小学英语知识点总结
小学英语知识点总结归纳
Contents
第一章 名词
1. 名词的数
2. 名词的格
第二章 代词
1. 人称代词
2. 物主代词
第三章 冠词 与 数词
1. 冠词
2. 数词
第四章 一般现在时态
第五章 现在进行时态
第六章 句型
1. 陈述句
2. 疑问句
3. 祈使句
4. There be 句型与have\ has
第七章 总结考试
第一章 名词 (Noun)
名词的概念
在生活中,我们会接触到各种各样的人和事物,用来表示这些人或事物名称的词就是名词。
一、名词的数
名词的数指名词的单数和复数形式。可数名词表示“一个”时用单数,“两个以上”时用复数;不可数名词表示量时,通常用“数词+单位+of+物质名词”的形式,如 a piece of bread (一片面包), 变为复数时,只须将单位名词变为复数, 如:two pieces of bread(两片面包)。
*名词复数的构成法则
1. 一般情况下在词尾加 s. 词尾读音
shop --- shops (商店) 在清辅音后读 [ s ]
bag --- bags (书包) 在浊辅音后读 [ z ]
window --- windows (窗户) 在元音后读 [ z ]
2. 以 s, x, sh, ch 结尾的单词在词尾加es。
class --- classes (班级) 词尾读音[ iz ]
box --- boxes (盒子)
match --- matches (比赛)
brush --- brushes (刷子)
3. 以“辅音字母 +y” 结尾的词, 变y为 i 加es.
story --- stories (故事) 词尾读音[ iz ]
4. 以“元音字母 +y” 结尾的词,在词尾直接加 s
key --- keys 词尾读音[ z ]
monkey --- monkeys
5.以 “o” 结尾的名词, 复数一般在词尾加“s”, 但个别加 “es”
tomato --- tomatoes (西红柿) 词尾读音[ z ]
potato --- potatoes (土豆)
zoo --- zoos (动物园)
photo --- photos (照片)
*(以 “o”结尾,复数加 “es”)口诀:
黑人(Negro)英雄(hero),左手拿着西红柿(tomato),右手拿着破土豆(potato),
头顶一个大芒果(mango)。
6. 以 f或 fe 结尾的词,多数变f或 fe 为 ves.
leaf --- leaves (树叶) 词尾读音[ vz ]
knife --- knives ( 小刀)
*(以f或fe结尾的单词,需把f或fe 变ves的单词)口诀:
妻子(wife)持刀(knife)去宰狼(wolf),小偷(thief)吓得发了慌,躲在架下(shelf)保己命,半(half)片树叶(leaf)遮目光。
*(以f或fe结尾的单词,直接加 “s”的单词)口诀:
长颈鹿(giraffe)站在屋檐(roof)下,左手拿着手绢(handkerchief),右手拿着高尔夫球(golf)。
例: roof --- roofs ( 屋顶)
7. 不规则名词复数的变化
man --- men (男人) tooth ---teeth (牙齿)
child --- children (儿童) mouse --- mice(老鼠)
foot --- feet (脚) woman --- women (女人)
8. 名词单复数形式一样
sheep --- sheep (绵羊) deer --- deer (鹿)
English --- English(英国人) Chinese --- Chinese (中国人)
*(不规则名词变复数)口诀:
男人,女人a变e;
鹅,足,牙齿oo变ee;
其实老鼠也好记ous变ic;
孩子加上ren,鱼鹿绵羊不用记。
二、名词所有格的构成法
1. 主要是在词尾加’ s 构成。如:
This is Tom’s desk. 这是汤姆的书桌。
That is Mike’s book. 那是迈克的书。
2. 如果原名词已经有复数词尾s ,则仅加一个’ . 如:
the teachers’ reading room 教师阅览室
the pupils’ pencil-boxes 学生们的文具盒
3. 如果原词是复数形式,但不是以s 结尾, 变为所有格形式需在后面加上’ s 。如:
the children’s palace 少年宫
men’s room 男厕所
*名词所有格口诀:
名词所有格,s前面加一撇’,复数s放在尾,后加一撇就完结,两人共有算一个,后面只加一个撇。
第二章 代词
一、人称代词
1.人称代词即表示“你、我、他、你们、我们、他们”等的词,它的人称、数和格的变化见下表:
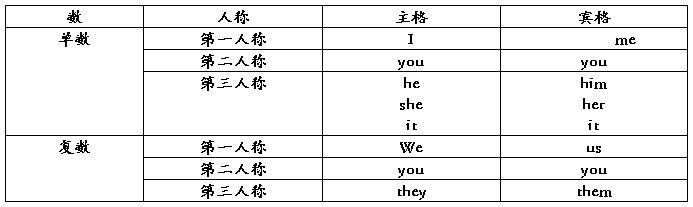
主格与宾格:
人称代词有主格和宾格两种形式。主格主要用来做句子的主语;宾格主要用作宾语。
人称代词主格用在句首作主语。She is sitting in a bus.她正坐在公共汽车上。
人称代词宾格在动词后作宾语。This pen is bad. I can’t write with it.这支钢笔不好,我没法用它写字。
2.人称代词的排列顺序
人称代词并列使用时,通常以下列顺序出现,请熟悉并记忆。
1) 单数代词:you and I; you and he ; he and I ; you, he and I
2) 复数代词:we and they ; we and you ; you and they; we, you and they
3) 第三人称单数代词:he and she
*人称代词排序口诀:人称代词并列观,注意顺序礼貌见;
单数人称二、三、一,复数人称一、二、三;
麻烦事情“我”站前,其他人称没意见;
两性并用为三单,男先女后是习惯。
二、物主代词
物主代词是表示所有关系的代词,分为形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。

名词性物主代词 = 形容词性物主代词 + 名词
例,Whose coat is this? 这是谁的上衣?
