20xx高考英语语法知识点归纳总结:主谓一致
二、名词和主谓一致
I. 名词的种类
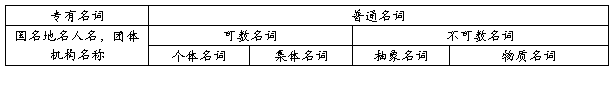
特别注意名词类别的相互转换
个体名词与抽象名词的相互转换

物质名词与个体名词的相互转换

抽象名词与个体名词的转换

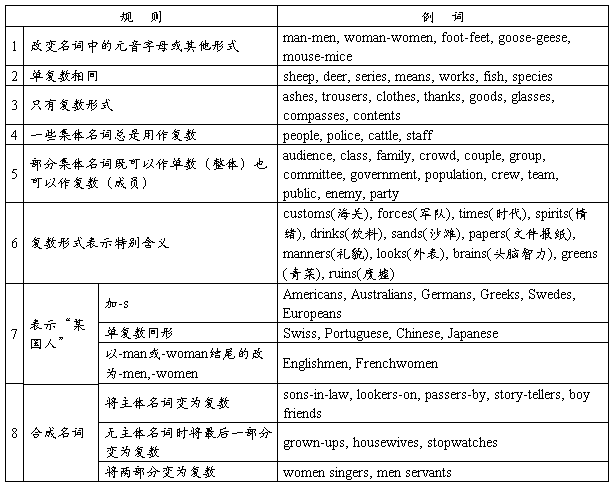
II. 名词的数
规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s或-es(参看有关语法书)。英语里有些名词的复数形式是不规则的,请看下表
III. 主谓一致

第二篇:20xx高考英语语法知识点归纳总结:定语从句
十二、定语从句
I. 定语从句起了形容词的作用,在句中修饰一个名词或代词。被修饰的词叫做先行词,引导定语从句的词叫关系词,他的作用一是放在先行词与定语从句中间起了连接作用,二是在从句中担当一个成分,并与先行词保持数的一致。
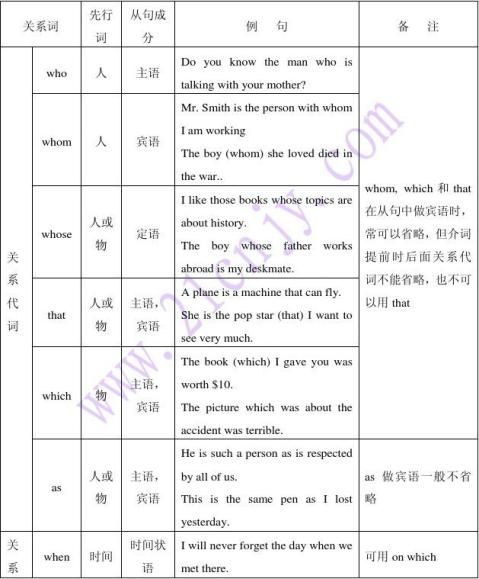

一、关系代词和关系副词的功能
关系代词和关系副词功能有三个:1)用来引导定语从句,在先行词和定语从句之间起纽带作用,使二者联系起来。2)关系代词和关系副词可作定语从句的一个成分。关系代词可作主语、宾语、定语;关系副词可作状语。3)关系代词和关系副词在从句中代替在他前面的先行词。
1、作主语
关系代词在定语从句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词的人称和数应与先行词一致。
All that is needed is a supply of oil.(引导词that在句中作主语)
The foreigner who visited our class yesterday is from Canada. (引导词who在句中作主语)
2、作宾语
在定语从句里作宾语的关系代词在口语中常被省去
The noodles (that) I cooked were delicious. (引导词 The fish (which) we bought was not fresh. (引导词
3、作定语
关系代词whose
注意:关系代词whose词放在主语和从句之间。
4、作状语
关系副词where, when和状语。
who,whom,whose,which,that和as。它们的用法如下:
1、who,whom的用法
who和whom指人,who在定语从句中作主语;whom在定语从句中作宾语,在限制性定语从句中可省略。在口语中可用who代替whom。
In the beginning, people who bought the tomato often got angry. (作主语) The person (whom) you should write to is Mr. Ball. (whom作宾语能省略)
His mother, whom he loved dearly, died in 1818. (whom引导非限制性定语从句,作宾语但不能省略)
2、whose的用法
whose 指人或物,在定语从句中作定语,指物时常可用of which取代。 I have a friend whose father is a mayor.
