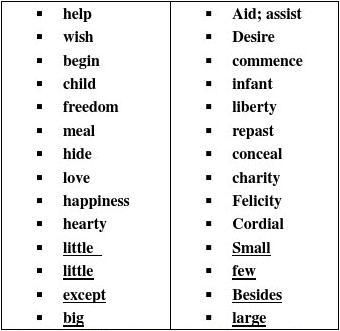
? 3.6Synonyms(page 3)
? Definition:are words that have the same or similar meanings .
1. Correct sentences
1,completeness in structure
3.agreement between the subject and the predicate verb
4.agreement between pronoun and antecedent
5.clear pronoun reference
6.ending sentences with full stops
7.joining clauses with conjunctions
8.a main clause in a complex sentences
9,proper use of comparisons
10.correct use of the tenses
3.1 Coordination
form of method that connects two sentences, which are of equal importance, by joining them with a coordinating conjunction is called coordination./When two or more things or ideas of equal importance are mentioned, coordinate clauses joined with a coordinating conjunction are used (and, but, or, nor, yet, so, and so, rather than, either…or…, neither…nor…, not only…but also… for,) this form or method is called coordination.
3.2 Subordination
? Subordination refers to the method by which a main and important idea is
stated, at the same time one or more less important ideas is or are expressed in subordinate clauses. / When an important idea in a main clause and one or more less important ideas in subordinate clauses are expressed, one part is more important than the other parts, those less important parts should be expressed with subordinate clause. This method is called subordination. (that who which where when…)
Relative pronouns and relative adverbs which can lead clauses:
? Subjective clause: that, what, how, when, where, which…, whether (but not if), how, who,
whose…, it is (was)…subjective clause;
? Objective clause: that (can be omitted), what, how, when, where, which…, whether (but
not if), how, who, whom, whose…;
? Adverbial clause (10 kinds):
a. Adverbial of time: when, what time, while, as, whenever, before, after, no sooner…
than…, hardly… when…, not…until/till…, as soon as, till/until, since;
b. Adverbial of place: where, wherever, everywhere
c. Adverbial of condition: if, unless, providing that, provided that, supposing, suppose that,
as long as, on condition that, in case; only if, once;
d. Adverbial of reason: because, since, as, for, seeing that, now that, considering that, in
that;
e. Adverbial of concession: though, although, even if, if even though, while, whereas,
whether…or (not)…, whatever, how…….ever,
f. Adverbial of manner: as, just as, as if, as though;
g. Adverbial of comparison: as…as…, the same as, such…as…, not so…as, than; h. Adverbial of purpose: so…that…, in order that…, lest, for fear that, in case;
i. Adverbial of result: so…that…, such… that…, so, that,
2.1 Requirements of effective sentences: Definition: one main idea and the idea is complete.
E.g. ×Born in Sichuan province, he later became a famous writer. ×I was born in 1970, so I went to xi’an.
Definition: clear and correct arrangement of the parts of a sentence. Easy to understand, its meaning cannot be mistaken, because the connection between its words conforms to grammar rules and usage. An incoherent sentence is often hard to understand and may be interpreted in different ways. (p. 62) ① Don’t separate words that are closely related unless it is necessary;
② Don’t use a pronoun with ambiguous reference;
③ Don’t use a dangling modifier or put a modifier far from the word it modifies; ④ Don’t make unnecessary or confusing shifts in person or number;
⑤ Don’t make unnecessary changes in the voice, tense or mood of verbs;
⑥ Don’t use different forms to express parallel ideas. ? express the idea clearly. (p29) e.g. × I like animal pets. × She was a girl and no less than 18 years old.
? ? 2.1.3.1 Use a pronoun instead of repeating a noun;
? 2.1.3.2 Use a word instead of a phrase with the same meaning, and use a phrase
instead of clause with the same meaning;
? 2.1.3.3 don’t repeat words or phrases, if possible, in a sentence or in one that
follows;
? 2.1.3.4 don’t use different words or phrases with similar meaning in the same
sentence;
? 2.1.3.5 Don’t repeat the same idea in different sentences except for emphasis.