It’s hers. 是她的。 hers= her coat
*关于物主代词的口诀:
物主代词很重要,译成汉语都有“的”,后面必须加上物,否则就要犯错误,
my your his her its our their 不放过。
形容词性是基础,除了我的 “mine”外,其他词尾“s”性
形物代能力差,出门常把名词加;名物代能力强,常来独去又独往。
三、反身代词
反身代词也叫“自身代词”,表示“**自己”。

I can do it by myself. 我自己能做这件事。
*反身代词的构成规律记忆口诀:
反身代词有规律,第三人称宾格加,其余开头用物主,复数-ves替-f
四、指示代词
This (这个)------- these (这些) 指近处的事物
That (那个)------- these (那些) 指远处的事物
例,This is a book. 这是本书。 These are some books. 这些是书。
That is a car. 那是辆小汽车。 Those are some cars. 那些是小汽车。
第三章 数词和冠词
一、数词
表示数目和顺序的词叫数词。数词又分基数词和序数词,基数词表示数量,序数词表示顺序。
1. 最基本的基数词如下表所示:

*基数词的写法 :21~99的两位数,十位与个位之间用连字符“-”。
例:21 twenty - one 32 thirty - two 99 ninety – nine
百位数:个位数基数词形式加“hundred”,表示几百,在几十几与百位间加上and。
例:101 a hundred and one. 320 three hundred and twenty 648six hundred and forty-eight
2.序数词的构成
1)一般来说,是由相应的基数词加词尾th构成。例,
four+ th--- fourth six + th --- sixth
seven + th --- seventh ten + th --- tenth
2)下面这些基数词在变为序数词时,有特殊的变化。例,
one --- first two --- second three --- third five--- fifth
eight --- eighth nine --- ninth twelve --- twelfth
3)十位整数序数词的构成方法是将基数词的词y 变成i,然后在加eth.例,
twenty --- twentieth thirty --- thirtieth
forty --- fortieth ninety --- ninetieth
4) 两位或两位以上的基数词变为序数词时,仅将个位数变成序数词。例,
twenty –one ------ twenty- first
thirty-five ------thirty-fifth
a hundred and fifty-three ------- a hundred and fifty- third
*基数词变序数词的口诀:
基变序,有规律;词尾加上th(fourth, sixth)
一、二、三,单独记;结尾字母t, d, d;(first,second,third)
八去t,九去e,(eighth,ninth);ve要用f替;(fifth,twelfth)
整十基数变序数,ty将y变成i ; th 前面有个e;
要是遇到几十几,前用基来后用序。
二、冠词
冠词分不定冠词和定冠词两种。 a或an是不定冠词,the是定冠词。a用在辅音音素之前,如 a desk, a tree ; an 用在元音因素之前,如 an apple, an hour, an English book.
1. 不定冠词(a, an)指人或事物的某一种类,表示“一个”,但不强调数量。
She is a teacher. That’s an orange.
2. 定冠词 the,是特指某(些)人、某(些)物,或指说话人与听话人彼此知道的人或物,或者是在上文提到过的人和事。
This is a bus. The bus is big.