We lived in a house whose window faces south.
3、which 的用法
which指物,在定语从句中作主语和宾语,作宾语时,在限制性定语从句中可省略。
They needed a plant which didn't need as much water as rice.(作主语,不能省略) It is used to record the tickets (which) passengers buy. (作宾语,可以省略)
He came late, which we all know. (作宾语,在非限制性定语从句中不省略)
4、that 的用法
that 多指物,有时也指人,在定语从句中作主语或宾语,指物时其用法和which大致相同,但也有区别。
All the people that come from the country work much harder. (指人,在从句中作主语,不能省略)
She is the only person(that) I can trust.(that
5、关系代词that和which的区别
(1)相同点
作宾语时都可省略。
)
作宾语,可省略)
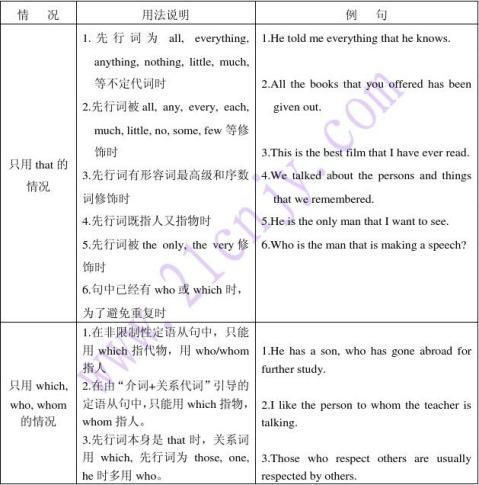
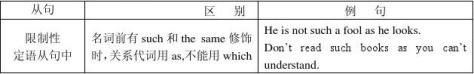
(2)用that,不用which的情况
①当先行词是不定代词all, everything, nothing, any, anything, little
,the only,the same等修饰时。
o now.
④当先行词是一个既指人又指物的并列词组时。
They were talking about the persons and things that they saw in the factory. ⑤当关系代词在定语从句中作表语时。
China is not the country that it was.
⑥当要避免与疑问词which重复时。
Which is the car that was made in Beijing?
⑦当先行词为the way, the time, the period等时,关系代词常用that,但通常被省略。
I don't like the way(that)you speak to her.
(3)用which,不用that的情况
①引导非限制性定语从句。
Football, which is an interesting game, is played all over the world.
②直接放在介词后作宾语时。
Language is the most important tool without which people can't communicate with each other.
6、关系代词who与that的区别
(1)当先行词是he、people、those等时,引导词常用who。
He who does not reach the Great Wall is not a true man.
Those who are for me, put up your hands.
(2)当引导词作定语从句的表语时常用that。
She isn't the little girl that she used to be.
He is the man that I asked for help yesterday.
7、as的用法
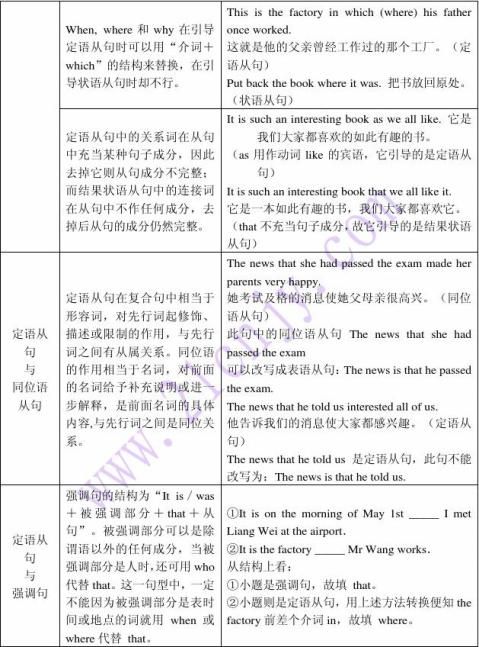
(1)as引导限制性定语从句通常构成such...as或固定搭配,as在从句中可作主语、表语或宾语。
)
Don’t read such books as are not worth such books as you can understand.