:
? to make the idea more important or the evidence more convincing.
? 2.1.4.1 Placing: the beginning and the end. E.g. The Americans say that China is the
? 2.1.4.2 active voice
? 2.1.4.3 Climatic sequence: from least important to most important ? 2.1.4.4 Subordination
? 2.1.4.5 Repeating important words
? 2.1.4.6 Balanced sentences: A sentence consists of two parts which are of the same
importance, the same structure and the same length with contrasted or similar ideas. ? 2.1.4.7 Periodic sentences: is one that is not complete in structure until it reaches the
last word, which is the most important word of the sentence. ? 2.1.4.8 Negative-positive statements: Negative→positive ? 2.1.4.9 Rhetorical questions ? Definition: the way to express one’s idea with different sentence patterns and different
sentence structures, mixing short and long, simple and compound or complex, loose and periodic sentences in a passage. Try to use as more coordination and subordination, inverted sentence pattern, emphatic sentence pattern as possible. ? ? 2.1.5.1 Subordination
? 2.1.5.2 Participle, infinite, prepositional phrases and adverbs ? 2.1.5.3
? 2.1.5.4 Emphasized sentence pattern: seldom, never, rarely, often, well, many a time, in
vain, not only, not until, hardly, scarcely, no sooner… than…, only, so+adverb/adjective, no, So … that…, no sooner…than…. ? 2.1.5.5
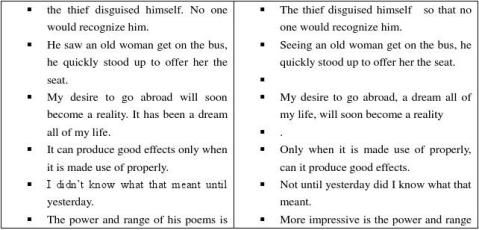

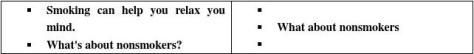
? 4.2 ways of developing a paragraph
? 4.2.1central idea → supporting details(evidence) →
good order of the supporting details ( good connection between the details)(close connection between the sentences)
4.2.3.1 development by time: the difference between chronological order and synchronological order
4.2.3.2 development by process
4.2.3.2.1 process: a step-by-step description of getting things ready; how to do things and what to do; the right sequence of the things to be done; well organized; chronological order used; in a clear way.
? 4.2.3.2.3 Words and Phrases Used in Writing Process Descriptions
? first(ly) then once
? next until as soon as
? lastly as at this point
? before while at the same time
? after when ……
4.2.3.3 development by space
? Development by space: description of what a place looks like and what are in the place.
E.g. a room, a house, a park, a university or college, a city, or, even a district or a country. ? Key factors in describing a place: (decided by the place where the describer stands )from
faraway to near; form outside sth to inside sth; form top to bottom; from the center to surroundings; from left to right…….
4.2.3.4 Development by Example
? Description: examples and illustrations can be used in a paragraph development, that is,
we can list examples to describe or explain a topic or subject.
? Topic in which examples should be used: Examples should be used in such topic as dry
and abstract theories.
? Features: convincing; forceful; vivid.
? Purpose: to make the readers understand the topic much more easily
4.2.3.5 Development by Comparison and Contrast
? Comparison: similarities and same points
? Contrast: differences and dissimilarities
4.2.3.6 Development by Cause and Effect
? Effect or results
? Causes or reasons
? Deduction (vs. induction)
? The relationship between effects or causes
? Examples
4.2.3.7 Development by Classification
? Classification: a way to divide a group into different kinds or categories.
? Principles of classification: the similar characteristics but the characteristics should be
unique. E.g. hobbies, occupations, personality traits, life style, languages, culture,
national identity…
6. Composing essays It should have something interesting and/or important , and if possible , something new , to say and that this something is expressed clearly accurately, and appropriately. And before we write ,we must decide on purpose and audience of our writing and try to adapt the style and language to suit our purpose and audience.