3. 不用冠词的情况:
1) 专有名词,物质名词,抽象名词前一般不用冠词。如,
Chinese, English, Jim等。
2) 名词前已经有this, that, my, your等词时,就不再用冠词了。如,
that mouse (那只老鼠)
3) 一些固定词组前不用定冠词。如,
at home 在家 go to school 去上学
*定冠词the的用法记忆口诀:
特指、重提和唯一,岛屿、海峡和海湾;
海洋、党派、最高级,沙漠、河流与群山;
方位、顺序和乐器,年代、团体与机关;
船名、建筑和组织,会议、条约与报刊;
姓氏复数、国全名,记住定冠the加在前。
*零冠词用法口诀:
月份、星期、节假洲,呼语、头衔职务前;
三餐、球类、惯用语,学科、棋类名词前。
第四章 形容词、副词
1)英语中大多数形容词、副词是可以分等级的,一般有三个等级:原级,比较级和最高级。形容词、副词的本来形式就是形容词的原级。如:John is a tall boy.
两者间进行比较用到形容词比较级。如:Jim is taller than John.
三者或者三者以上进行比较用形容词的最高级。Mike is the tallest of the three boys. (形容词最高级前面要加定冠词the)
2).形容词、副词比较级和最高级有规则变化和不规则变化
规则变化
① 单音节或双音节的形容词(或副词)比较级+er最高级+est
small-smaller-smallest等
② 以e结尾的词,比较级+r,最高级+st即可
nice-nicer-nicest
③ 以辅音字母+y结尾的,变y为i+er或est
easy-easier-easiest
④ 双写最后一个辅音字母+er或est
hot-hotter-hottest
⑥ 一些双音节及多音节形容词或副词前要加more和most,如:
difficult---more difficult---most difficult
不规则变化:
good/well-better-best,
bad-worse-worst
many/much-more-most
little-less-least
far-further -furthest(表示程度) far-farther-farthest(表示远近)
old-older-oldest(表新旧,作表语) old-elder-eldest(表兄弟姊妹之间的长幼,作定语)
3).比较级前的修饰词:a little, a lot, much, even; far; still
4)形容词、副词比较级的特殊用法
①形容词/副词比较级+than+ any other+单数名词(+介词短语)"表示"比同一范围的任何一个人/物都……",含义是"最……"。
例如,Mike gets to school earlier than any other student in his class.
= Mike gets to school earlier than any of the other students in his class. = Mike gets to school earlier than the other students in his class. = Mike gets to school earliest in his class.注意:Mike gets to school earlier than any student in Tom's class.
②"the+形容词比较级+of the two+……"表示"...是两者中较…的"。
如,Look at the two boys. My brother is the taller of the two.
③"比较级+and+比较级"表示"越来越……"。He is getting taller and taller.
④"the+比较级,the+比较级"表示"越…,越…,"。The more careful you are,the fewer mistakes you'll make
5).最高级常用句型结构
①"主语+be+ the+形容词最高级+单数名词+in/of短语"表示"……是……中最……的"。
如,Tom is the tallest in his class./of all the students.
②"主语+be+ one of the+形容词最高级+复数名词+in/of短语"表示"…是……中最……之一"。
如,Beijing is one of the largest cities in China.
③序数词+最高级
Hainan Island is the second largest island in China.
第五章 介词
介词(Preposition)
一、 概述:介词是英语中很活跃的词,一般置于名词之前。它常和名词或名词性词语构成介词短语。同一个介词常和不同的词语搭配形成固定搭配,表示不同意义。
1.at 用在具体的时刻和中午前面。
如:at 6:00, at seven thirty, at noon
2.on用在具体星期、日期前面。
如:on Monday, on September 1st
3.in 用在年、月、季节或早上、下午、晚上的前面。
如:in 2008, in February, in spring, in the morning
时间的排列顺序:由小到大
如:at two in the afternoon 在下午2点
on September 1st ,2006 2006年9月1日

二、 常用介词的基本用法
at ①表示时间: I go to school at seven every day 我每天早上7点去上学。
②表示在某一具体地点: He is standing at the bus stop 他站在公共汽车站。
③表示动作的方向、目标: Let me have a look at the picture 让我看看这幅图。
④用于某些固定搭配: at once 立刻、马上 at last 最后
at the same time 同时 at first 开始时 not at all 一点也不
about ①表示大约时间: I's about six o'clock now. 现在大约6点钟了。
②表示地点;在…周围
Everything about me is so beautiful 我周围的一切都那么美好。
③关于,对于: We are talking about the news. 我们正在谈论新闻。
after ①在……之后: After dinner I watch TV. 晚饭后我看电视。
②在……后面: He came into the room after me. 他在我后面进了房间。
behind ①在……之后: There is a bike behind the tree. 树后有一辆自行车
②比……晚,迟于: The train is behind time. 火车晚点了
by ①在……旁: He is sitting by the bed. 他正坐在床边。
②到……时候: We have learned three English songs by now.