He lent me as much money as he had.
(2)such…that…与such…as
“such…that…”表示“如此……而“such…as…”表“像……的意思,用来引导定语从句,as在从句中充当主、宾或表语等。
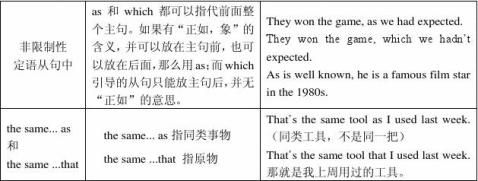
(3)而“the same…as…”表同种类的东西。试比较(指同一本书)
This is the same book as I lost.(并不是原来的那一本)
(4)as 引导非限制性定语从句
as作关系代词,还可用来引导非限制性定语从句,可以用来代替一个句子或单词,as引导的句子可放在句首、句末或句中。
The moon, as is known to everybody, travels round the earth once every month. As is known to everybody, the moon travels round the earth once every month.
四、关系副词
英语中的关系副词有where,when,why等。
1、when的用法
when指时间,修饰表时间的先行词,在定语从何中作时间状语。
July and August are the months when the weather is hot.
2、where的用法
where指地点,修饰表地点的先行词,在定语从句中作地点状语。
She will go home where she can rest.
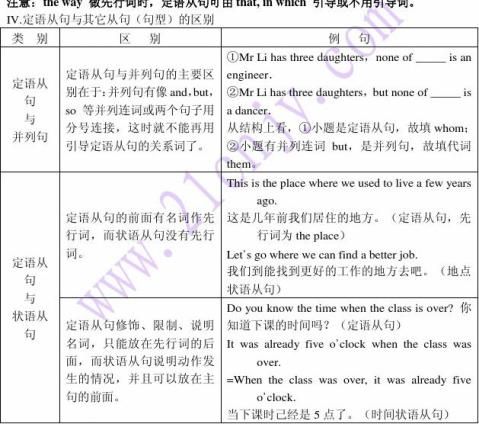
注意:先行词为表示时间、地点的名词时,关系词不一定都用when或where。如果关系词在定语从句中作主语或宾语,就要用关系代词which或that。 This is the factory that/which we visited last year.
I won't forget the time that we spent in the countryside.
3、why的用法
why指原因,修饰名词reason,在定语从句中作原因状语。
This is the reason why he did so.
Do you know the reason why he left early?
五、“介词+关系代词”用法
“介词+关系代词”因此,下面仅就几种常见的“介词+关系代词”
1、介词+which
介词+which在关系分句中分别作时间,代替相应的关系副词when,where和why。
2、介词+which(指物)
介词+which(指物)/whom(分句主谓常须倒置。
3指物)/whom(指人),在定语从句中作主语
指物)/whom(指人),在关系分句中作主语,说明整体中的部分。
China has a lot of islands, one of which is Taiwan.
There are a lot of students here,none of whom like the film.
4、介词+which(指物)/whom(指人),在关系分句中作目的、方式或地点状语 这种结构中的介词一般受动词或介词后的名词所制约。
Could you tell me for whom you've bought this coat?
5、介词+which(指物)/whom(指人),用于被动结构的关系分句中,作状语,说明动作的发出者。
The wolf by which the sheep was killed was shot.
The man by whom the wolf was shot was a good hunter.
6、名词+of which,代替whose+名词,在关系分句中作定语。
I saw some trees, the leaves of which (=whose leaves)were black with disease. He mentioned a book, the title of which (=whose title )I've forgotten.