? 6.1 Criteria of a good composition
? 6.1.1 Idea complete new interesting or attractive
? 6.1.2 the process of illustration or explanation or deduction or induction
clear accurate appropriate
? 6.1.3 Diction accuracy appropriateness idiomatic
? 6.1.4 Sentences:
? Correct complete in structure and correct in grammar punctuation
capitalization a single complete idea
? Effective unity coherence conciseness emphasis
variety
? Paragraphs transition connection logic construction
information perspectives of instruction figurative
speech
? 6.1.5 complete essay’s structure beginning middle ending
2. Steps in Writing a Composition
2.1 Deciding on a topic or theme or title according to the hints and directions provided
Example 1 (directions):
Now deciding on the topic or giving the title of the essay according to the 3 directions or hints, choosing the best answer from a, b, c and d:
a. 近年来,大学生发现找工作很难
b. 为什么会出现这种现象?
c. 如何解决这个问题?
Now deciding on the topic or giving the title of the essay according to the 3 directions or hints, choosing the best answer from a, b, c and d:
a. College Students’ Job-Hunting
&b. Is it really difficult for college students to find a job?
c. Job hunting, the college students’ dilemma
d. Strategies for college students find a job
a.有人认为中国应该鼓励拥有私家车
b.也有人认为中国不应该鼓励拥有私家车
c.私家车在中国的前景
a. Private cars in China
b. Owning Private Cars
&c. Should private cars be encouraged in China?
d. Buy or not to buy, it’s a question
2.1.1 Working out a plan
? A. the decision on the title
? B. the main idea or central idea of the whole passage
? C. the structure of the composition
? D. the topic sentence of each paragraph
? E. the related and important details and facts
? F. the conclusion of the composition
? Example 1. Wealth or health, which is more important?
? Details (pick out the one or ones which is or are not closely related to the title):
1. health is the most important thing to a person
2. if a person is not healthy, it is impossible for him to do anything
3. people can get anything they want if they make no efforts to do so
4. health cannot be bought with money
5. health and wealth are contradictory
6. it is unlikely that one can keep healthy forever
7. work all day and all night instead of caring about their health
8. lead a regular life
9. diet and exercises
10. in order to be healthy, one should eat delicious food and expensive food with high protein 11 good mood and optimistic living attitude
12. health is the prerequisite to wealth
2.1.3 Deleting all the irrelevant or unimportant or unnecessary facts
2.1.4 deciding on our purpose
emphasize the relevant details; avoid the irrelevant and negative details which don’t have any help to your purpose
2.3 Revising the first draft
2.3.1 structure
2.3.2 content
2.3.3 supporting details and facts (enough? relevant? Logical? convincing?)
2.3.4 organization: introductory paragraph leads to the main point? Topic sentence of each paragraph are related to the theme? the arrangement of the supporting details and paragraphs?
2.3.5 sentences: correct and effective; wordy? Closely related to each other? Variety?
2.3.6 diction: appropriateness; Chinglish or created words? Unidiomatic?
? ? 3.1.1 aim:
3.1.2 function: to decide from what point to start, and in which direction to go.
3.1.3 ways to begin a composition:
3.1.3.1 relevant background material
3.1.3.2 the time and place of the event to be described
3.1.3.3 a quotation
3.1.3.4 a question
3.1.3.5 a statement
3.1.3.6 figures or statistics
3.1.3.7 a definition
3.2.1 aim: to explain and prove the central idea or theme with supporting details or facts.
3.2.2 function: to provide forceful and convincing details or facts to illustrate the theme.
3.2.3 requirements of the details and facts: clear and logical arrangement; informative, appropriate, natural, forceful and convincing details and facts.
?
?
? 3.3.1 aim: to give the readers a deep and final impression; to show the writer’s writing
purpose by repeating the central idea and drawing a conclusion.
? 3.3.2 principles of writing the end: thought-provoking; repeating the central idea but not
introduce a new idea.