到现在为止,我们已经学会了三首英文歌曲。
③以……方式: I go to school by bus. 我乘公共汽车去上学。
④用于某些固定搭配: one by one 一个接一个 by the way 顺便说一句
for ①为,给,替: I'll make a card for my teacher. 我要给老师做张卡片。
②由于: Thank you for helping me. 谢谢你帮我。
③表示给(某人)用的: There is letter for you. 这儿有你一封信。
in ①在……里面: The pencil is in the desk. 铅笔在课桌里。
②在一段时间里: We have four classes in the morning. 我们上午有四节课。
③用,以: What's this in English? 这用英语怎么说?
④在某一年份,季节,月份: in 2002, in spring, in January
⑤表示状态,服饰: Helen is in yellow. 海伦身穿黄色衣服。
⑥在……方面: He is weak in English. 他的英语不行。
⑦用于某些固定搭配: in front of 在……前面 in the end 最后
in time 及时
like ①像……样: He looks like his father. 他像他的父亲。
②这样,那样: Don't look at me like that. 别那样看着我。
③怎样: What's the weather like? 天气怎样。
near 靠近,在……附近: My bed is near the window. 我的床在窗户旁。
of ①的(表示所属关系): This is a photo of my family. 这是一张我家的照片。
②……的(用于所有格): He is a friend of mine. 他是我的一个朋友。
③表示数量(与连词连用):
One of us is from Beijing. 我们中有一个来自北京
④想到,谈到: I often think of them. 我常常想到他们。
⑤用于某些固定搭配: of course 当然 because of 因为,由于
on ①在……上面: There are some apple on the tree. 树上有些苹果。
②在(星期)天,在某天的上午(下午,晚上):On Sunday在星期天 on Sunday morning 在星期天的上午 on March 8 在3月8日
③用于某些固定搭配: on duty 值日 on time 准时
over ①在……正上方: There is a lamp over the table. 桌子上方有一盏灯。
②遍及,穿过: There is a bridge over the river. 有座桥横跨那条河。
③超过,不止: She is a little over 2. 她两岁多了。
to ①到,往,向: He walks to the window. 他走向窗户。
②表示时间、数量, 到……为止
Please count from ten to thirty. 请从10数到30.
③向,对,给: Happy New Year to you all. 大家新年好。
under What's under your desk? 你书桌底下是什么?
with ①和,写: Could you go home with me? 你能和我一起回家吗?
②表示伴随状态,带有: Who's that girl with glasses? 那位戴眼睛的女孩是谁?
between ,among ,around
①between:在两者之间 The school is between the bank and bookstore.
②among:在三者或者更多的之中
There are some American students among us .
③around:环绕,在…..的周围,在……的四周
They arrived at a zoo with high mountains all around it .
他们到达了四周有高山环绕的山\
in front of , There is a car in front of the house .房子前面有一辆小汽车。?
along ,across ,through
①along: 沿着 Go along Zhongshan Road and turn right at the second crossing .