7、介词+which(指物)/whose(指人),修饰后边的名词。
The driver was the man from whose room she had stolen the maps.
比较:介词+which+不定式。此种用法多见于正式文体中,相当于一个带有主语和谓语的定语从句。
She had only 1.87 with which to buy(=she could buy)Jim, her husband, a present. At last he had something about which to write (=he could write) home.
六、限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
1、限制性定语从句
定语从句分限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句两种。限制性定语从句为先行词不可缺少的定语。如果将这种定语从句省去,主句的意思就会不完整或失去意义。这种从句和主句的关系十分密切,写时不用逗号分开。
She has found the necklace that she lost 2 years ago. (限制性定语从句) This is the man who came to see you yesterday. (限制性定语从句)
It happened at the time when I left the office.
2、非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句和主句的关系不十分密切,只是对先行词作附加的说明,如果去掉,主句的意思仍然清楚。这种从句和主句之间往往用逗号分开,一般不用that来引导。
Yesterday, I met Li Ping, who seemed to be busy. (非限制性定语从句) In Britain, which has a population of 55. 8 million, 110,000 people die from smoking each year. (非限制性定语从句)
3、限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句的区别
(1)形式上不同
非限制性定语从句在书写时往往用逗号和主句分开,而限制性定语从句不用逗号与主句分开。
Last night I saw a very good film,which was about the Long March.
The man whom I met in the street was a driver.
(2)可否省略的不同
限制性定语从句是先行词在意义上不可缺少的定语,如果去掉,主句的意思就不完整或失去意义,而非限制性定语从句是对先行词作的附加说明,即使去掉,主句的意思仍然完整。
I was the only person in my office who was invited.
They set up a state of their own, where they would be free to keep Negroes as slaves.
(3)关系代词的不同
非限制性定语从句不能用that代替who,whom和which,并且关系代词在非限制性定语从句中作宾语时也不能省略,但在限制性定语从句中却恰恰相反。如:
This is the best film (that) I have ever seen.
She sang a new song, which we liked very much.
(4)翻译方式不同
限制性定语从句往往译在先行词之前,而非限制性定语从句往往译为一个并列的句子。
She is the nurse who looks after the children.她就是照料这些孩子的阿姨。 This note was left by Xiao Wu, who was here a moment ago.这个条子是小吴留的,她刚才到这儿来过。
比较:
He has a brother, who lives in Beijing. (有一个哥哥。)
He has a brother who lives in Beijing. (可能有几个哥哥,其中一个是住在北京的。)
4、as与which在非限制性定语从句中的用法区别
as和which作为关系代词都可以用来引导非限制性定语从句,指代整个主句所表达的内容,在从句中作主语或宾语,但它们在用法上是有区别的,这一点许多学生往往搞不清楚。现就它们引导非限制性定语从句时的用法简述如下:
(1)相同之处
当从句位于主句之后,引导词指代整个主句所表达的全部意义时,as和which可以互换。
The elephant is like a snake, as/which everybody can see.
He is an Englishman, as/which I know from his accent.
(2)不同之处
①as引导非限制性定语从句时,位置比较灵活,可位于主句之前,也可位于主句之中或之后,而which引导非限制性定语从句只能位于主句之后,不能谓语主句之前。
Robert is good at languages, as we all know. 罗伯特擅长学语言,这我们都知道。 As is known to all, China will be an advanced and powerful country in 20 or 30 years’ time.
Air, as we know, is a gas.
注意:as引导非限制性定语从句常有“如同……那样”的含义,因此在一些固定结构如as we know/as is known to all(众所周知),as we all can see(正如我们大家都能看到的那样),as has been said before/above(正如前文所述),as has been
pointed out(正如所指出的那样),as might be imagined(可以想象得到),as might be expected(正如所预料的那样),as is often the case(情况常常是这样)等中,一般不能用which代替as。
②搭配上,在由the same或such所修饰的名词后通常用as作关系代词引出限制性定语从句。
I have got into the same trouble as he (has).