4. Types of writing: whether the composition should be developed chronologically or by the arrangement of ideas or other ways is determined by types of writing because writing types or styles decide on the organization of the writing.
? 4.1.1 definition
? Description is to describe sth. or sb.
? 4.1.2 usage
? Description of persons; Description of objects; Description of scenes
? 4.1.3 principles: logical; from general points to specific points; from top to bottom; from
appearance to inside world; from faraway places to near places; from left to right…
? 4.1.4 topics of description: My Grandfather;…
? 4.2.1 definition
? Narration is to retell the story of an event or a series of events.
? 4.2.2 usage: stories; biographies; histories; news items.
? 4.2.3 principles: purposes and main idea; details; context; organization and point of view. ? 4.2.4 topics: My Childhood; The Last Day I Spent in England…..
? 4.3.1 definition
? Exposition means explaining ideas or opinions, some products or the process of making
sth. or doing sth. ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
4.3.2 usage
product specification; ideas; process of making sth. or doing sth.
4.3.3 principles: objectively; clearly;
4.3.4 ways of developing an exposition (p. 142.) 4.3.5 topics: Specification of Kadak Digital Camera; Male Chauvinism; How to Make Jiaozi; Chinglish…. ? 4.4.1 definition
? Argumentation means debating or trying to persuade or convince others to accept an idea. ? 4.4.2 usage: contradictory ideas; beliefs; opinions; political essays; e.g. speeches on
policies, editorials of newspapers, articles on political or theoretical questions….
? 4.4.3 principles: a clear and brief theme; sufficient and convincing and forceful
supporting details and facts; good logic; clear organization; and attitude
? There Is No Lei Feng in Real Life
? Saving Money Is a Stupid Habit
? A Friend in Need Is a Friend indeed
? No Pains, No Gains
? ? ? ?
-
商务英语写作总结报告
重庆科技学院关于商务英语写作实训报告学院:_法政与经贸学院__专业班级:_国贸11-3___学生姓名:____XXX___学号:2…
-
写作实训总结
外语教学综合实验中心实训课程学习总结课程名称英语写作一专业班级13级英语班学生姓名学号指导教师开课学期20xx至20xx学年1学期
-
《英语写作(二)》课程实训总结
外语教学综合实验中心实训课程学习总结课程名称英语写作二专业班级英语班学生姓名学号指导教师戴水姣开课学期20xx至20xx学年第2学…
-
英语写作实训任务书
湖南高速铁路职业技术学院应用英语专业英语写作实训任务书铁道运输系外语教研室一实训目的1本课程的实训目的是通过一周的集中训练按照本课…
-
外贸英语函电实训总结
为期四天的外贸英语函电实训总结已经结束,在这四天里,我们严格按照实训要求操作,完成了一系列有关于外贸英语函电写作的步骤,在实训过程…
-
商务英语写作总结报告
重庆科技学院关于商务英语写作实训报告学院:_法政与经贸学院__专业班级:_国贸11-3___学生姓名:____XXX___学号:2…
-
商务英语实训报告
为了培养我们的创新精神和实践能力,提高我们的综合素质。进行了为期一周的实训,实训中我们互相学习和进步着。在实训期间,我们既要对理论…
-
英语实训报告
外国语学院20xx—20xx学年第一学期英语视听实训报告姓名***学号*******专业英语指导教师***外国语学院20xx年x月…
-
英语写作实习报告
实习报告实习名称系别年级专业学生姓名指导老师写作课程实习外语系20xx级英语唐瑛、陈红邵阳学院20xx年x月x日一、实习时间:20…
-
英语专业写作实习报告
实习报告实习名称系别年级专业实习时间学生姓名指导老师英语写作课程实习外语系唐志钦杨柳邵阳学院20xx年x月x日一、实习时间:20x…
-
[秘书写作]办公室秘书个人工作总结(例文)
[秘书写作]办公室秘书个人工作总结(例文)一年来,在政府办公室领导的带动下,在全体成员的帮助下,我从文书岗位转到秘书岗位后,紧紧围…