沿着中山路走然后在第二个十这路口向右拐。
②across: 横过(平面物体)
③through: 贯通,通过The students walked through the gate
口诀1:
年月周前要用in, 日子前面却不行。 遇到几号要用on,上午下午又是in。
要说某日上下午, 用on换in才能行。午夜黄昏用at, at用在时分前,
口诀2:
in在……里,out在……外,在旁边的是beside,靠近的为by 。
on在……上, under在……下,above在上头, below在底下。口诀5:
口诀3:①早、午、晚要用in
in the morning 在早上 in the afternoon 在下午I n the evening 在晚上in the day 在白天
②黎明、午、夜、点与分用at
at dawn, at daybreak 在黎明时候 at noon 在中午 at night 在夜间
at six o'clock 在6点钟 at 7:30 在7点半
③年、月、年月、季节、周用in。
in 1986 在1986年 in April 在四月 in December 1986 1986年12月
in spring 在春季 in summer 在夏季 in autumn 在秋季 in winter 在冬季
小处at大处in
三、 介词的固定搭配
1)介词和名词的连用 2)动词和介词的连用
at arrive at/in 到达 at first 起初;开始 get off 下车
at last 最后 help sb. With sth. 帮组某人做某事 at school 在上课在上学 ask for 请求 at the moment 此刻 get up 起床 at home 在家;无拘束
laugh at 嘲笑 at present 现在 learn from 向……学习
at work 上班,在工作 look after 照顾 at the same time 同时
look for 寻找 think for 想到
on worry about 担心 on duty 值日 listen to 听
on holiday 度假 l ook at 看;注视 on time 准时 talk about 交谈;谈
on the left/right 在左/右边 wait for 等候;等
on the radio 在广播中 thank for 为……而感谢
on foot 步行 on sale 出售;降价出售 on TV 在电视上播放
be afraid of 害怕 on the phone 在电话中 be careful with 小心;关心
on the way 在路上 be interested in 对……感兴趣 be good at 善于
in be proud of 感到自豪 in all 总体 be crazy about 酷爱
in class 在课堂上 be late for 干某事迟到 in English 用英语
in short 总之 in a hurry 匆忙地 by+交通工具
in the end 最后 by bus/train/plane/air/ship/bike/sea/land…
in bed 躺在床上 lots of/a lot of 许多,大量 in danger 在危险中
at most 至多in fact 事实上 at least 至少 in time 及时地
at once 立刻;马上 in a minute 立刻 in order to 为了
第六章 一般现在时态
一、一般现在时的定义
一般现在时是表示现在经常反复发生的动作,存在的状态或习惯性的动作的时态。
二、一般现在时的结构
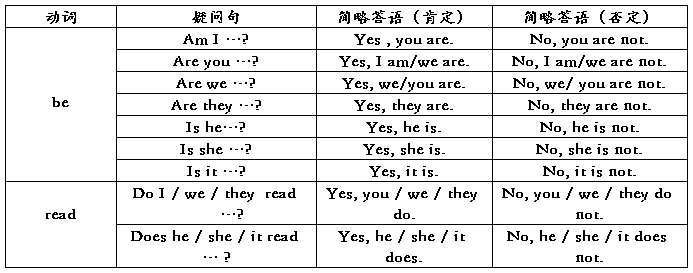
一般现在时用行为动词的原形,但第三人称单数作主语时,动词的词尾要加-s 或- es。现在以连系动词be 和行为动词read为例,对一般现在时的肯定句、否定句、疑问句及其简略答语的构成以表格形式加以说明:

连系动词be 的各种形式常与代词或not缩写成一个词。助动词do,does 一般只有与not 缩写。联系动词be缩写形式如下
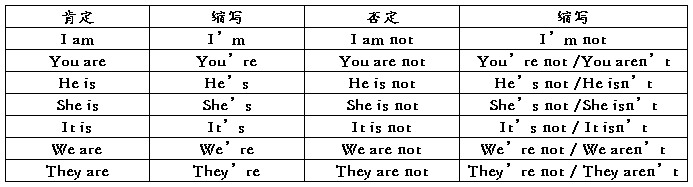
动词do not 的缩写形式为don’t,does not 的缩写形式为doesn’t。
二、 动词加-s 或-es (动词第三人称单数)
当主语是第三人称单数时,谓语动词需加-s 或-es
1. 一般在词尾加 –s
例:work—works leave --- leaves swim --- swims
2. 以字母s,x,ch,sh 或o结尾的词加-es
例:pass--- passes fix ---fixes teach --- teaches do--- does
3. 以辅音字母加y结尾的词,先变y为i再加-es
例:study --- studies carry --- carries fly --- flies cry --- cries
三、 一般现在时的用法
1. 表示经常或习惯性的动作。常与often(经常), always(总是), sometimes(有时), every day(每天), on Sundays/Mondays 等表示频度的时间状语连用。
一般现在时的时间状语有:today, often, sometimes, always, usually, every day ( week, month, year,…) , this year, once a week ( month, year,…) 一周(月,年)一次
例句:I get up at 6 o’clock every day.
He often goes to school by bike.