I've never heard of such a moving story as he is telling.
③which引导的从句在意义上相当于一个并列句,可以用and this代替,意思是“这件事”;as引导的从句主要起连接上下文的作用,表达说话人的观点、看法,并指出主句内容的根据或出处等。例如:
He sold his bicycle, which surprised me. (=He sold his bicycle, and this surprised me.)
As is known to all, China is the country with largest population in the world.
④当which在从句中指代的是先行词本身而不是主句时,不可用as代替which。 The apple tree, which I planted last year, has not borne any fruit.
The book, which I bought yesterday, is very instructive.
⑤在从句中作主语时,which既可作系动词be的主语,也可作实义动词的主语,而as只可作系动词be的主语。
He married her, which was natural. (可用as代替which)
He saw the girl, which delighted him. (不可用as代替which)
He was late for class again, which made the teacher very angry. (不可用as代替which)
⑥as引导的从句在意义上不可与主语相悖,而which引导的从句则不受此限制。例如:
Mummy treats me like a baby, which I can't bear.
The result of the experiment was very good, which we hadn't expected.
The weather turned out to be very good, which was more than we could expect.
七、特殊的先行词
1、当先行词是way意为:方式、方法,时引导定语从句的关系词有三种情况:
1)in which 2)that 3)不填。
Tell me the way (不填;in which; that)you came here.告诉我你是怎么来的。
2、当先行词是time意为:次数,时引导定语从句的关系词有两种情况:1)不填 2)that。
This is the first time I have been here.这是我第一次来这里。
3、当先行词是one of+复数名词时,定语从句的谓语动词用复数。
He is one of the students who were praised yesterday.他是昨天受到表扬的学生之一。
4、当先行词是the (only) one of+复数名词时,定语从句的谓语动词用单数。 He is one of the students who was praised yesterday.他是昨天唯一受到表扬的学生。
-
高一英语语法归纳总结1
高一英语语法归纳总结定语从句的归纳一几个基本概念1定语从句的定义用作定语的从句叫定语从句2先行词被定语从句所修饰的3定语从句的位置…
-
高中英语语法归纳总结
打铁教育科目英语授课老师王茂林TheEducationofDatieSubjectEnglishTeacherHenry高中英语语…
-
高一英语语法归纳总结[1]1
chu高一英语语法归纳总结定语从句的归纳一几个基本概念1定语从句的定义用作定语的从句叫定语从句2先行词被定语从句所修饰的3定语从句…
-
高中英语语法知识点总结
高中语法知识点总结第一章冠词高考对冠词的考查集中在基本用法上主要既反映在对泛指特指及固定短语冠词的考查抽象名词物质名词的具体化依然…
-
高中英语语法归纳总结
高中英语语法权威解析目录第01章名词性从句第02章It用法及其句型和固定搭配讲解第03章高中英语语法中的省略现象第04章主谓一致第…
-
高考英语语法大全:固定搭配用法总结【重点精华】
高考英语语法大全:固定搭配用法总结【重点精华】1.It’sthefirsttimethat……….(从句中用现在完成时)Itwas…
-
高中英语语法难点总结
关系词先行词从句成分例句Who人主语Doyouknowthemanwhoistalkingwithyourmother?Whom人…
-
高一英语必修2第4单元短语知识点归纳和总结
高一英语必修2第4单元短语和知识点归纳和总结一、重点短语归纳和总结1.asa_________结果是;作为结果2.die_____…
-
高中英语语法总结
高中英语语法简单总结高中语法难在复杂要记忆的知识点太多太杂我结合高中的语法要求大纲简单总结了我个人认为比较主要的知识点大体把握思路…
-
最新高一英语知识点总结
高一英语知识点总结上册重点词组1fondof喜爱爱好接名词代词或动词的ing形式例如Hesfondofswimming他喜欢游泳A…
-
主谓一致语法总结
主谓一致语法总结----安顺一中曹方平供稿一.就近原则:在notonly…butalso,not…but,neither…nor,…