2. 表示客观事实,普遍真理。
例句:Two and two are four.二加二等于四。
The earth moves around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。
第七章 现在进行时态
一、 现在进行时的定义
现在进行时是表示在现在某一时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作的时态。
二、 现在进行时的构成
现在进行时由“系动词(am,is , are) + 现在分词(动词加-ing形式)”
构成。现在以动词work为例,对现在进行时的肯定句、否定句、疑问句及简略答语列表说明:

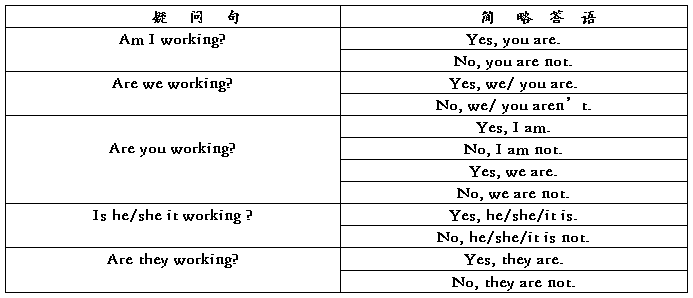
三、 现在分词的构成
1. 一般在动词原形末尾加-ing。
stay --- staying do --- doing listen --- listening
2. 以不发音的字母e 结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing。
make --- making ride --- riding give --- giving
3. 以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节词,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ing。
put --- putting sit --- sitting run --- running
4. 以ie 为重读音节结尾的单词,先去掉e,把i 变为y,再加 –ing。
lie --- lying die --- dying
四、 现在进行时的用法
1. 表示现在或说话时正在进行的动作,常和下列时间状语连用:now, at this moment, at present, these days (years), this term … 有时也与look , listen 等连用。
例句:Look, what are the monkeys eating?
看,那些猴子在吃什么?
2. 表示当前一直或反复在进行的动作或难以终止的动作。
例句:They are running and jumping all the time.
他们一直在跑啊跳啊。
第八章 一般将来时
一般将来时
一. 意义:
表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或重复发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。如:tomorrow , soon , next Monday , next year , next weekend , this afternoon , this evening ……
二. 构成及变化
一般将来时常用的两种结构
be going to+动词原形 : 表示打算、准备做的事或即将发生或肯定要发生的事。
shall/will+动词原形 : 表示将要发生的动作或情况,没有太多的计划性, 还用来表示意愿
1. be going to +动词原形
肯定句 主语+ be(am /,is,/ are) going to +动词原形+其它成份
My sister is going to learn English next year. 我姐姐准备明年学英语。
2. 否定句
主语+be(am / is / are)not going to +动词原形 +其它成份
I am not going to(go to)the cinema tonight. 我今天晚上不打算去看电影。
3. 一般疑问句
Be (am / is / are)+主语+going to+动词原型+其它成份…?
Is your father going to play basketball with you ?No , he isn’t.
你父亲打算和你去打篮球吗?不。
4. 特殊疑问句 特殊疑问词(Wh-)+一般疑问句 ?
Where are you going to spend Spring Fesital.? 春节你打算在哪过?
5. 注意: be going to 结构后面习惯上不跟 go , come 等表位移的动词,
一般用该动词的进行时形式表示。如:
He’s going to New York next week.下周他要去纽约.
2. will /shall +动词原形
(在书面语中,主语是第一人称时,常用shall ,在口语中,所有人称都可以用will)
1. 肯定句 主语+will/shall+动词原形+其它成份
I (shall) write to him next week. 下周我将给他写信。
2. 否定句 主语 + will /shall+ not + 动词原形 +其它成份
They won’t watch TV this evening.今天晚上他们不看电视。
3. 一般疑问句 will/shall+主语 +动词原形+其它成份
Will you stay at home with us tomorrow ? 明天你和我们呆在家里好吗?
4. 特殊疑问句
特殊疑问词(Wh-) +一般疑问句
When will your father be back? 你爸爸什么时候回来?
附 :
Shall I /we …常用来征求对方意见,而问对方是否愿意,或者表示客气的邀请,常用Will you…?他们的回答比较灵活。
1.Shall we go to the park?
肯定Sure , let’s go.
否定 No , let’s go to the cinema.
2. Will you please come to my birthday party next week?
肯定Yes, I will. / Sure.
否定 I’m sorry. I’m afraid I can’t.
第九章 一般过去时
一般过去时态
过去时的时间状语:last(year, week, day, month, weekend)
Yesterday( morning, afternoon, evening).
I saw him yesterday in the street.
也可表示过去某个时间经常发生的动作,可与always, often 连用
Liming always went to school on foot last year.
(a) be 动词的过去式:
I/He/she/it was(not)…. You/we/they were….
一般疑问句was, were 放在句首。
(b) 动词过去式:
肯定句: I watched cartoons.
She visited the zoo.
一般疑问句:
Did you read book last night? Yes, I did. No, I didn't.
Did she clean the desk just now? Yes, she did. No, she didn't.
否定句:
They didn't go the park yesterday.
He didn't make model ships last week.
(3) 动词过去式的变化:
规则动词的变化:
A: 大部分动词直接在单词后面 +ed 比如: planted,watered,climbed。
B: 以e结尾的动词直接 +d, 比如: liked。
C: 以辅音字母 +y结尾的,直接去y +ied 比如: study-studied
D:以元音+辅音结尾的动词,必须双写最后一个辅音 比如: stop –stopped
不规则动词的变化:
is/am-was, are-were,
do-did,
have/has-had, make-made, fly-flew/u:/
eat-ate, take-took, run-ran, sing-sang, drink-drank 等等
第十章 句型
一、陈述句
定义:凡是说明一件事情,提出一个看法,或是表达一种心情的句子都是陈述句。大多数的句子都是陈述句,陈述句可以用肯定式和否定式。
肯定句变否定句
肯定句变否定句就是加not no 或表示否定的词
英语的句子重要取决于动词而动词又有时态的变化因此在不同的时态的句子中的位置不同。
二、疑问句
疑问句是用来提出问题的,疑问句又包括:一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、反义疑问句和选择疑问句。
一、一般疑问句:
1. 一般疑问句又可以叫做yes/no句型,需要用yes或no来回答。
2. 一般疑问句的基本结构:

3. 变一般疑问句的方法:(一调,二变,三问号)
当句中有Be(am, is, are)动词的时候:
1、将Be(am, is, are)提前,放于句首(大写);
2、将人称变换,第一人称变第二人称
(I→you, we→you, my→your, our→your),第二人称变第一人称(you→I, you→we, your→my, your→our),第三人称不变(一变二,二变一,三不变)
3、在句尾加问号“?”
4、回答: 肯定: Yes , 主语+be. 否定: No, 主语+be+not.
当句中没有Be动词, 有情态动词的时候:
1、提前can, may,放于句首(大写);
2、将人称变换,第一人称变第二人称(I→you,we→you,my→your,our→your),第二人称变第一人称(you→I,you→we,your→my,your→our),第三人称不变(一变二,二变一,三不变)
3、在句尾加问号“?”
4、回答: 肯定: Yes , 主语+can. 否定: No, 主语+can+not.
句中没有Be动词和情态动词can的时候:
1、在句首加Do或Does,当主语是第三人称单数的时候用Does,其它都用Do
2、将人称变换,第一人称变第二人称(I→you,we→you,my→your,our→your),第二人称变第一人称(you→I,you→we,your→my,your→our),第三人称不变(一变二,二变一,三不变)
3、在句尾加问号“?”
4、回答:肯定: Yes , 主语+do/does 否定: No, 主语+do/does+not.
其它在句中要变换的词有some→any, am→are
英语里只有三种人称.
第一人称:我,我们,(I),we 【me, us】 (我),我们
第二人称:你,你们,(you),you 【you ,you】 ( 你),你们
第三人称:他,她,它(he, she, it,) 【him, her ,it 】他们they【them】还有一些人名也算第三人称,比如Kangkang, Jane.像your father(你的爸爸)这也算第三人称. 第三人称单数指他(he) 她(she) 它(it)或者单个人名,第三人称复数是都用they 他们/她们/它们
此外,不可数名词在用法上也同于第三人称单数。
二、特殊疑问句:
以疑问代词what, who(whom), whose, which 或疑问副词when, where, how, why 放在句首提问的句子叫做特殊疑问句,答语只要针对问句中的疑问代词或疑问副词来回答,不用yes 或no。
1.疑问词 + 一般疑问句 (疑问词作宾语、表语、状语或定语)。
What do you want? 你要什么?
When do you have English class? 你们什么时候有英语课?
Whose coat is this? 这是谁的大衣?
How did he know it? 他是怎么知道它的?
Why did you say this? 你为什么要这么说?
Which is your umbrella? 哪个是你的雨伞?
Where were these buses made? 这些巴士是哪儿制造的?
2.疑问代词作主语或作主语的定语时,词序与陈述句相同:疑问代词 (+名词)+谓语。
Who teaches your brother Japanese? 谁教你弟弟日语?
What is in the box on the table? 桌上那个盒子里装的是什么?
Whose handwriting is the best in your class? 你们班里谁的书法最好?
*疑问代词:who: 主语、宾语、表语、用来提问表示“人”的各种成分。
whose: 用来提问“谁的”。
which: 用来提问“哪一个/位”。
what: 提问表示“干什么”等意思
*疑问副词:when: 提问在何时。
where: 提问在何地
why: 提问表示原因的短语或句子
how: 提问表示程度或方式的副词或短语
*由疑问词how 构成的短语引导的问句
how old (表示年龄)多大了, how long(表示时间或物体的长短)有多长 , how many + 复数名词 表示多少 , how much + 不可数名词 表示多少 , how far (表示距离)多远
三、祈使句
一、祈使句:用来表示下达命令、提出要求、建议和劝告的句子。说话的对象通常是第二人称you ,习惯上常省略。祈使句的肯定句谓语动词用原形,否定句一般用don’t, never开始。
1.肯定祈使句
句型 1 :动词 let + 第一、三人称宾格代词 + V.
例句:Let’s go to school.
让我们去上学吧。
Let me try.
让我试一试。
Let him come upstairs.
让他上楼吧。
句型 2:动词 + 其他部分
例句:Please open the door .
请开门。
Turn to page two.
请将书翻到第二页。
Listen to me.
请听我讲。
Stop talking.
别说话。
二、否定祈使句 (一般在句首加 Don’t.)
1.Climb the tree ,please. 请爬树。 (肯定句)
Don’t climb the tree! 不要爬树。 (否定句)
2.Open the door. 打开门。 (肯定句)
Don’t open the door. 不要开门。 (否定句)
三、陈述句变祈使句
1.You can’t make faces in class. 你不能在课堂上做鬼脸。
Don’t make faces in class. 不要在课堂上做鬼脸。
2.You can’t read in bed. 你不要在床上看书。
Don’t read in bed. 不要在床上看书。
四、there be与have\has 句型
一. “There be” 句型
“There be +某 (些)人或物 + 某地(或某时)”是指“某地(时)存在某人 (或某物)”。谓语be 必须在数上和主语保持一致。如果主语中既有单数又有复数,be 的形式变化与它最近的主语相一致。
(一)结构
There be (is \ are ) +某……
1) There is + ①可数名词单数
②不可数名词
2)There are + 可数名词复数
(二)用法
1. 肯定句: There is \ are + _________.
2. 否定句:There is \ are + not ____________
3. 一般疑问句:Is\Are + there … ? Yes, there is \are. No, there is \ are not.
(三)There be 句型中的 be 与离它最近的名词有关。
例, There is an apple and two pears on the table.
There are two pears and an apple on the table.
二、have \has 句型
是指某人有某物 (表示所有、拥有关系)
I \ We \You \ They \ 人名(复数)\事物(复数)+ have …
He \She\ It \ 人名(单数)\ 事物(单数) + has …
-
小学英语知识点总结大全
绝大多数形容词有三种形式,原级,比较级和最高级,以表示形容词说明的性质在程度上的不同。形容词的原级:形容词的原级形式就是词典中出现…
-
小学英语知识点总结
一、小学英语形容词性物主代词1、形容词性物主代词8个:Myyourhisheritsouryourtheir我的你的他的她的它的我…
-
小学英语知识点总结
一、小学英语形容词性物主代词1、形容词性物主代词8个:Myyourhisheritsouryourtheir我的你的他的她的它的我…
-
小学英语知识点总结大全
小学英语知识点汇总目录第一章词汇分类集中复习.........................阿.................…
-
小学英语知识点总结
南海区小学五年级上学期期末考试英语模拟试题广东省佛山市大沥镇东秀小学冯文慧听力部分(50%)一、听录音,选择听到的单词的字母编号,…
-
小学英语毕业复习知识点总结1
小学英语毕业复习知识点总结第一部分;基础知识1.字母:26个字母的大小写2.语音:元音的发音五个元音字母:AEIOU()12个单元…
-
小学英语知识点总结
一、小学英语形容词性物主代词1、形容词性物主代词8个:Myyourhisheritsouryourtheir我的你的他的她的它的我…
-
上海牛津小学英语语法知识总结
上海牛津小学英语语法知识总结一般现在时1、定义:表示经常发生或习惯性的动作、状态。句中通常有usually,often,every…
-
小学英语知识点总结
小学英语知识点总结名词所有格的形式和用法。(1)名词所有格一般是词尾加′s构成,如:theboy’sbag;ourteacher’…
-
牛津小学英语复习总结
牛津小学英语(3B)基本知识点复习纲要一、必须会默写的单词1.动物:dog狗cat猫2.水果:apple苹果banana香蕉3.衣…
-
小学英语介词总结
介词(Preposition)一、概述介词是英语中很活跃的词,一般置于名词之前。它常和名词或名词性词语构成介词短语。同一个介词常和…